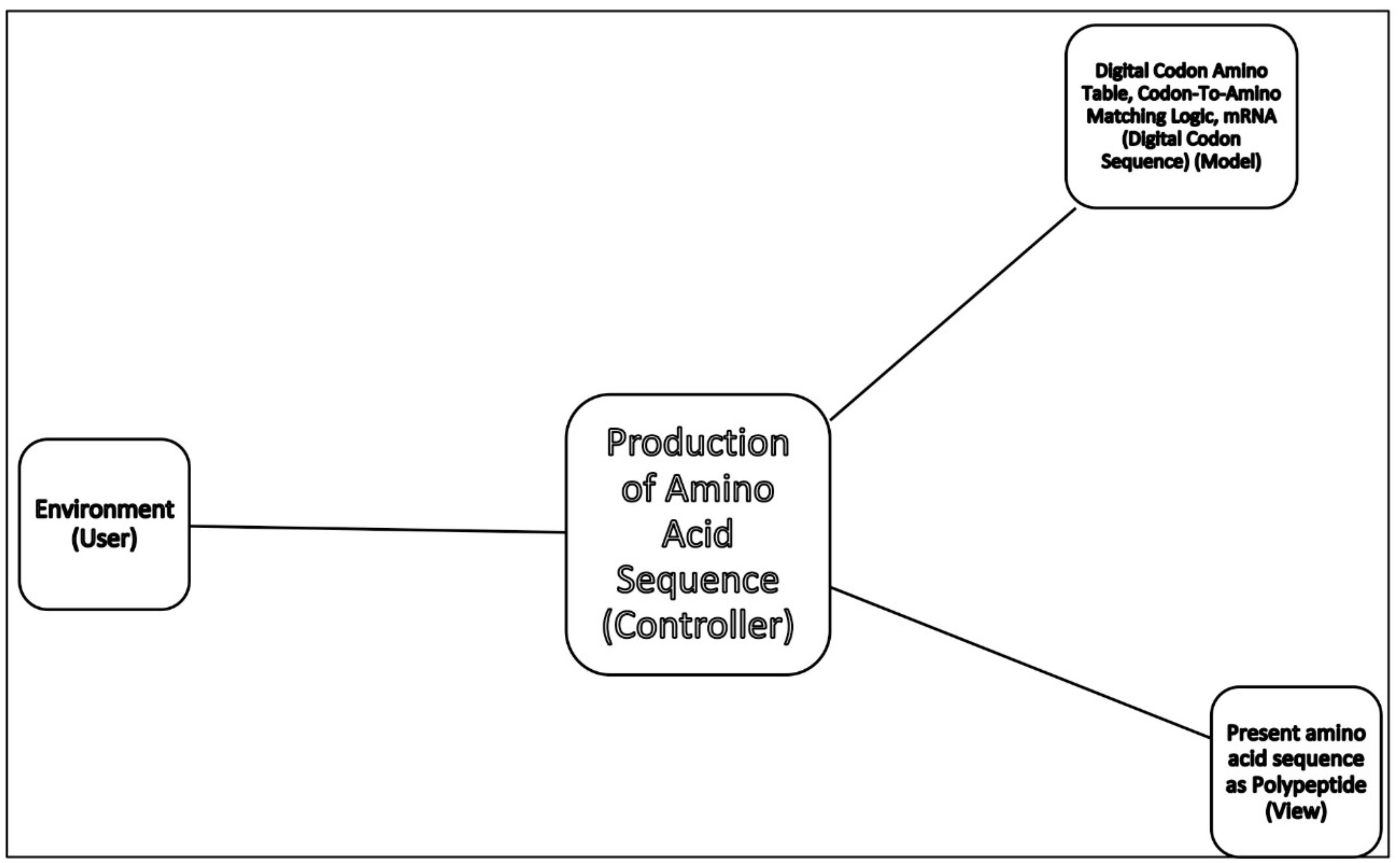
43 which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids
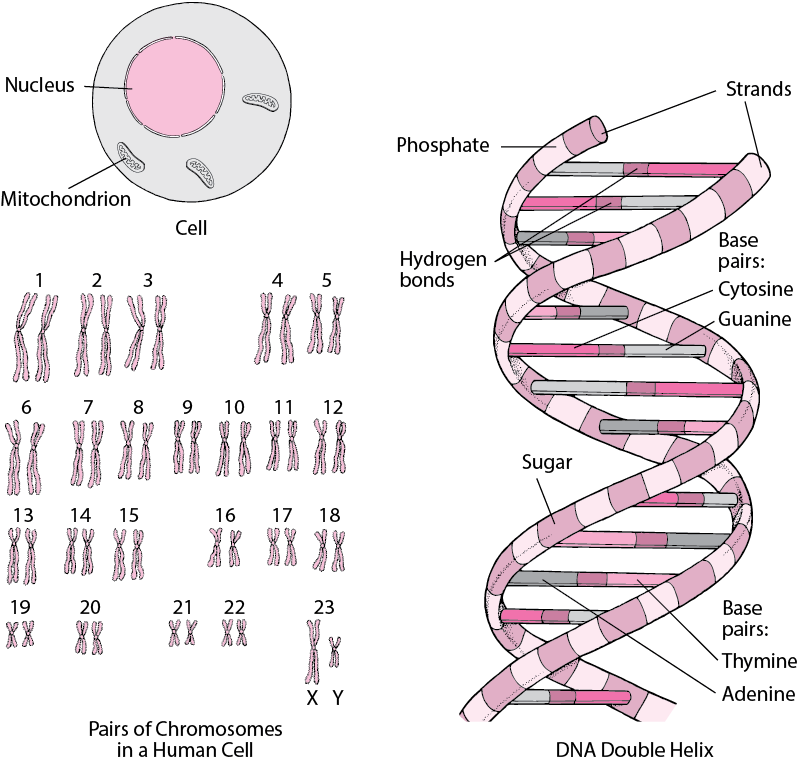
DNA and RNA study guide (Version 2) 10. What type of RNA is responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis? tRNA 11. The messenger RNA will carry the DNA's instructions out of the nucleus to the: Ribosome 12. Given the following DNA strand, what would the mRNA strand be? T A C G T T G C A A U G C A A C G U Transcription and Translation - Cell Biology, Genetics ... The copying of DNA to RNA is relatively straightforward, with one nucleotide being added to the mRNA strand for every nucleotide read in the DNA strand. The translation to protein is a bit more complex because three mRNA nucleotides correspond to one amino acid in the polypeptide sequence.
Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino ... Find an answer to your question Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? (Points : 1) 1 2 3 4 Which two structures are first to …

Which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids
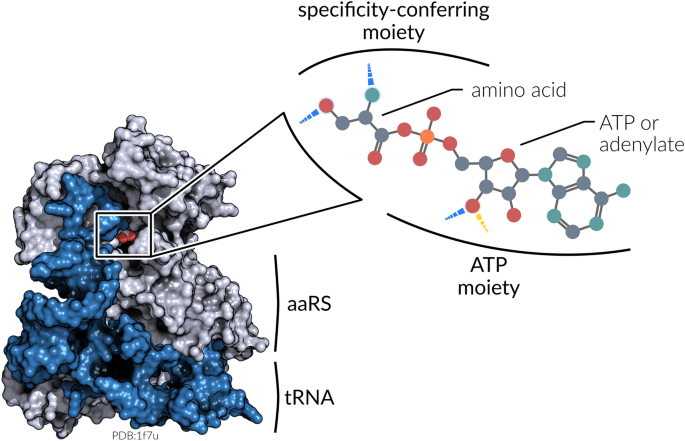
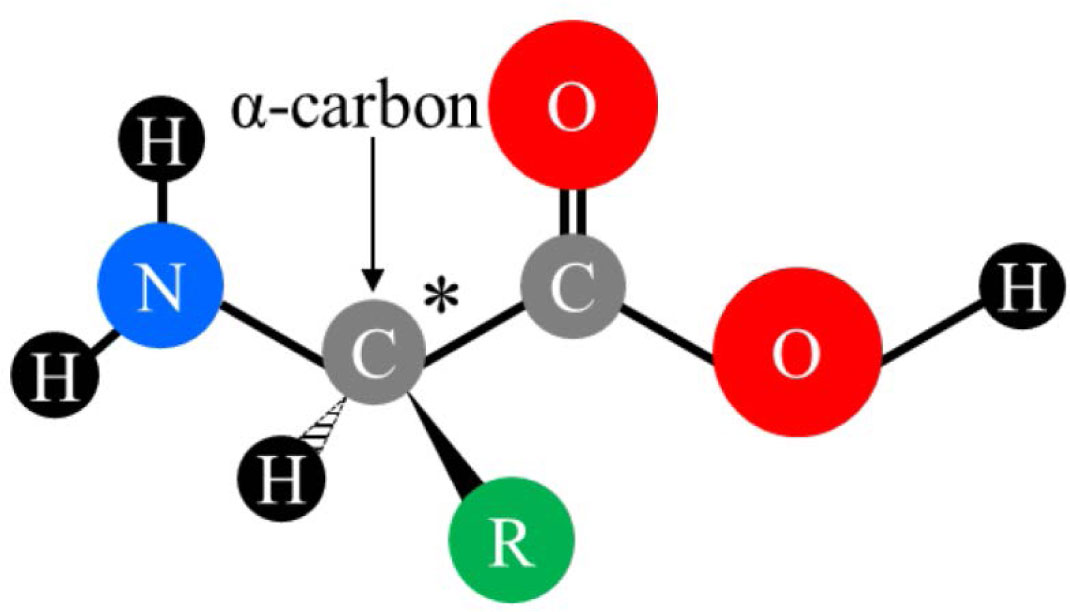
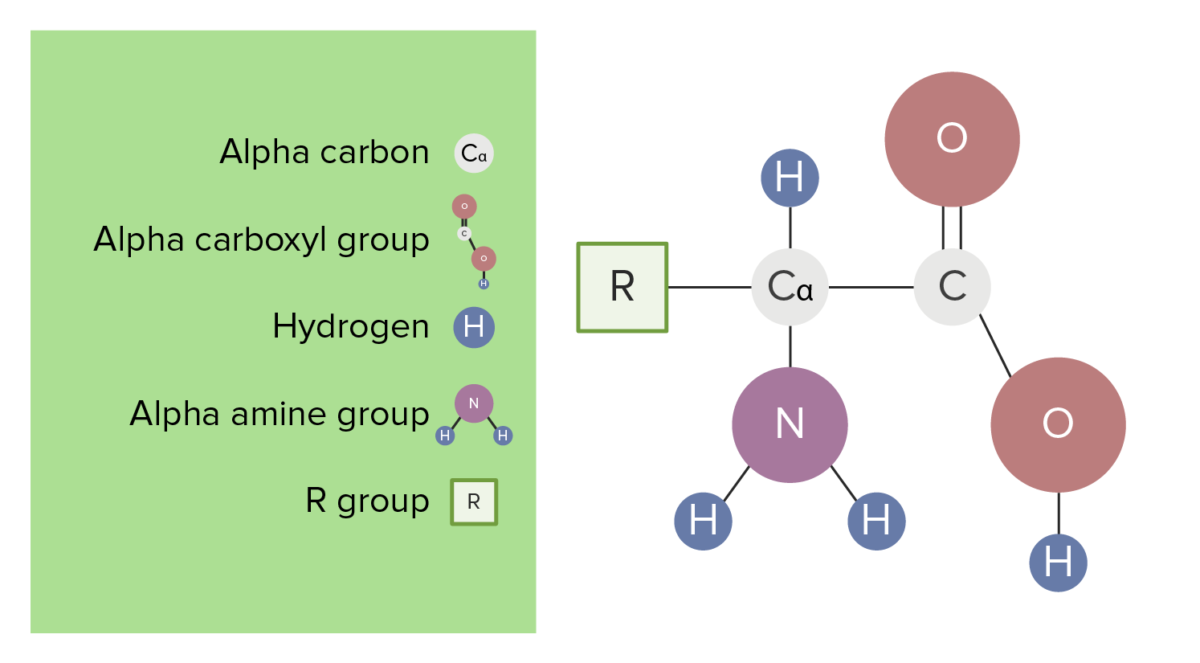
Role And Structure Of Ribosomes - Translation - MCAT Content Take a look at the diagram below to see how these are arranged relative to each other: Incoming aminoacyl-tRNAs(a tRNA with an amino acid covalently attached) enter the ribosome at the A site. The peptidyl-tRNA(a tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain) is held in the P site. Essential Amino Acids: Chart, Abbreviations and Structure ... Although amino acids are often shown in textbooks as the right-hand structure, they actually mostly exist as the left-hand structure. The simplest, and smallest, amino acid is glycine for which the R-group is a hydrogen (H). They can be subdivided according to their properties, dictated by the functional groups they possess. 1. Describe the structure of a monosaccharide. 2. Describe ... When the amino acids connect to each other by a peptide bond in a form of three-dimensional structure they form a polymer that is known as protein. Proteins are formed at the end central dogma by the process of transcription and translation.
Which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids. DNA_and_RNA_study_guide_Answer_Key - DNA and ... - Course Hero Use the following table to answer the following questions 15. Analyze the following DNA sequence: A T G C G A T C T A G C U A C G C U A G A U C G What is the correct order of amino acids represented by this DNA sequence? Tyrosine-Alanine-Arginine-Serine 16. List three stop codons. Amino Acids and Proteins: Terms | SparkNotes Amino acids in a form of neutrality where the carboxyl group and amino group are ready to donate and accept protons, respectively. Polar As opposed to non-polar, referring to the hydrophilic or "water loving" qualities of amino acids. Non-polar As opposed to polar, Referring to the hydrophobic or "water fearing" qualities of amino acids. Amino Acid Side Chains: Function & Examples - Video ... The Structure of Amino Acids. It would be pretty hard to take a count of all of the English words you know. The English language has over one million words, but they are all made using the same 26 ... Chapter 2: Protein Structure - Chemistry The major building block of proteins are called alpha (α) amino acids. As their name implies they contain a carboxylic acid functional group and an amine functional group. The alpha designation is used to indicate that these two functional groups are separated from one another by one carbon group.
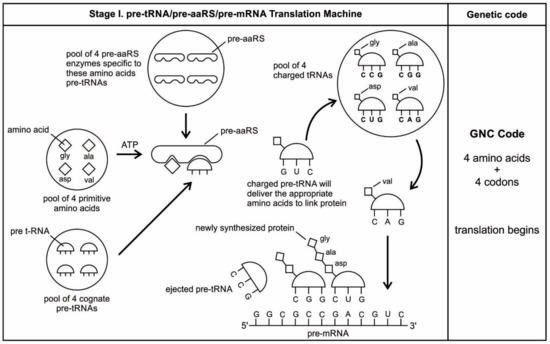
DNA Translation - Initiation - Elongation - TeachMePhysiology Every tRNA molecule possesses an anticodon that is complementary to the mRNA codon, and at the opposite end lies the attached amino acid. tRNA molecules are therefore responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosome in the correct order, ready for polypeptide assembly. Which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing ... The correct answer would be tRNA . tRNA ( transfer ribonucleic acid) is a type of RNA which brings amino acid to a ribosomal site which is then added to the growing polypeptide chain. The charged tRNA which has a complementary anti-codon site to the codon of mRNA brings the specific amino acid to the A site of the ribosomal complex. Polypeptide: Definition, Formation & Structure - Video ... Carboxyl groups appear in all amino acids since the latter are made up of an amino group and a carboxyl group. A carboxyl group consists of a hydroxyl (OH) bonded to a carbon, which is double... PDF Proteins: Three-dimensional Structure sequence of amino acids. In discussing protein structure, three further lev-els of structural complexity are customarily invoked: • Secondary structure is the local spatial arrangement of a polypeptide's backbone atoms without regard to the conformations of its side chains. • Tertiary structurerefers to the three-dimensional structure of ...
Biology 5.09 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? 2. Which two structures are first to combine in translation? 1 and 4. Which structure holds the original code from the DNA gene? 4. Which structure will become the product of translation? 3. Related questions. 5.09 Quiz: RNA makes protein Flashcards | Quizlet Look at the diagram. Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? 2. Which two structures are first to combine in translation? 1 and 4. Which structure holds the original code from DNA gene? 4. Which structure will become the product of translation.... Related questions. QUESTION. K12 Biology Semester 2 Unit 1 Flashcards - Quizlet mRNA enters the cytoplasm and moves to a ribosome which type or types of RNA most directly carries genetic instructions for building a specific protein mRNA what take place during transcription RNA is made from DNA Which Structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids tRNA Which two structures contain codons and anticodons Amino Acids- Properties, Functions, Sources and its ... There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids and all have common structural features - an amino group (-NH3+), a carboxylate (-COO-) group and a hydrogen-bonded to the same carbon atom. They differ from each other in their side-chain called R group. Each amino acid has 4 different groups attached to α- carbon. These 4 groups are: Amino group, COOH,
Enzymes - Structure, Classification, and Function Enzymes are a linear chain of amino acids, which give rise to a three-dimensional structure. The sequence of amino acids specifies the structure, which in turn identifies the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Upon heating, enzyme's structure denatures, resulting in a loss of enzyme activity, that typically is associated with temperature.
5.09 Quiz: RNA Makes Protein Flashcards | Quizlet 5.09 Quiz: RNA Makes Protein. Refer to the diagram to answer the question. Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? Refer to the diagram to answer the question. Which two structures are first to combine in translation?
Central Dogma Part 3 Flashcards | Quizlet The tRNA is responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosome. The tRNA contains an anti-codon that matches up with a codon, when it does this it will release an amino acid. How does the structure of a ribosome enable its function?
Which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing ... So the first one is which structure brings in the amino acid think about it about it tRNA look at it like this tRNA is the Transfering so you have T for transfer so it's tRNA its' an easy way to remember it. The second one is mRNA and tRNA the third one is mRNA and the last one is like amino acid.
What might result from a replication error? | Course Hero How does the structure of a tRNA molecules enable its function? Answer: The tRNA is responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosome. The tRNA contains an anti-codon that matches with a codon, when it does this it will release an amino acid.
The Ribosome: Structure, Function and Location - Video ... The ribosome is the cellular structure responsible for protein synthesis, the process that creates new protein molecules. Examine the importance of the ribosome's structure, function, and location ...
4 Levels of Protein Structure (With Diagram) The primary structure of a protein is the order of these amino acids in the backbone of each of the polypeptide chains comprising the molecule. The primary structure of a polypeptide chain is delineated beginning with the amino acid occupying the polypeptide's N-terminus.
7 Types of RNA with Structure and Functions - Microbe Notes They are ribonucleotides, therefore, they form a hydrogen bond with mRNA, and form ester links with amino acids which combine the mRNA and amino acids during translation. Figure: Transfer RNA (tRNA) - (a) tRNAs are represented as cloverleaf structures in two dimensions.
How to Read the Amino Acids Codon Chart? - Genetic Code ... When the number of amino acids adds up (usually > 30 units) and the polypeptide chain folds into a 3D structure, we call it a "protein". There are three features of codons: Each codon specifies an amino acid. The full set of relationships between codons and amino acids is summarized as a Condon Chart or Table.
Amino Acid Residue Overview & Examples | What is Amino ... In summary, amino acids are the building block that makes up proteins. A group of two or more amino acids bonded together is an amino acid residue. Each amino acid has different properties, and ...
1. Describe the structure of a monosaccharide. 2. Describe ... When the amino acids connect to each other by a peptide bond in a form of three-dimensional structure they form a polymer that is known as protein. Proteins are formed at the end central dogma by the process of transcription and translation.
Essential Amino Acids: Chart, Abbreviations and Structure ... Although amino acids are often shown in textbooks as the right-hand structure, they actually mostly exist as the left-hand structure. The simplest, and smallest, amino acid is glycine for which the R-group is a hydrogen (H). They can be subdivided according to their properties, dictated by the functional groups they possess.
Role And Structure Of Ribosomes - Translation - MCAT Content Take a look at the diagram below to see how these are arranged relative to each other: Incoming aminoacyl-tRNAs(a tRNA with an amino acid covalently attached) enter the ribosome at the A site. The peptidyl-tRNA(a tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain) is held in the P site.




























0 Response to "43 which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids"
Post a Comment