44 free body diagram inclined plane
Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in (Figure). Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in ...Definition of weight, vector form: →w=m→gw...Net external force: →Fnet=∑→F=→F1+→F2+...Newton’s second law, vector form: →Fnet=∑...Newton’s second law, component form: ∑→Fx... Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley. A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W1 exerted by the earth on the box. 2) The normal force N. 3) The force of friction Fk. 4) The tension force T exerted by the string on the block m1. B) free body diagram of block m 2 (right of figure below)
Activity A: Redirection of force Get the Gizmo ready: Turn Off the External force.Click Reset. Set the Angle to 30° and the Weight to 300 N. Question: How does an inclined plane redirect a force? 1. Observe: Select the FREE-BODY DIAGRAM tab. Make sure Magnitude is on. A free-body diagram is a picture that uses vectors to show the different forces acting on an object.

Free body diagram inclined plane
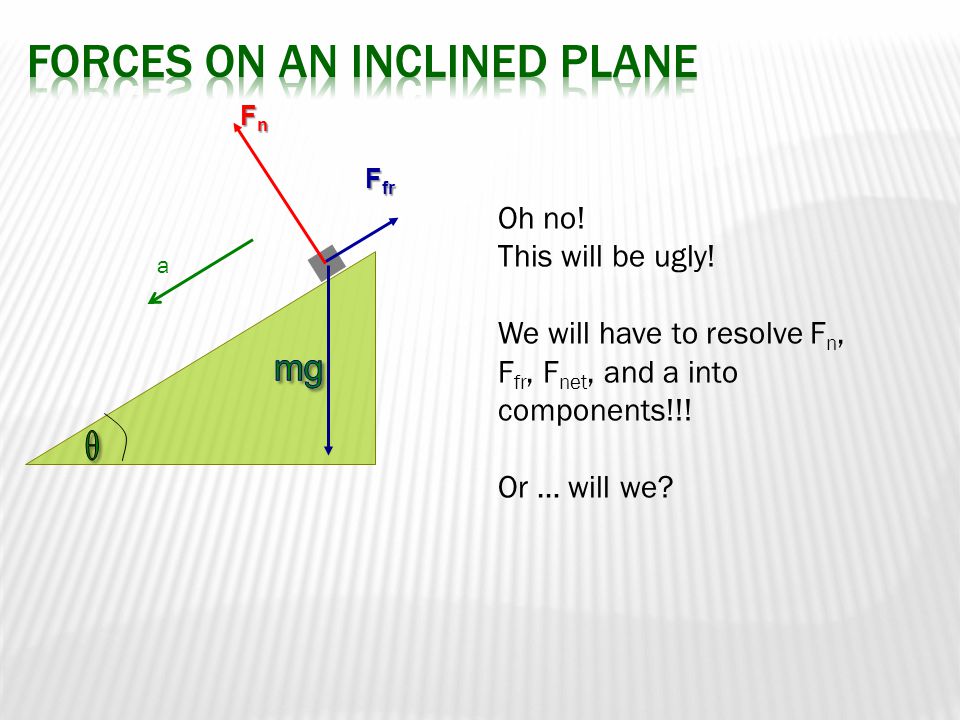
A free-body diagram for a mass on an inclined plane: Gravity acts downward. The component of F g perpendicular to the surface is cancelled out by the normal force the surface exerts on the mass. The free-body diagram is also shown, with the forces split into components parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane. Because there is no acceleration, any coordinate system is fine - a system parallel and perpendicular to the ramp is pretty convenient, though, because two of the forces are along those directions. Solution a). Free Body Diagram The box is the small blue point. In the diagram below, W is the weight of the box, N the normal force exerted by the inclined plane on the box, F a is the force applied to have the box in equilibrium and F s the force of friction opposite F a. b) The box is at rest, hence its acceleration is equal to 0, therefore the sum of all forces acting on the box is equal ...
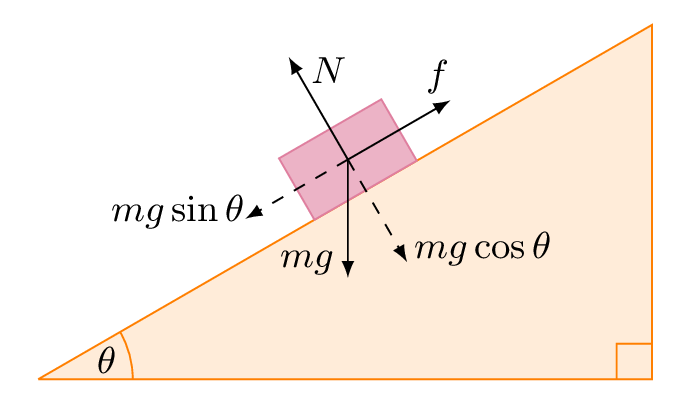
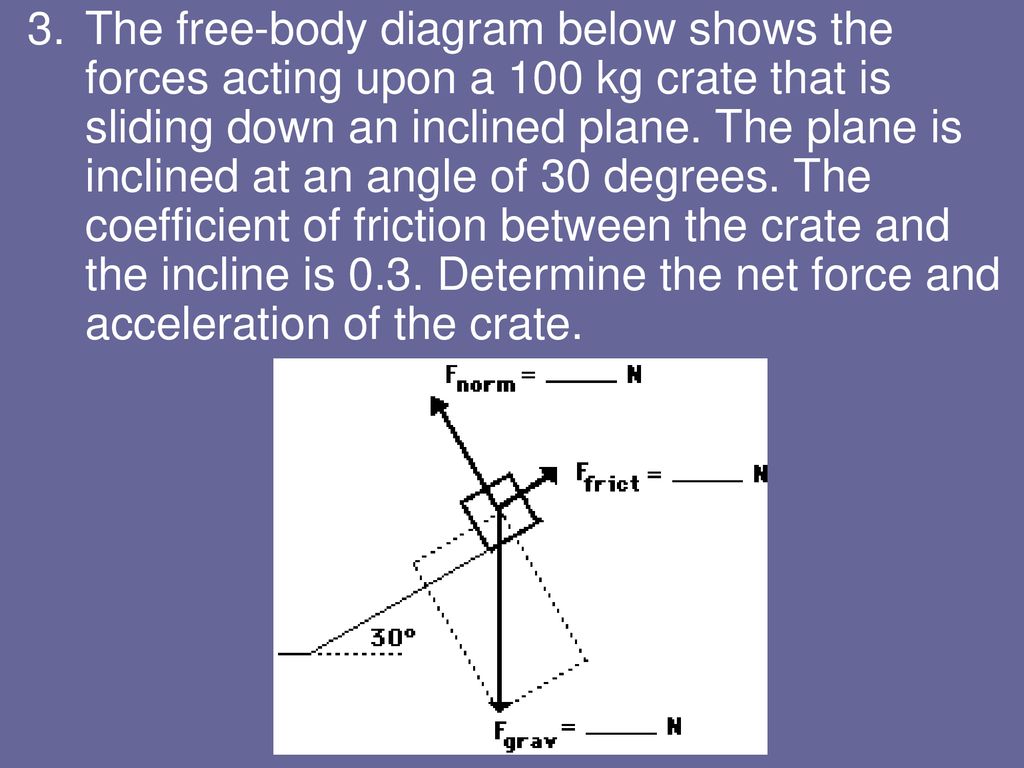
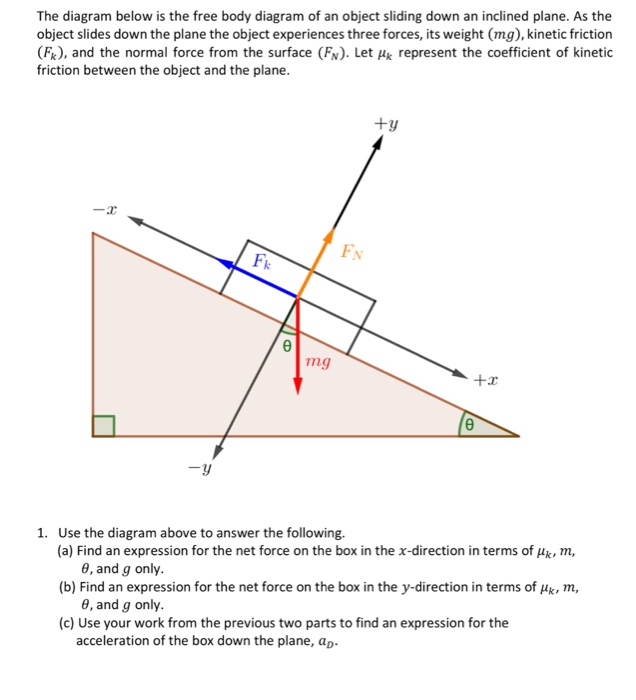
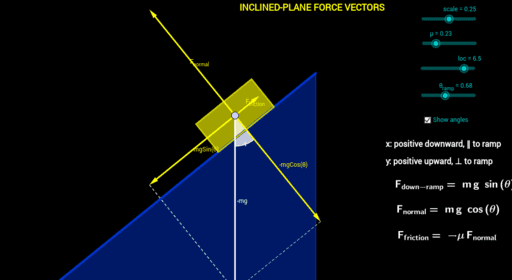
Free body diagram inclined plane. The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the incline is 0.3. Determine the net force and acceleration of the crate. Free Body Diagram of an Inclined Plane in TikZ. April 21, 2021 February 9, 2021 by admin. In this tutorial, we will draw a free body diagram of an inclined plane with a load resting on top of it in LaTeX using TikZ package. We will draw a triangle to represent the inclined plane, a rectangle for the load, then add arrows with labels to ... Figure 8.3. 1: A block sliding down an inclined plane. The corresponding free-body diagram is shown on the right. Figure 8.3. 1 above shows, on the left, a block sliding down an inclined plane and all the forces acting on it. These are more clearly seen on the free-body diagram on the right. I have labeled all the forces using the F → b y, o ... How to write Newton's second law for forces on an incline. 1) Draw a free body diagram for the object (see Figure 3). Remember to rotate the coordinate axes to ...
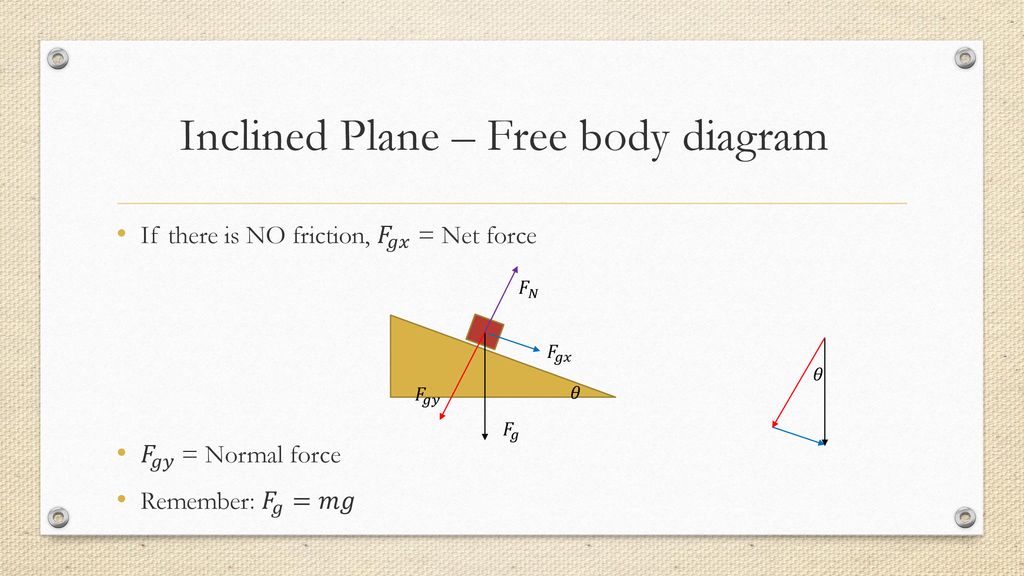
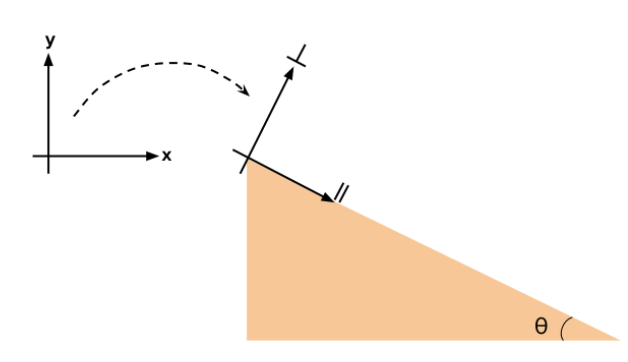
An inclined plane is basically a ramp. It is a flat surface that is sloped rather than horizontal. When solving problems about objects on an incline, it is convenient to choose a coordinate system with axes parallel and perpendicular to the surface as shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 1 Any time we deal with forces vectors in 2-dimensions we need to resolve “off axis” or “diagonal” vectors into ... A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram: Free Body Diagram of an Inclined Plane in TikZ. In this tutorial, we will draw a free body diagram of an inclined plane with a load resting on top of it in LaTeX using TikZ package. We will draw a triangle to represent the inclined plane, a rectangle for the load, then add arrows with labels to highlight different forces. 1. A free - body diagram, isolated - body diagram, or force diagram is a diagram in which the forces acting on a body are represented by arrows. Be sure to include in the diagram all the forces acting on the object, and since it is a vector quantity, the arrow is responsible for pointing out its direction and direction, while the length of the arrow gives …
As shown in the above image, the free body diagram of a rectangular block on an inclined plane shows various forces acting on the rectangular block. Forces acting on the rectangular block are used to understand the motion of the rectangular block in different conditions. I'm a bit confused about free body diagrams on inclined planes with frictions. ... Here are the free body diagrams without the weights resolved. Share. Cite. Improve this answer. Follow edited Feb 5 '16 at 16:26. answered Feb 5 '16 at 16:06. Farcher Farcher. Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in Figure. Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in the problem-solving strategy. Solution. We start by creating a diagram for the first object of interest. In Figure(a), object A is isolated (circled) and represented by a dot. You will learn how to draw free body diagrams (FBD) when a mass is attached to a string. You will also learn how to draw FBD in case of inclined plane systems
by W Moebs · 2016 — Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in (Figure). Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in ...
[Free body diagram. Wikipedia] The free-body diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Free Body Diagram On An Inclined Plane
Example: A block on an inclined plane. A simple free body diagram, shown above, of a block on a ramp illustrates this. All external supports and structures have been replaced by the forces they generate. These include: mg: the product of the mass of the block and the constant of gravitation acceleration: its weight. N: the normal force of the ramp.
7 Jan 2021 · 2 answersIf instead of decomposing into perpendicular and parallel force components, you use the 'regular' x and y axis as you did to get Eq. (2), ...
Correct answers: 3 question: A free body diagram of a brick on an inclined plane is shown below. What is the mechanical advantage of the inclined plane? Free body diagram A. 0.625 B. 1.25 C. 1.67 D. 2.5
This java applet shows the free-body force diagram for a block sits on an inclined plane. Usage: Click the circle near the right edge and drag the mouse up/down to change the angle of inclination theta 。. 2. Red Arrow represents the gravitational force. ( which has two green force components).
This video introduces and explains both free body diagrams and objects on an inclined plane for A Level Physics.A free body diagram is used to display the fo...
Vocabulary: coefficient of friction, efficiency, force, free-body diagram, friction, inclined plane, mechanical advantage, mechanical energy, normal force, resultant force, simple machine, vector, work, work-energy theorem. Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) [Note: The purpose of these questions is to activate prior knowledge and get students thinking. Students are ...
Draw the free body diagram of both the spheres, together and separately. ... Problem 6: Find the reactions R1 and R2. Problem 7: Two rollers of weight P and Q are supported by an inclined plane and vertical walls as shown in the figure. Draw the free body diagram of both the rollers separately. 15
24 Jul 2013 — Examines the forces on an object sitting on an inclined plane thoroughly.
Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in Figure. Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in the problem-solving strategy. Solution. We start by creating a diagram for the first object of interest. In Figure(a), object A is isolated (circled) and represented by a dot. Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free ...
Investigating the free-body diagram of a stationary object on an inclined plane November 2017 3 front face, and there is no need to put emphasis on what is inside it during the activity. The watch we use in this activity is the Apple Watch Series 2 with 38 mm aluminium case, possessing a mass of 28.2g, and the long version of the polymer sport ...
Example 1: A Jet Plane. a) A plane moves with constant velocity at an angle of 30.0 o (θ = 30.0 o) above the horizontal due to the action of four forces, the weight W , the lift L , the engine thrust T, and the air resistance R. b) The free-body diagram of the plane. The black dot represent the plane. 15
The Free-Body Diagrams for Inclined Planes Concept Builder challenges a learner to utilize an understanding of force types in order to construct a free-body diagram for an object moving along an inclined plane. Learners select force arrows from an arrow bank and label the arrows with a force type. There are 32 questions organized into 8 Question Groups and spread across three different levels ...
The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the incline is 0.3. Determine the net force and acceleration of the crate. Solution: The force of gravity in the given problem can be ...
[Free body diagram. Wikipedia] The free-body diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Pictorial Explanation Of Inclined Plane
Solution a). Free Body Diagram The box is the small blue point. In the diagram below, W is the weight of the box, N the normal force exerted by the inclined plane on the box, F a is the force applied to have the box in equilibrium and F s the force of friction opposite F a. b) The box is at rest, hence its acceleration is equal to 0, therefore the sum of all forces acting on the box is equal ...
The free-body diagram is also shown, with the forces split into components parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane. Because there is no acceleration, any coordinate system is fine - a system parallel and perpendicular to the ramp is pretty convenient, though, because two of the forces are along those directions.
A free-body diagram for a mass on an inclined plane: Gravity acts downward. The component of F g perpendicular to the surface is cancelled out by the normal force the surface exerts on the mass.

















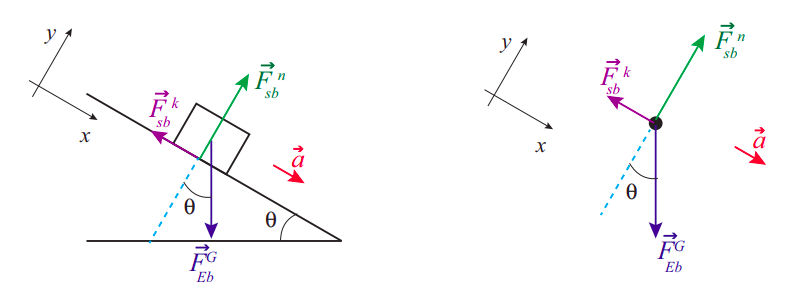









0 Response to "44 free body diagram inclined plane"
Post a Comment