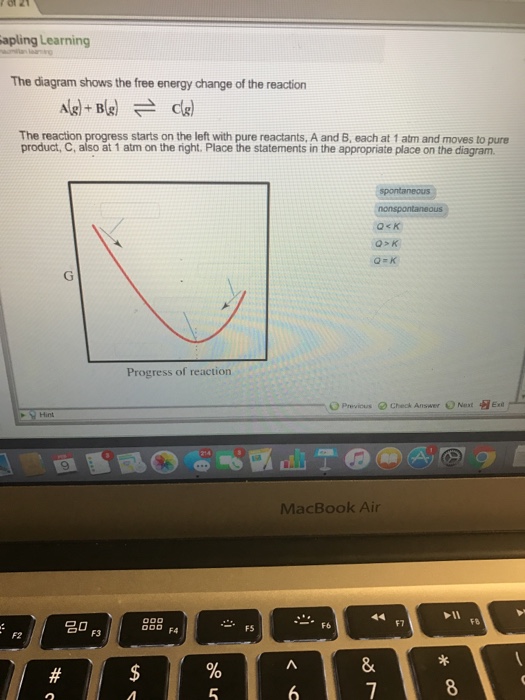
40 the diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction
Problem: The diagram for the free energy of the reactionA(g) + B(g) ⇌ AB(g)The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, each at 1 atm and moves to pure product, AB, also at 1 atm on the right. Select the true statements.a. The difference between the top left of the curve and the minimum of the curve corresponds to ΔG standard.b. The diagram below shows how the free energy, G, changes during a hypothetical reaction {eq}A(g) + B(g) \to AB(g). {/eq} On the left are pure reactants, each at 1 atm, and on the right is the pure ...
Figure 3-21 presents an energy diagram for the reaction X→Y. The solid line in the energy diagram represents changes in energy as the reactant is converted to product under standard conditions. The dashed line shows changes observed when the same reaction takes place in the presence of a dedicated enzyme.

The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction
The Diagram Shows The Free Energy Change Of The Reaction Yahoo. Amarante Pruvost. October 16, 2021. October 16, 2021. Ag Bg ABg The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants A and B at 1. The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A g B g C g. Exergonic reactions are also called spontaneous reactions, because they can occur without the addition of energy. Reactions with a positive ∆ G (∆ G > 0), on the other hand, require an input of energy and are called endergonic reactions. In this case, the products, or final state, have more free energy than the reactants, or initial state. The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A (g) + B (g) = AB (g) In the diagram, the reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, each at 1 atm, and moves to pure product, AB, also at 1 atm, on the right. Identify the point of the curve where AG = 0.
The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction. Transcribed image text: The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A(g) + B(g) = AB(g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure ... The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A(g) + B(g) – AB(g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, each at 1 atm, and moves to pure product, AB, which is at 1 atm on the right. Select the true statements. The x on the graph corresponds to AG of this reaction. At ... Most reactions involve the elimination of one mole of gas, so there is a similar standard entropy change of reaction. c The activity of most of the metals is the same. d The partial pressure of the reacting gas is the same for all reactions. MS15a, Gibbs Free Energy and Phase Diagrams 11/00 . The system can, in fact, lower its free energy even further by splitting up into a solid of composition X. S B. and a liquid of composition X. L B (shown on both diagrams). The gibbs free energy of the solid is given by point (4) on the g(X. B) diagram and that of the liquid by point (5) on ...
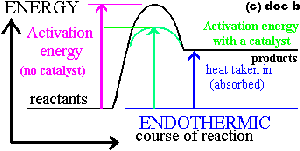
The diagram below shows a galvanic cell based on the reaction. Assume that the temperature is 25°C. (d) The diagram includes a salt bridge that is filled with a saturated solution of KNO 3. Describe what happens in the salt bridge as the cell operates. As the cell operates, NO 3 − ions flow toward the Al half-cell Energy Diagram - Energy Graph - Energy Chart - Energy diagrams - energy graphs - energy charts - energy diagram showing an energy plot via free energy vs. course of reaction, i.e. reaction coordinate. Energy diagram shows the following energy transition states and parameters: substrate, transition state, activation energy, product and change in ... The free energy change, ... How would the value of ∆G o, and hence the spontaneity (feasibility) of this reaction change as the temperature increases? Explain your answer. ... The following incomplete diagram shows the apparatus that can be used to measure the The diagram shows the profile of the energy changes for a reaction. Which energy change represents the energy needed to break chemical bonds so that new products can form ? [et-59]
The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction (heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. G Select the true statements. Progress of reaction At equilibrium, all of A and B have reacted to form pure AB | The entropy change. This problem has been ... The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, each at 1 atm and moves to pure product, C, also at 1 atm on the right. Place the statements in the appropriate place on the diagram. Question: The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, each at 1 atm and ...
19.10 The accompanying diagram shows how the free energy, G, changes during a hypothetical reaction A(g) + B(g) → C(g). On the left are pure reactants A and B, each at 1 atm, and on the right is the pure product, C, also at 1 atm. Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false. (a) The minimum of the graph corresponds to the equilibrium mixture of reactants and products ...
The accompanying diagram shows how the free energy, G, changes during a hypothetical reaction A(g) + B(g) C(g).On the left are pure reactants A and B, each at 1 atm, and on the right is the pure product, C, also at 1 atm. Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false.a
⚗️PLEASE HELP!!!! The energy diagram shows the change in energy during a chemical reaction. Which - Brainly.com
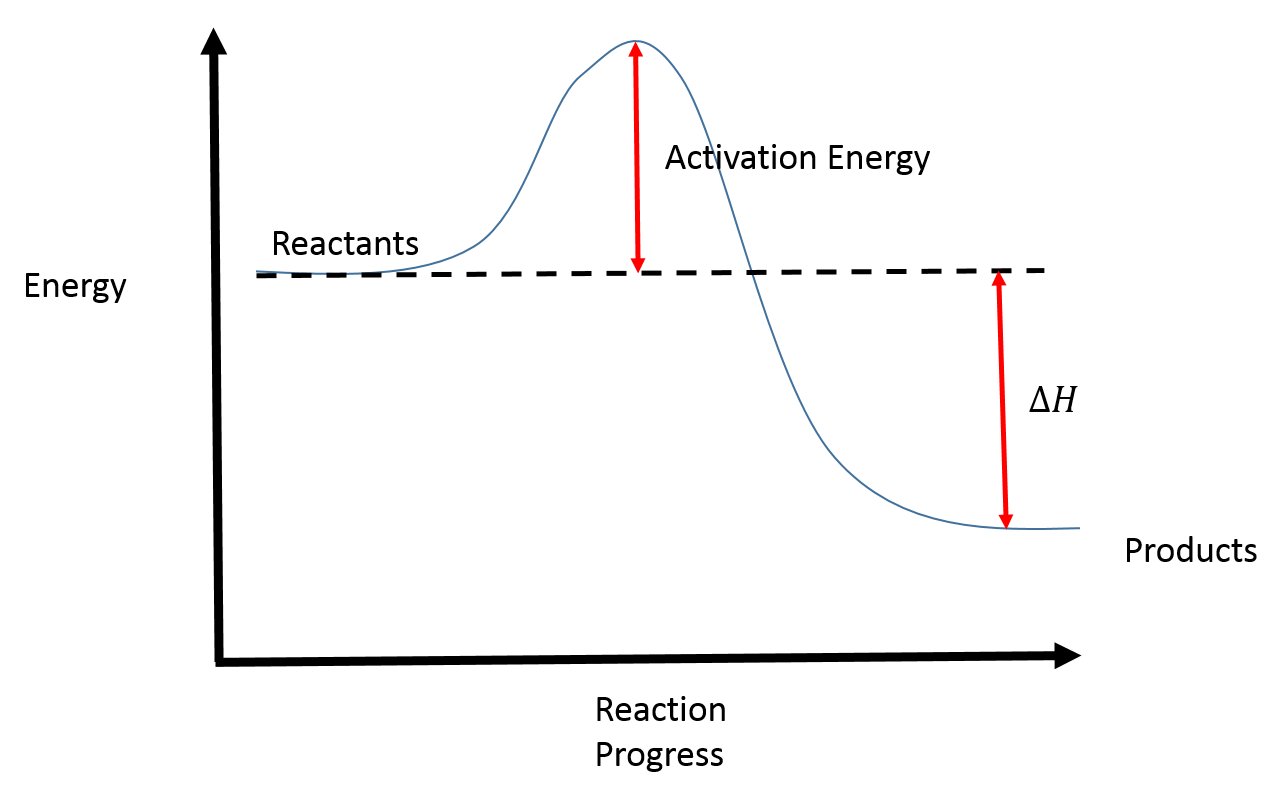
Typically, we envision reactions proceeding left to right along the reaction coordinate, so often, the activation energy is only noted for the forward reaction. The activation energy on the diagram below shows the barrier to be 102.6 kJ mol-1. Barriers are measured in energy per mole (typically kJ mol-1).
reaction. This is because energy is taken in from the surroundings. An upwards arrow shows that energy is taken in Question. Look at the energy level diagrams below.

Relief Showing the Head of a Winged Genius (Neo–Assyrian Period, reign of King Ashurnasirpal II (883–859 BCE)) // Mesopotamian, Assyrian
For the conversion of diamond to graphite, C(diamond) → C(graphite), the standard free energy change (ΔGrxn) is-2.90 kJ/mol. this reaction is____ ... The diagram to the right shows energy for two reactions, A and B. Which reaction has the higher ΔGrxn? ... such as bacteria. These organisms, like all organisms, rely on chemical reactions ...
Reactions are classified as either exothermic (H < 0) or endothermic (H > 0) on the basis of whether they give off or absorb heat. Reactions can also be classified as exergonic (G < 0) or endergonic (G > 0) on the basis of whether the free energy of the system decreases or increases during the reaction.. When a reaction is favored by both enthalpy (H o < 0) and entropy (S o > 0), there is no ...
In the diagram of the changes in free energy during a chemical reaction, which term is best represented by the circled letter "A"? Reactants An inexpensive biosensor to measure blood glucose was developed based on the fact that the enzyme glucose oxidase binds to the six-carbon sugar glucose and converts it to glucolactone and hydrogen peroxide.
An energy level diagram for an exothermic reaction. In an endothermic reaction, the products are at a higher energy than the reactants. This means that the enthalpy change of the reaction (∆ H ...
The free energy change, ΔG, of the reaction is negative, so the reaction is considered exergonic and spontaneous. In reaction B, the stability of the substrate is ... The diagram shows the catalytic hydrolysis of sucrose into the molecules glucose and fructose by the enzyme sucrase. Identify the role of each component in the diagram.
The The diagram the free free energy of the reaction diagram shows energy change of the ... The entropy change for the reaction is positive.
The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction. A (g) + B (g) ⇌ AB (g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, at 1 atm and moves to pure product, AB, also at 1 atm on the right. Select the true statements. A. The "x" on the graph corresponds to ΔG of this reaction. B.
Ellingham diagram shows variation in standard Gibbs free energy change with temperature for the formation of the oxide. The Ellingham diagram shows straight line upward slope with the formation of oxide, but in case of ZnO there is a sudden change. Ellingham diagram helps in selecting the suitable reducing agent.
The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A (g) + B (g) rightarrow C (g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B. each at 1 atm and moves to pure product, C, also at 1 atm on the right. Place the statements in the appropriate place on the diagram. spontaneous nonspontaneous Q< K Q> K Q= K.
GDie diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A (g)+ B (g) AB (g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, each at 1 atm and moves to pure product, AB, also at 1 atm on the right. Select the true statements. The "X" on the graph corresponds to AG of this reaction.
This page introduces Gibbs free energy (often just called free energy), and shows how it can be used to predict the feasibility of reactions. If you have already read the page about how to do this with total entropy changes, you will find a little bit of repetition on this page. Standard Gibbs free energy change, ΔG° Calculating ΔG° This is how standard Gibbs free energy change is ...
SOLVED:The accompanying diagram shows how the free energy, G, changes during a hypothetical reaction A(g)+B(g) \longrightarrow C(g) . On the left are pure reactants A and \mathrm{B}, each at 1 \mathrm{atm}, and
The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A(g) + B(g) AB(g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants.4 answers · Top answer: So here's the problem term for Chapter 19 part, eh? This is asking if the minimum off the ...
Energy changes in a reaction are calculated by bond energies and shown by energy diagrams. Heat energy is released when fuels burn. ... Energy diagrams show the level of energy of the reactants ...
The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B. each at 1 atm and moves to pure product, AB, also at 1 atm on the right. Select the true statements. At equilibrium, all of A and B have reacted to form pure AB.
19.10 The accompanying diagram shows how the free energy, G, changes during a hypothetical reaction A(g) + B(g) → C(g). On the left are pure reactants, each at 1 atm, and on the right is the pure product, also at 1 atm. (a) What is the significance of the minimum in the plot?
Problem Details. The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A (g) + B (g) ⇌ C (g). The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B each at 1 atm and moves to pure product, C, also at 1 atm on the right. Place the statements in the appropriate place on the diagram. spontaneous.
The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A (g) + B (g) = AB (g) In the diagram, the reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, each at 1 atm, and moves to pure product, AB, also at 1 atm, on the right. Identify the point of the curve where AG = 0.

Marina City Theater, Chicago, Illinois, Roof and Partial Concrete Frame Development Drawing (1961-1962) // Bertrand Goldberg American, 1913-1997
Exergonic reactions are also called spontaneous reactions, because they can occur without the addition of energy. Reactions with a positive ∆ G (∆ G > 0), on the other hand, require an input of energy and are called endergonic reactions. In this case, the products, or final state, have more free energy than the reactants, or initial state.

Bamboo-Covered Stream in Spring Rain (Ming dynasty (1368–1644), dated 1441) // Xia Chang Chinese, 1388-1470
The Diagram Shows The Free Energy Change Of The Reaction Yahoo. Amarante Pruvost. October 16, 2021. October 16, 2021. Ag Bg ABg The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants A and B at 1. The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A g B g C g.


















0 Response to "40 the diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction"
Post a Comment