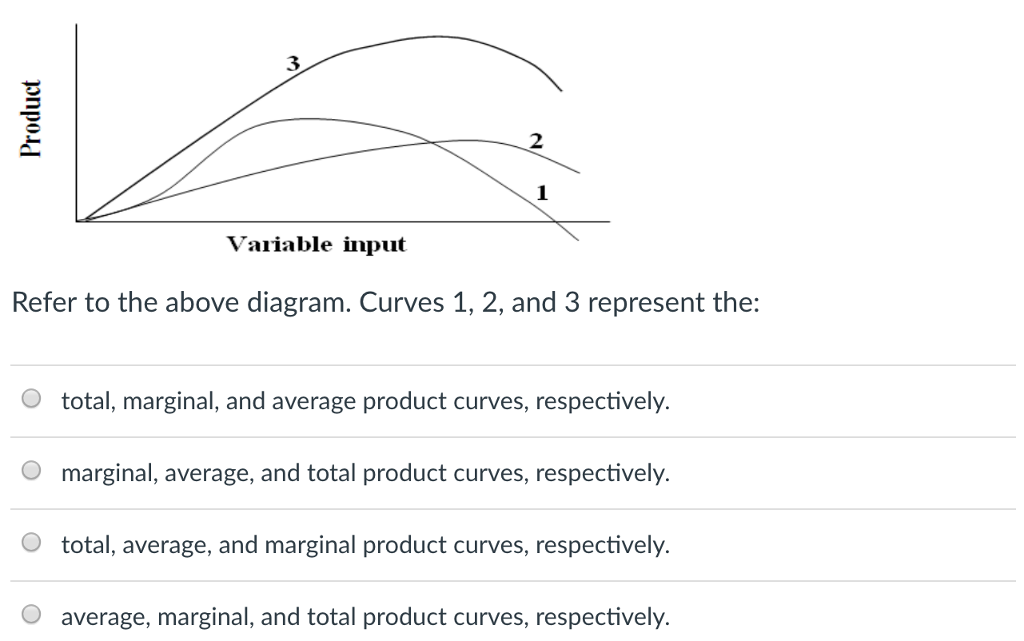
43 in the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent
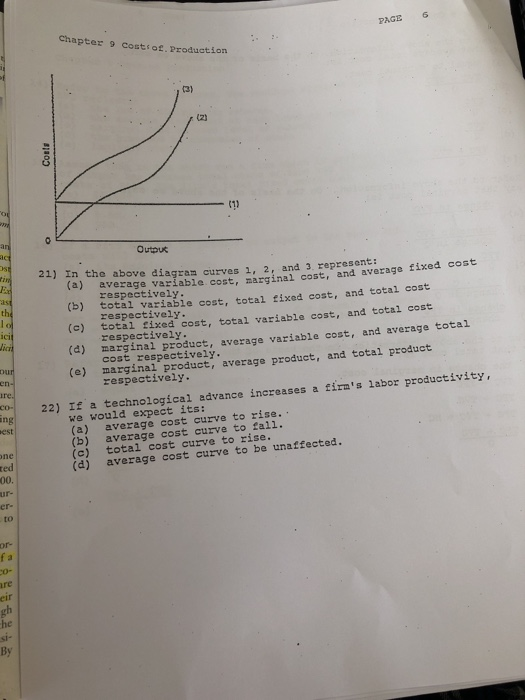
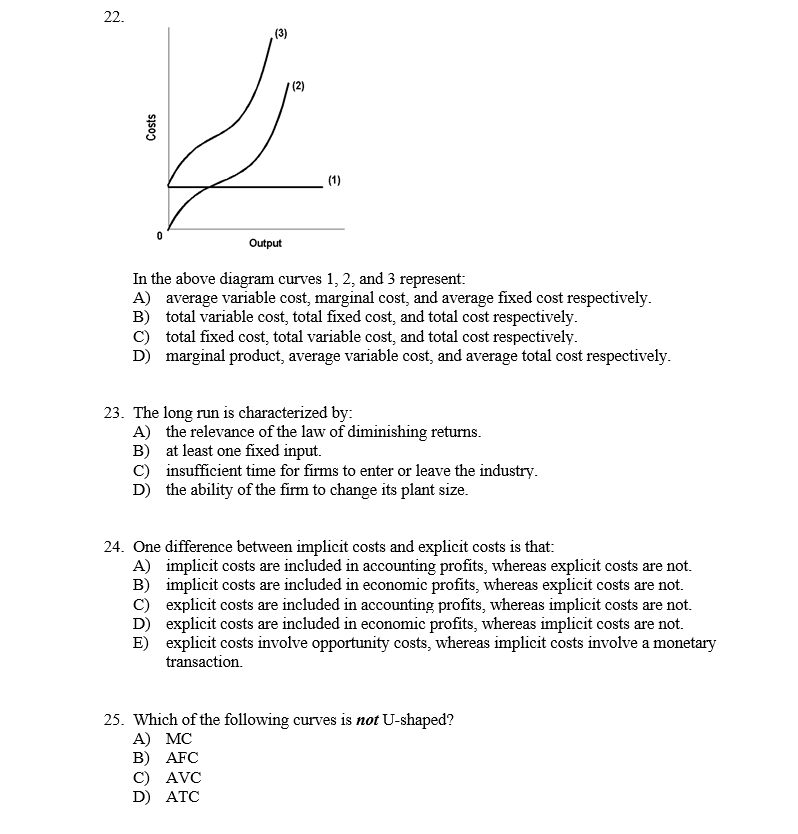
9. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the ... In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: A. average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B. marginal, average, and total product curves respectively . C. total, average, Just from $13/Page. Order Essay . Continue to order Get a quote. Post navigation. Microeconomics: Chapter 9 Flashcards - Quizlet In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. In the figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC curves respectively. The diagram suggests that: when marginal product lies above average product, average product is rising.
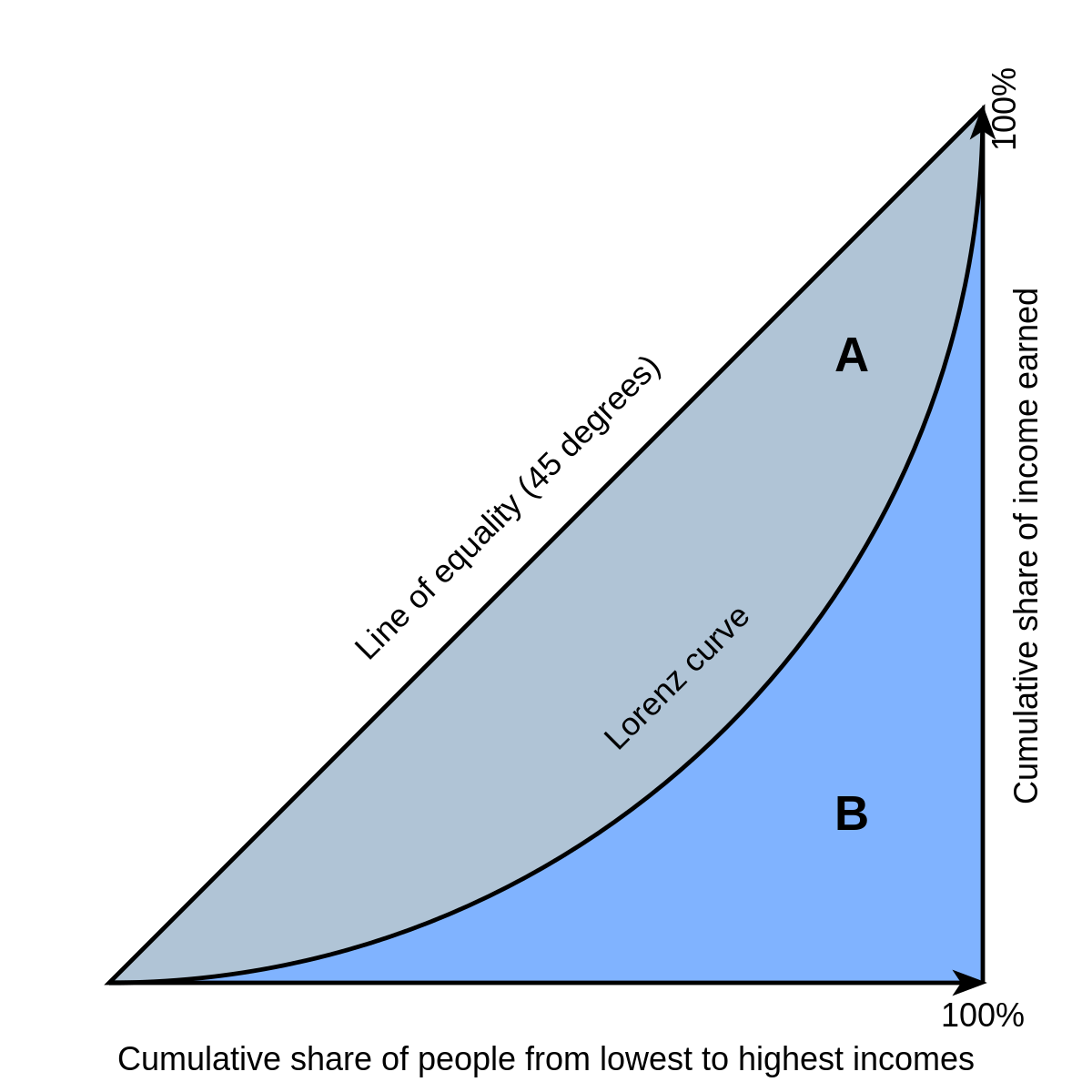
PDF UNIT 1 Microeconomics - Online Campus 1 Part C Use Figure 2.6 to answer the next five questions. Each question starts with Curve BB' as a country 's production possibilities curve. 3. Suppose there is a major technological breakthrough in the consumer-goods industry, and the new technology is widely adopted. Which curve in the diagram would represent the new produc-tion ...

In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent
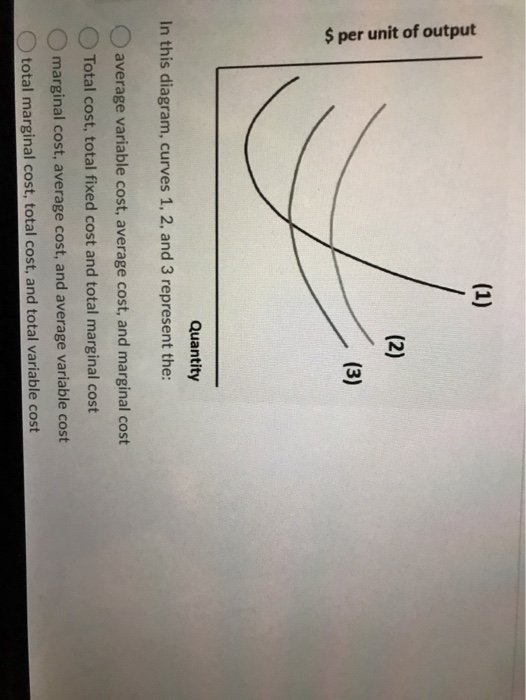
[Solved] 10. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: A. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively.2 answers · Top answer: Option C is correct The horizontal one which is constant shows the fixed costs at any given price and quantity, they do not change during operation. Curve ... 1 Product 2 Variable input 3 In this diagram, curves 1, 2 ... Consider the following cost curves. (1) $ per unit of output (2) (3) Quantity In this diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: 0 average variable cost, average cost, and marginal cost Total cost, total fixed cost and total marginal cost marginal cost, average cost, and average variable cost total marginal cost, total cost, and total variable cost Heating Curves and Phase Diagrams (M11Q2) - UW-Madison ... Figure 2. A heating curve and phase diagram for water. Solution. While anywhere along the line segment BD represents a phase change from solid to liquid, and points Y and Z are both on that line, the correct answer is D. At point Y, the phase change is occurring at the same pressure (1 atm) that was used to construct the heating curve.
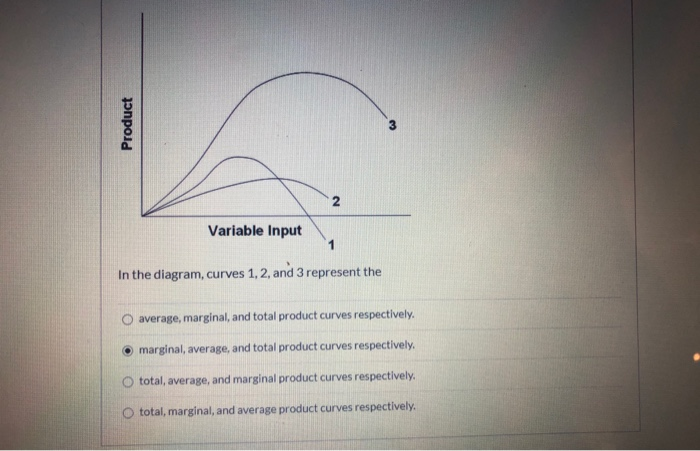
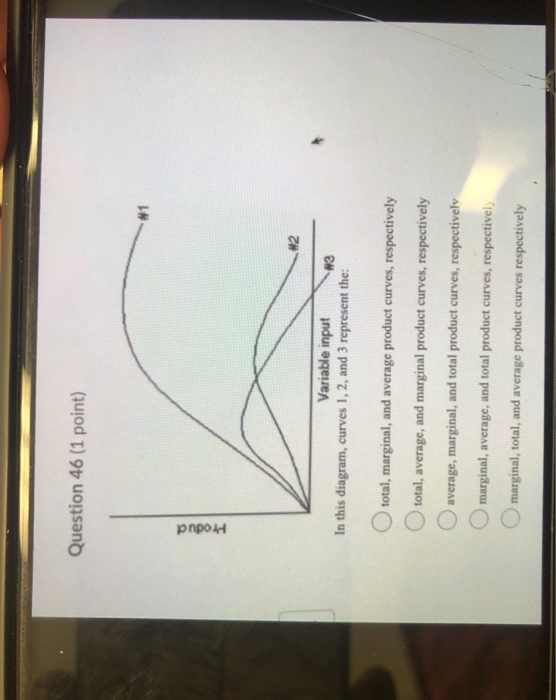
In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent. 1.2 Calculus of Parametric Curves - Calculus Volume 3 ... We start by asking how to calculate the slope of a line tangent to a parametric curve at a point. Consider the plane curve defined by the parametric equations. x(t) = 2t + 3, y(t) = 3t − 4, −2 ≤ t ≤ 3. The graph of this curve appears in Figure 1.16. It is a line segment starting at (−1, −10) and ending at (9, 5). 24 In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A ... 24 In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A average marginal and. 24 in the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent. School University of Tunku Abdul Rahman; Course Title ECON FHBM1014; Uploaded By DoctorCaribou179. Pages 8 This preview shows page 6 - 8 out of 8 pages. Answered: #3 #2 Variable input # 1 In this… | bartleby #3 #2 Variable input # 1 In this diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: Product. Question. total, marginal, and average product curves, respectively.1 answer · Top answer: Step 1 From the above diagram we can say that,Number 1 is Marginal product since it can be negative.Num... Edgeworth Box Diagram | Consumption | Goods | Microeconomics The allocation A 2 is superior to A 0. In the above diagram, allocation cannot cross the indifference curves. This is because all allocations are Pareto efficient. There are different allocations in the box diagram. The indifference curves are tangent at A 1, A 3 or A 4. All tangent point in the box diagram is efficient. The indifference curves ...
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: a. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. b. total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. c. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. d. marginal product, average variable cost, and average total cost respectively. PDF 1. In the diagram below, the direct rays of the Sun are ... 1) A 3) C 2) B 4) D 12. Which date is represented by the diagram? 1) March 21 3) September 23 2) June 21 4) December 21 13. During one complete rotation of the Earth on its axis, which position receives the least number of hours of daylight? 1) A 3) C 2) B 4) D 14. The passage of the Moon into Earth's shadow causes a 1) lunar eclipse 3) new Moon Solved Output In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent ... Output In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. O marginal product, average variable cost, and average total cost respectively. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. Graphing Calculator - Mathway Free graphing calculator instantly graphs your math problems.
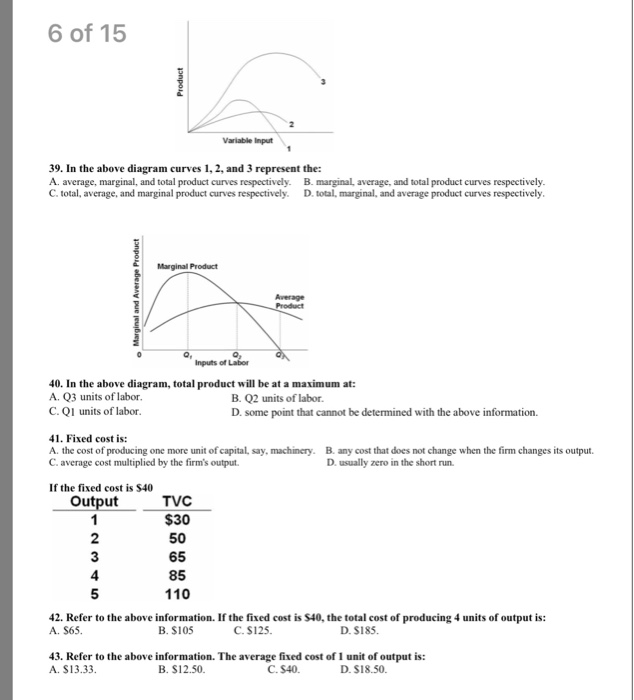
Figure shows four PV diagrams. Which of these curves ... Which of these curves represent isothermal and adiabatic processes respectively? Solve Study Textbooks Guides. Join / Login >> Class 11 ... Process 1, 2 and 3 are respectively. ... Medium. View solution > The cycle on a P V diagram is represented as. Medium. View solution > The P-T diagram for an ideal gas is shown in the figure, where AC is an ... PDF UNIT 1 Macroeconomics LESSON 1 - Denton ISD possibilities curve. Part A Use Figures 1.1 and 1.2 to answer Questions 1 and 2. Fill in the answer blanks, or underline the correct answer in parentheses. 1. If the economy represented by Figure 1.1 is presently producing 12 units of Good B and zero units of Good A: [Solved] #1 #2 Variable input In this diagram, curves 1, 2 ... Answer to #1 #2 Variable input In this diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: #3 O total, marginal, and average product curves, respectively total, average, and margi | SolutionInn In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A ... 11. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: A) average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B ) marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. C) total, average, and marginal product curves respectively. D) total, marginal, and average product curves respectively. 12.
Stress Strain Curve - Relationship, Diagram and ... Stress strain curve is the plot of stress and strain of a material or metal on the graph. In this, the stress is plotted on the y-axis and its corresponding strain on the x-axis. After plotting the stress and its corresponding strain on the graph, we get a curve, and this curve is called stress strain curve or stress strain diagram.
Microeconomics (ECON-2302) Flashcards | Quizlet In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: ~ average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. ~ total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. ~ total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. ~ marginal product, average variable cost, and average total cost respectively.
PDF 1.Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in ... A)above position 1 B)below position 3 C)between position 1 and position 2 D)between position 2 and position 3 3.Positions 1, 2, and 3 in the diagram below represent the noon Sun above the horizon on three different days during the year, as viewed from Binghamton, New York. At which position was the noon Sun on January 21, as viewed from Binghamton?
PDF UNIT 1 Microeconomics LESSON 2 - Denton ISD 1. Activities 2, 3, 4 and 5 2. Visuals 1.2 and 1.3 Procedure 1. Give a lecture on scarcity. (A) Wants are unlimited. ... Which curve in the diagram would represent the new produc-tion possibilities curve? (Indicate the curve you choose with two letters.) BD' 4. Suppose a new government comes into power and forbids the use of automated machinery and
Microeconomics Chapter 9 Flashcards | Quizlet
A cyclic process ABCD is shown in the P-V diagram. Which ... A cyclic process ABCD is shown in the P-V diagram. Which of the following P-T curves represent the same process ? (1) (2) (3) (4) Practice questions, MCQs, Past Year ...
10.4 Phase Diagrams - Chemistry Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
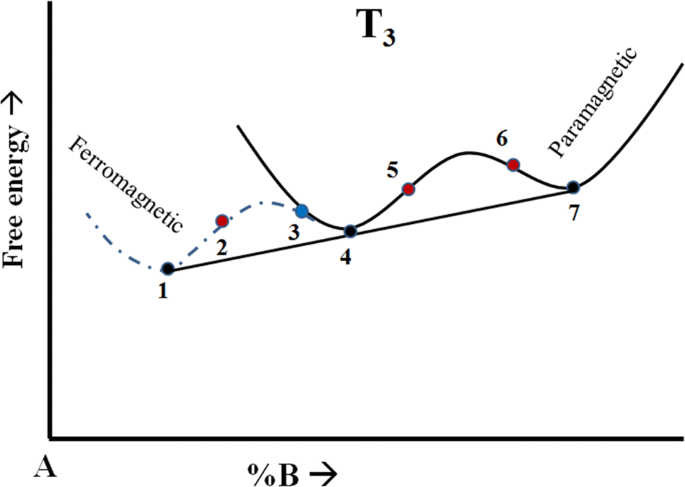
A typical UCST-type phase diagram, curve 1, curve 2 and ... Download scientific diagram | A typical UCST-type phase diagram, curve 1, curve 2 and curve 3 represent crystallization temperature curve, spinodal curve and binodal curve, respectively from ...
1 Product #2 Variable input #3 In this diagram, curve… #1 Product #2 Variable input #3 In this diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: O marginal, total, and average product curves respectively marginal, ...1 answer · 1 vote: Option 5 is the correct answer total, average and marginal product curves respectively. Thanks!..
An ideal gas undergoes four different ... - Toppr Ask When a thermodynamic system undergoes a change in such a way that no exchange of heat takes place between it and the surroundings, the process is known as adiabatic process. Graph 4 is isobaric process, 1 is isochoric. Of 3 and 2,3 has the smaller slope (magnitude) hence is isothermal. Remaining process is adiabatic. So graph 2 is adiabatic.
How to Tell If a Graph Represents a Function A curve drawn in a graph represents a function, if every vertical line intersects the curve in at most one point. Question 1 : Determine whether the graph given below represent functions.
revcosts In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: A. ATC, MC, AFC, and AVC curves respectively. B. AFC, MC, AVC, and ATC curves respectively. ... The above diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. In ...
PDF UNIT 1 Microeconomics Key - FCPS Use the axes in Figures 2.3, 2.4 and 2.5 to draw the type of curve that illustrates the label above each axis. 1 Microeconomics LESSON 2 ACTIVITY 2 Answer Key UNIT GOOD A Increasing opportunity cost per unit of Good B GOOD B Figure 2.3 Production Possibilities Curve 3 GOOD B GOOD A Zero opportunity cost per unit Figure 2.4 Production ...
Heating Curves and Phase Diagrams (M11Q2) - UW-Madison ... Figure 2. A heating curve and phase diagram for water. Solution. While anywhere along the line segment BD represents a phase change from solid to liquid, and points Y and Z are both on that line, the correct answer is D. At point Y, the phase change is occurring at the same pressure (1 atm) that was used to construct the heating curve.
1 Product 2 Variable input 3 In this diagram, curves 1, 2 ... Consider the following cost curves. (1) $ per unit of output (2) (3) Quantity In this diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: 0 average variable cost, average cost, and marginal cost Total cost, total fixed cost and total marginal cost marginal cost, average cost, and average variable cost total marginal cost, total cost, and total variable cost
[Solved] 10. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: A. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively.2 answers · Top answer: Option C is correct The horizontal one which is constant shows the fixed costs at any given price and quantity, they do not change during operation. Curve ...






















0 Response to "43 in the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent"
Post a Comment