45 draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.
How do I calculate the bond order for H2- and H2+? | Socratic Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals. CN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond ... Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3. In the third step, fill the molecular orbitals using the energy and bonding properties of the overlapping atomic orbitals.
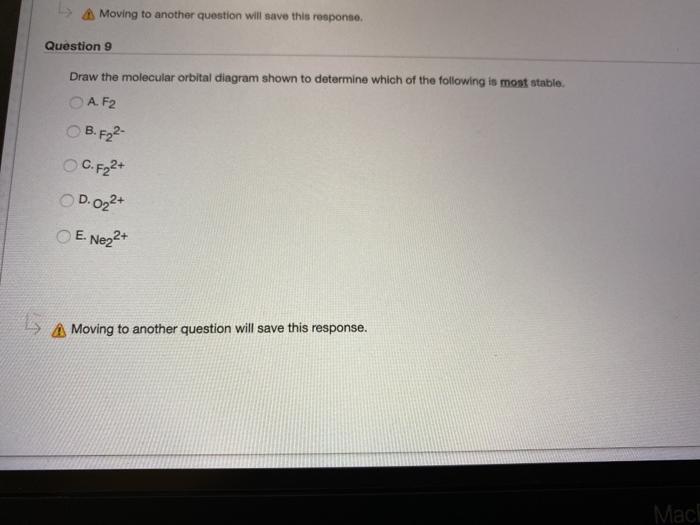
Solved Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. F22+ F2 Ne22+ O22+ F22-Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. F22+ F2 Ne22+ O22+ F22-
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.
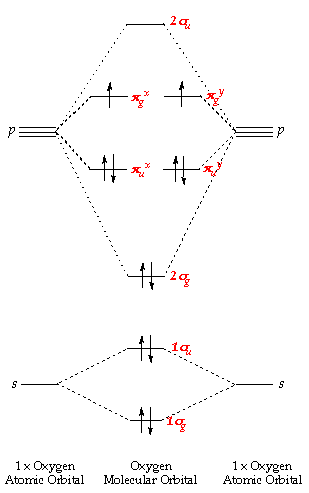
Comments on: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... Comments on: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. 37 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable based on their bond order Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals O, F2, Nez • Nez2 • F₂2. • F2 022 • F22. Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the scope of this text) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.. PDF Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules molecular orbitals in this example, in a more general example there may be many molecular orbitals. Of all the possible molecular orbitals in a structure, two are so special they get their own names. One is called the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO), because it is the highest energy orbital holding electrons. C22- Molecular Orbital Diagram Answer to Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. N22+ B22+ B B2 CeV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of the lowest energy molecular orbital with respect to the 3s orbital of sulfur. [Answered] Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... The most stable element based on the molecular orbital diagram is . Explanation: Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) was proposed by Hund and Mulliken. The theory describes the bonding in molecules, elements, or atoms. The theory uses Molecular Orbital (MO) diagram to explain the bonding between atoms. For example, to determine the stability of an atom, bond order is calculated. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which ... 2+ has only 10 electrons, so the most electrons are in bonding molecular orbital with bond order 3. So, the molecule is most stable. 55) Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O 2 2 ⁻ B) Ne 2 2 ⁺ C) O 2 2 ⁺ D) F 2 2 ⁺ E) None of the above are paramagnetic.
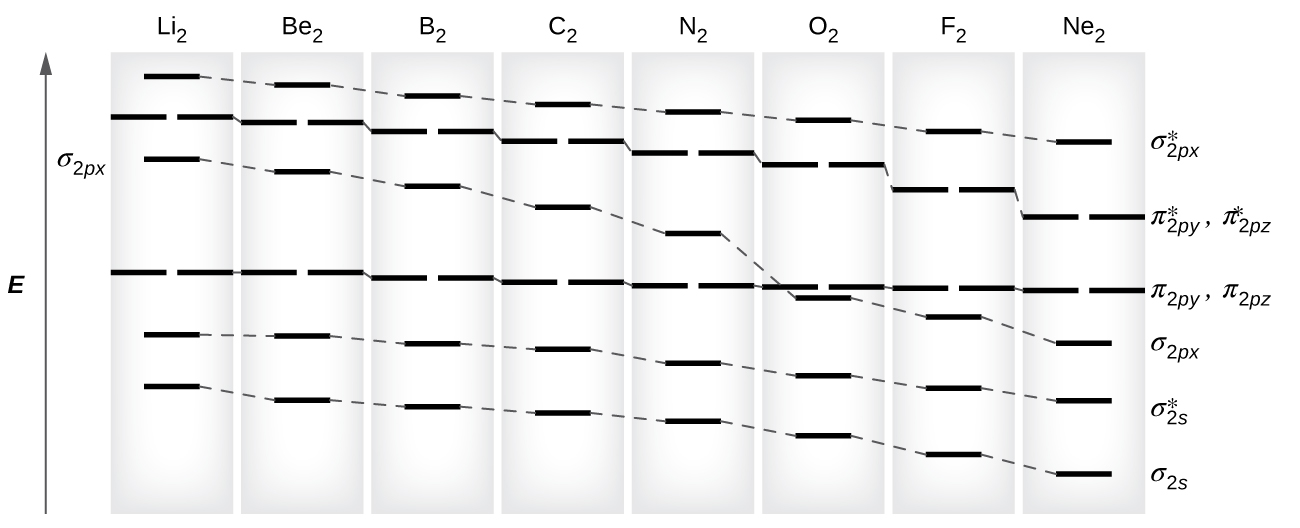
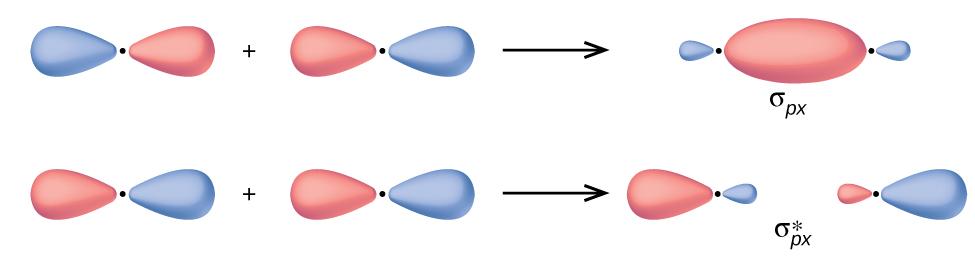
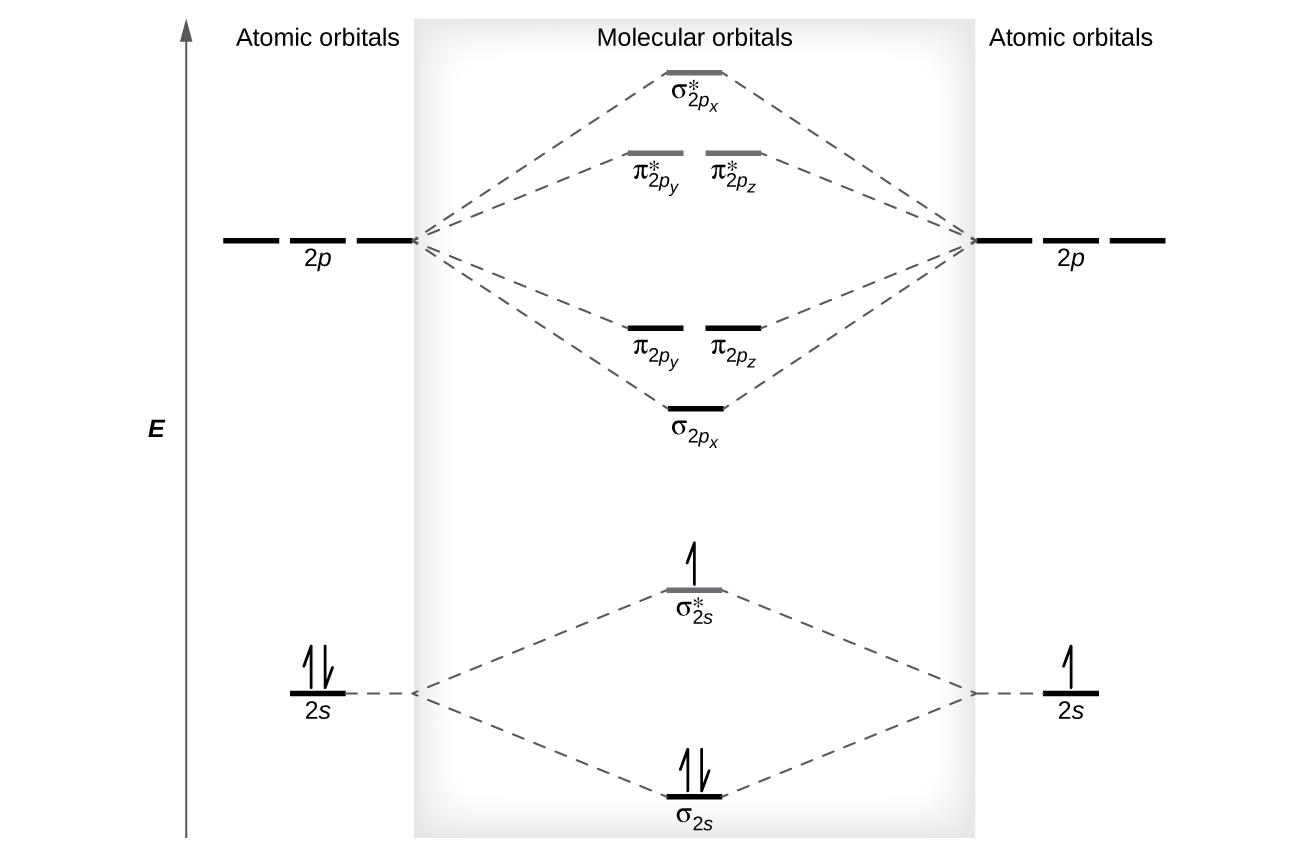
chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2 ... The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding combinations. Recitation Week 10 (test 3 - Recitation 2) - GitHub Pages 1) Draw the molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following is most stable. A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. a. f22+ b. ne22+ c. f22- d. o22+ e. f2 40 o2+ molecular orbital diagram - Wiring Diagrams Manual Draw molecular orbital diagram of O2 or N2 with magnetic ... Draw molecular orbital diagram of O 2 or N 2 with magnetic behavior and bond order. Medium Solution Verified by Toppr As it can be seen from the MOT of O 2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
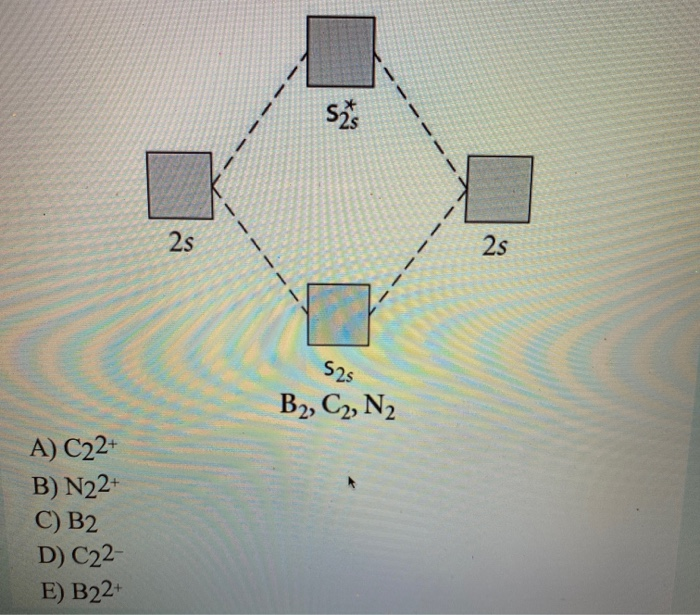
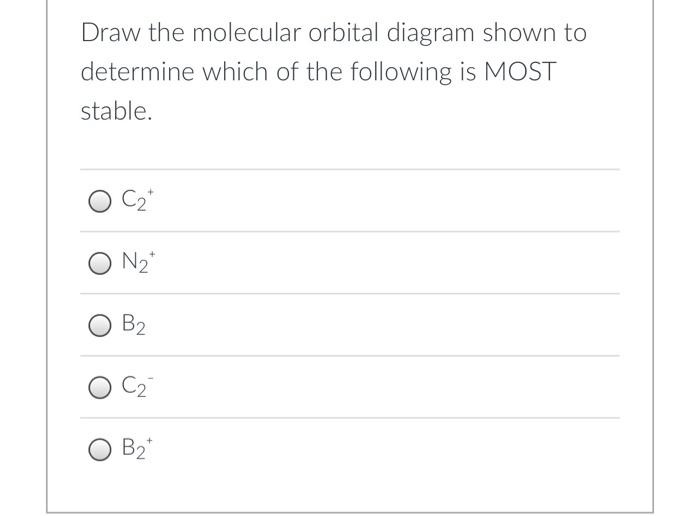
Solved Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. N22+ C22+ C22- B22+ B2. Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. N22+ C22+ C22- B22+ B2. 7.7 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Fundamentals Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Chemical bonding Flashcards - Quizlet 60) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A) C2^2+. B) N2^2+. C) B2. D) C2^2−. E) B2^2+. D) C2^2−. 61) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+. draw the lewis structure for the molecule ch3ch2cch. how ... Step 3: Determine the Number of Bonds in the Molecule. … Step 4: Choose a Central Atom. … Step 5: Draw a Skeletal Structure. … Step 6: Place Electrons Around Outside Atoms. How many sigma bonds are in a pi bond? The number of sigma bonds present is one and the number of pi bonds present in a double bond is one. Triple bond is defined as the chemical bond between two atoms that have six bonding electrons.
IONIC REACTION Cl + Cl _ OO Correlation Diagrams. Observe ALLOWED Diels Alder Rxn. Plane of symmetry. Step 1 Draw Rxn, Include curly arrows. Ignore substituents! Step 2 Identify ...69 σελίδες
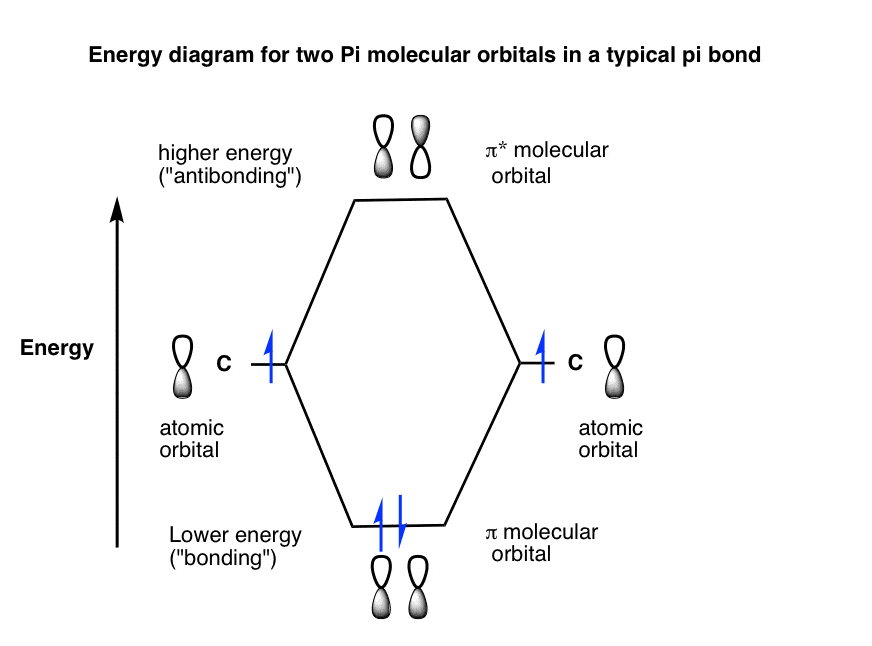
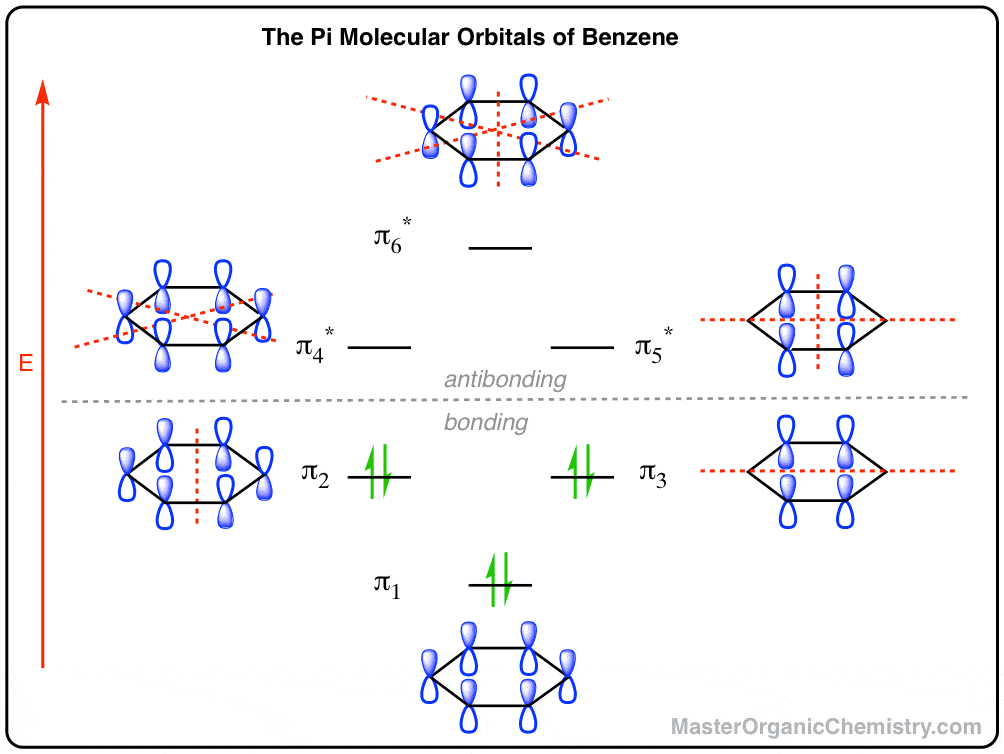
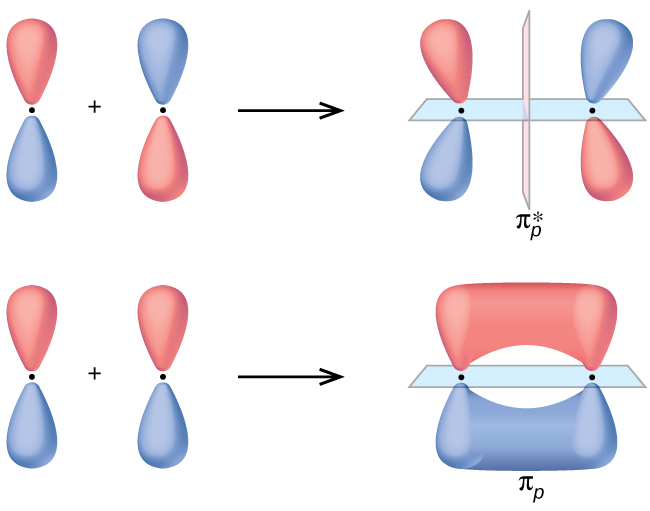
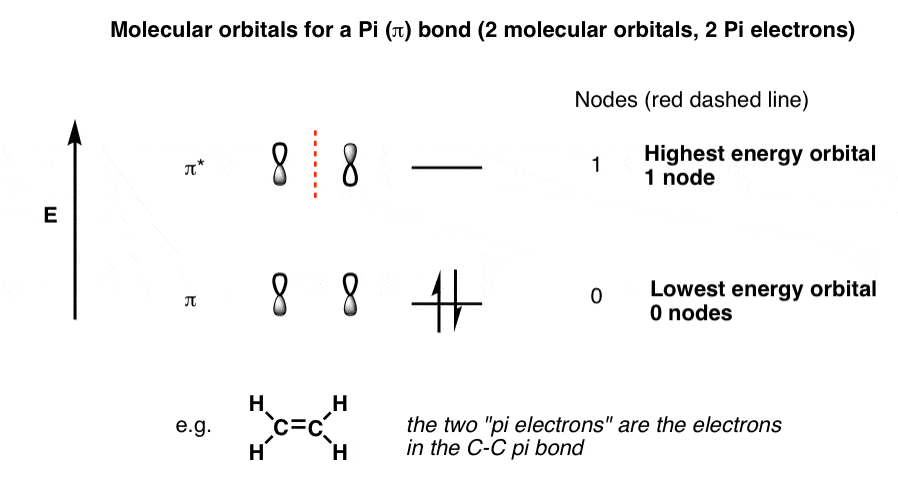
36 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping ...
30 Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine ... A f2 b f22. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Use molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which is most stable a o22 bf2 c f22 d f22 e ne22 a.
[ANSWERED] Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To ... Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Most Stable. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A. F2 2 + B. Ne2 2 + C. F2 2 - D. O2 2 + E. F2. Answer
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A.... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A. F22+ B. Ne22+ C. F22- D. O22+ E. F2
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ B5. Περιγράμματα Μαθημάτων ... 18 Σεπ 2019 — Know the most successful cosmological models and their predictions. • Solve complex exercises by applying the new knowledge. • Explain how the ...525 σελίδες
Answered: Draw the molecular orbital diagram… | bartleby Solution for Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. B2, N2^2+, C2^2-, B2^2+, C2^2+
By writing molecular orbital configuration for NO,CO,O2 ... "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the diagram.
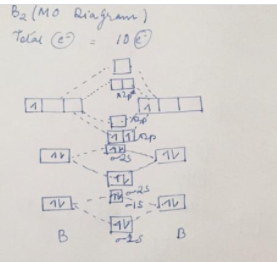
MO Diagrams - GitHub Pages #1. Draw the MO diagram for `B_2`. First step is to determine which MO diagram we're using. In this case, we're using the standard one. Draw out the MO diagram and label in the valence electrons. Boron has 2 electrons in the `2s` orbitals and 1 electron in the `2p` orbital. That's it for the MO diagram of `B_2`!
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Chem Flashcards - Quizlet Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A) C22⁺ B) N22⁺ C) B2 D) C22⁻ E) B22⁺
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine. School Shoreline Community College; Course Title CHEM 161; Uploaded By tranthuynhi1792000. Pages 337 This preview shows page 318 - 325 out of 337 pages. ...
a. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine ... a. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B_2^2+, B2, C_2^2-, B_2^2- and N_2^2+ b. Draw the Lewis structures and molecular orbital diagrams ...
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the scope of this text) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures.
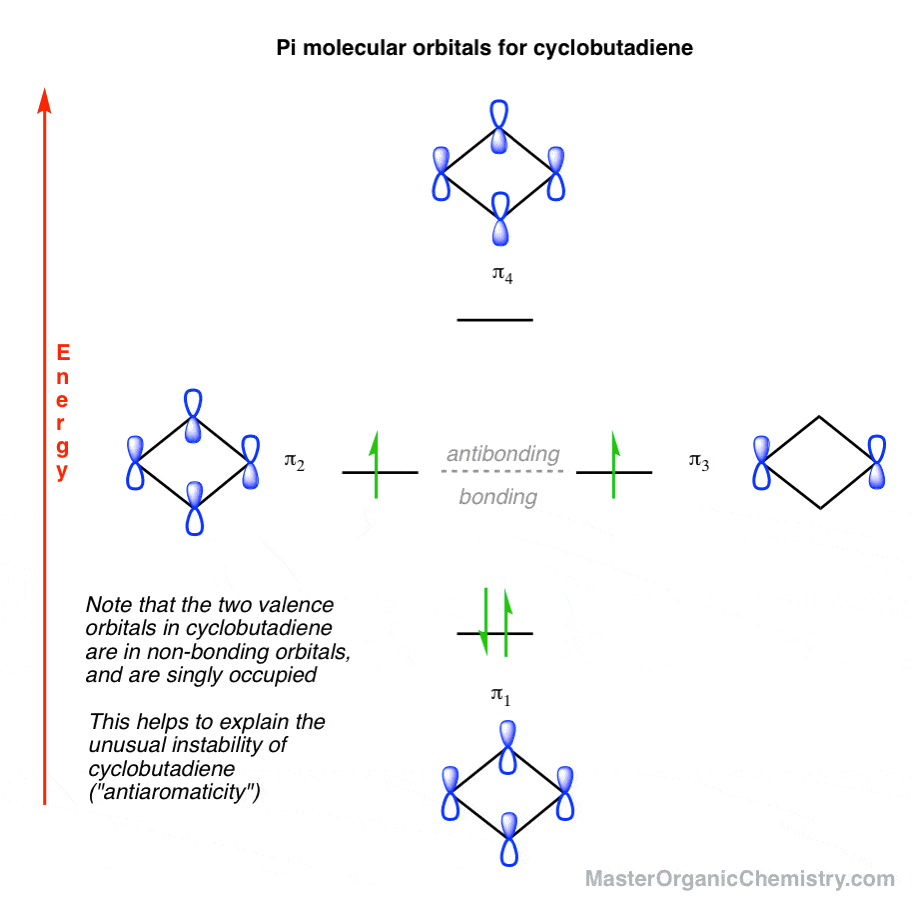
37 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable based on their bond order Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals O, F2, Nez • Nez2 • F₂2. • F2 022 • F22.
Comments on: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... Comments on: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.


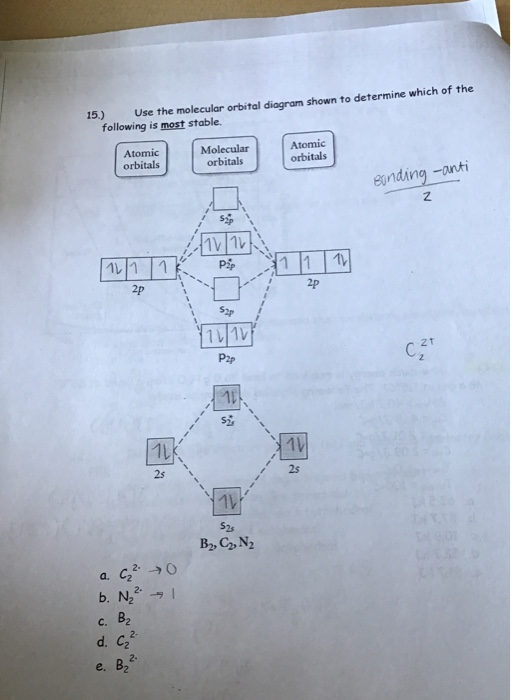



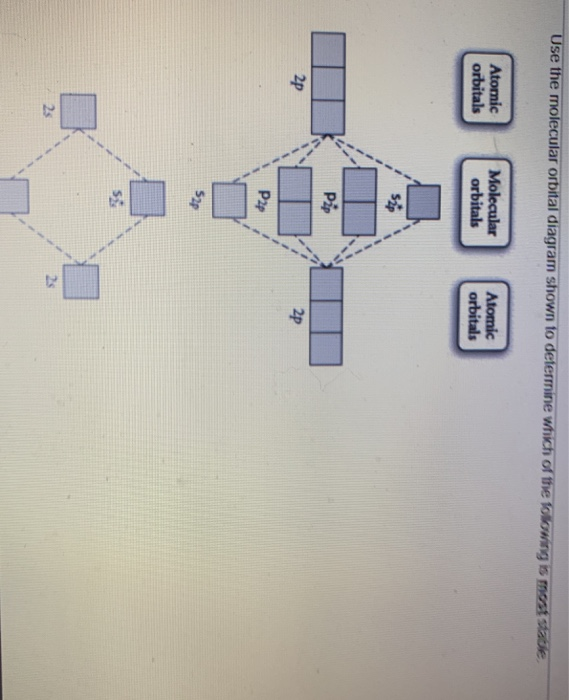
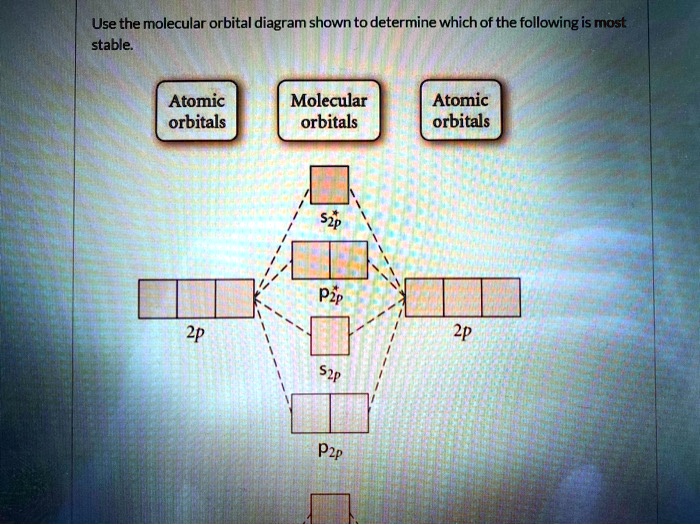
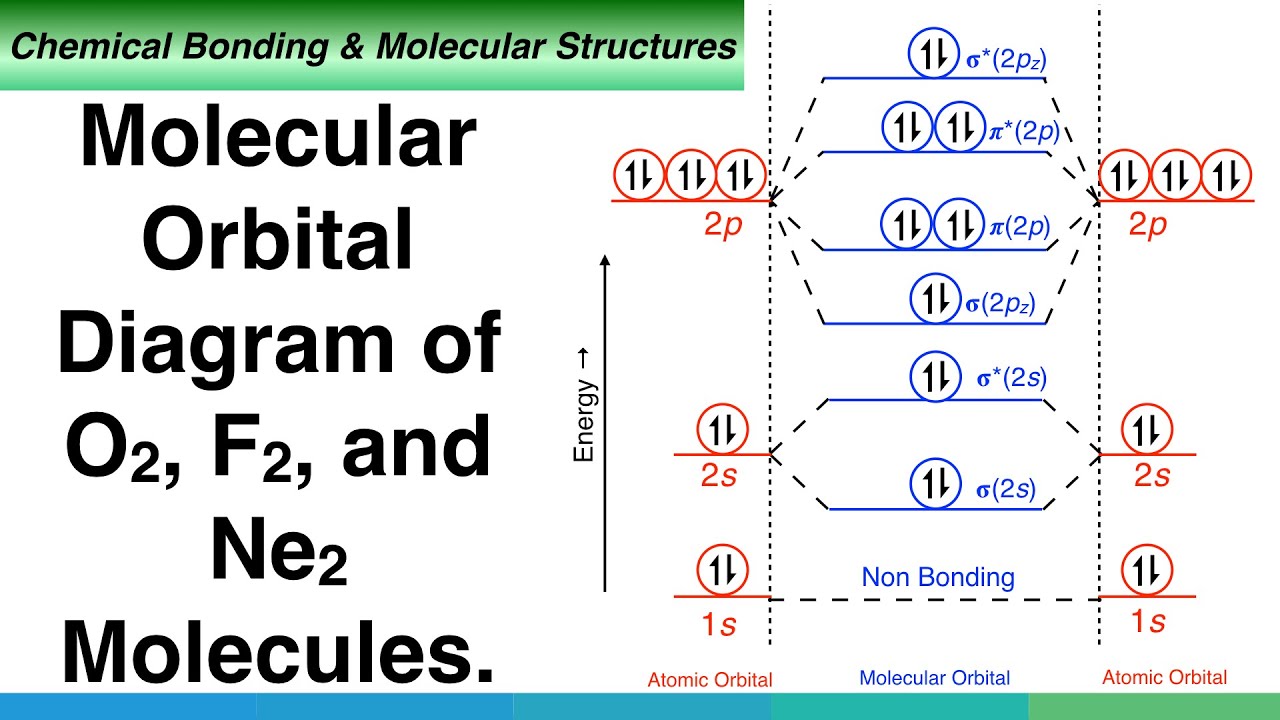
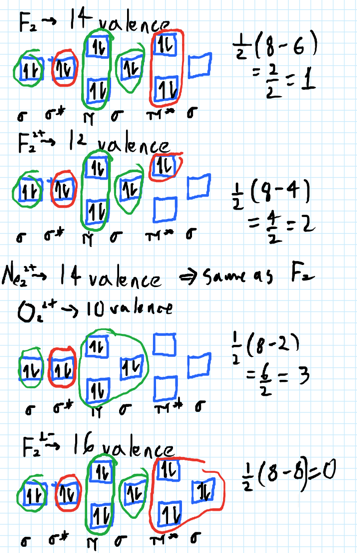








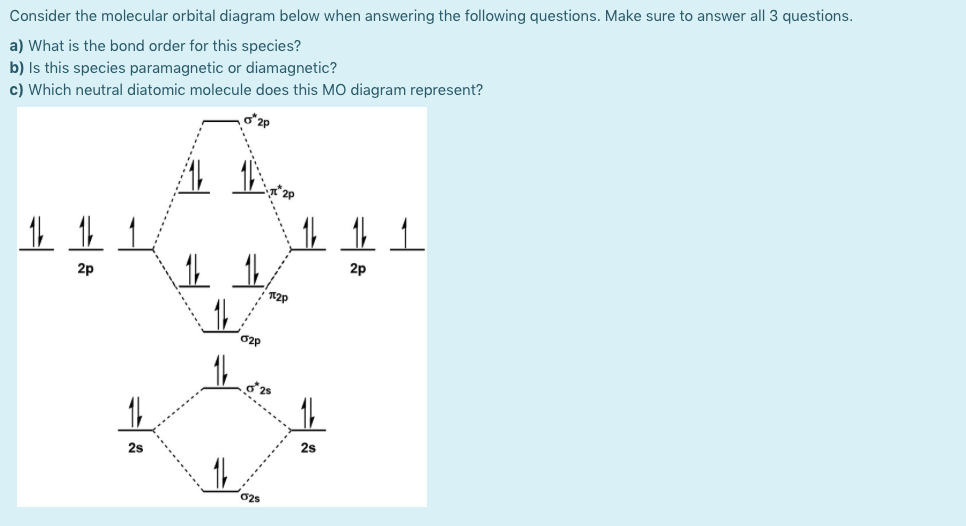

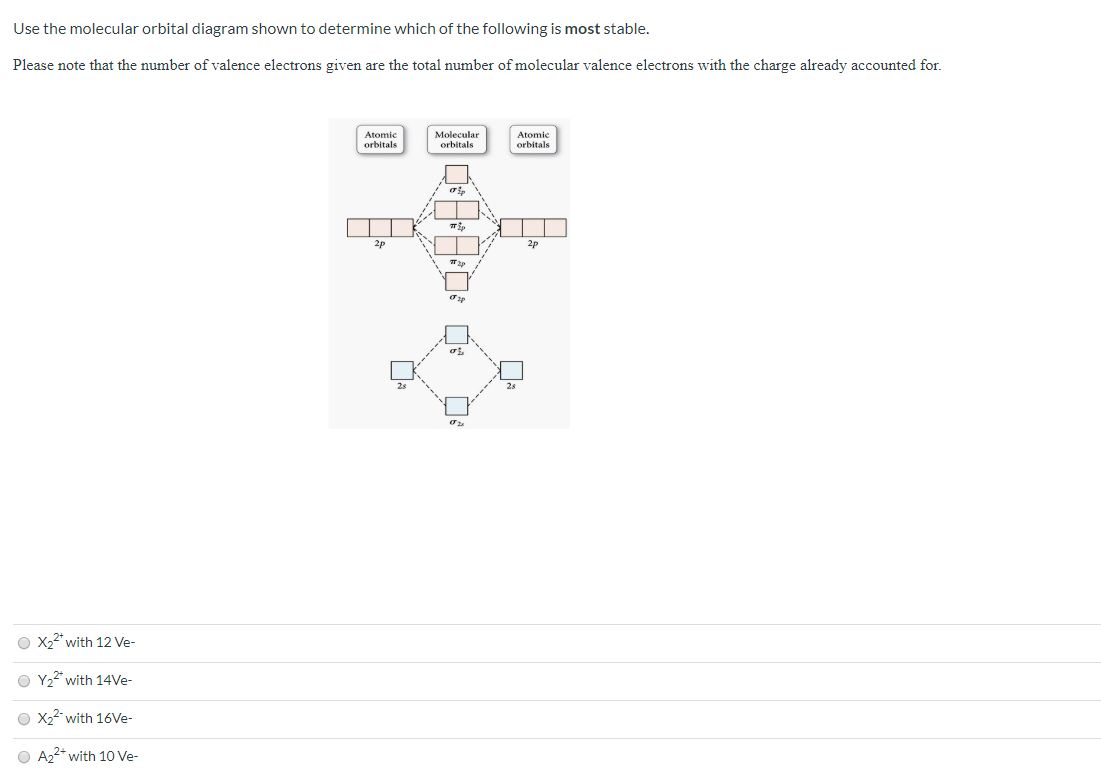
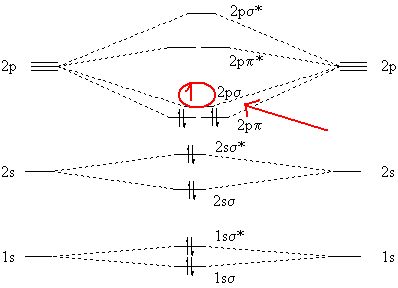



0 Response to "45 draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable."
Post a Comment