42 pauli exclusion principle diagram
Pauli exclusion principle | physics | Britannica Pauli exclusion principle, assertion that no two electrons in an atom can be at the same time in the same state or configuration, proposed (1925) by the Austrian physicist Wolfgang Pauli to account for the observed patterns of light emission from atoms. JEE Main 2022, 2023, 2024 Syllabus [Updated] - Download PDF Pauli's exclusion principle and Hund's rule, electronic configuration of elements, extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals. Chemical bonding and molecular structure Kossel - Lewis approach to chemical bond formation, the concept of ionic and covalent bonds.
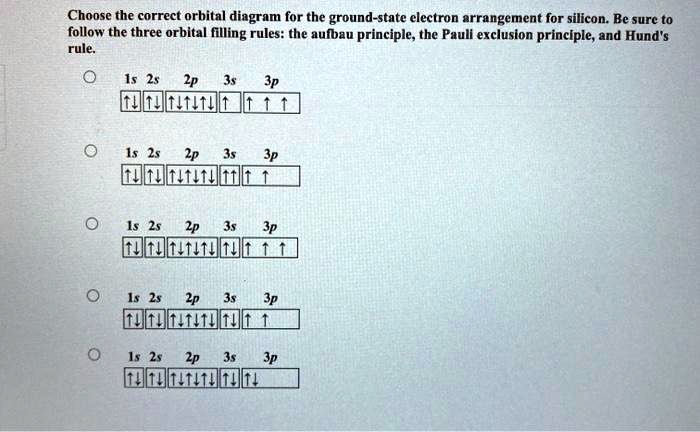
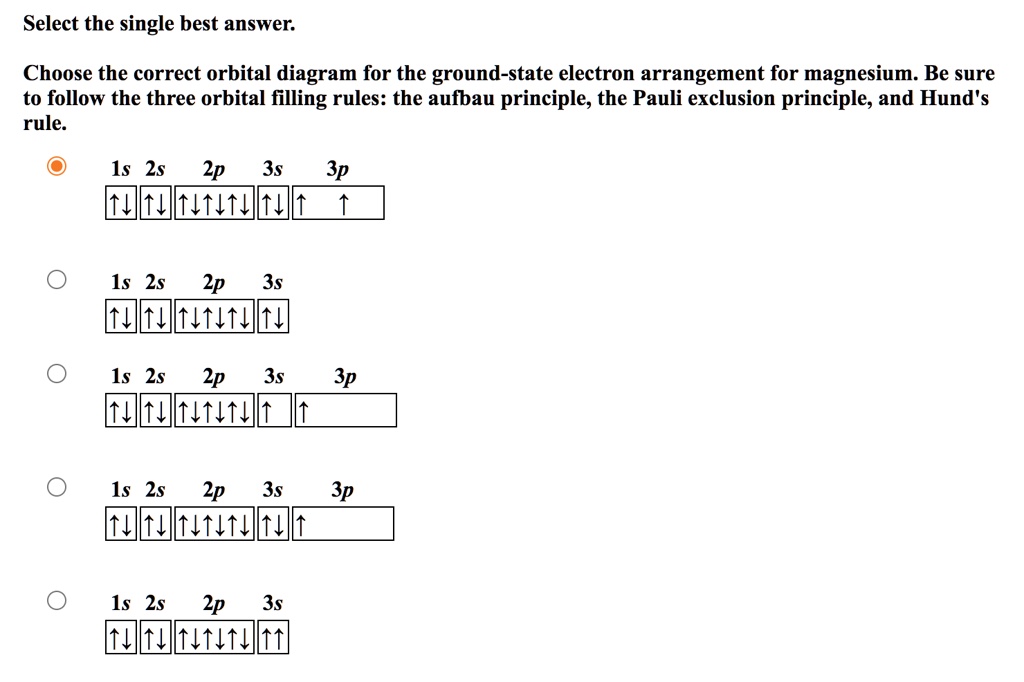
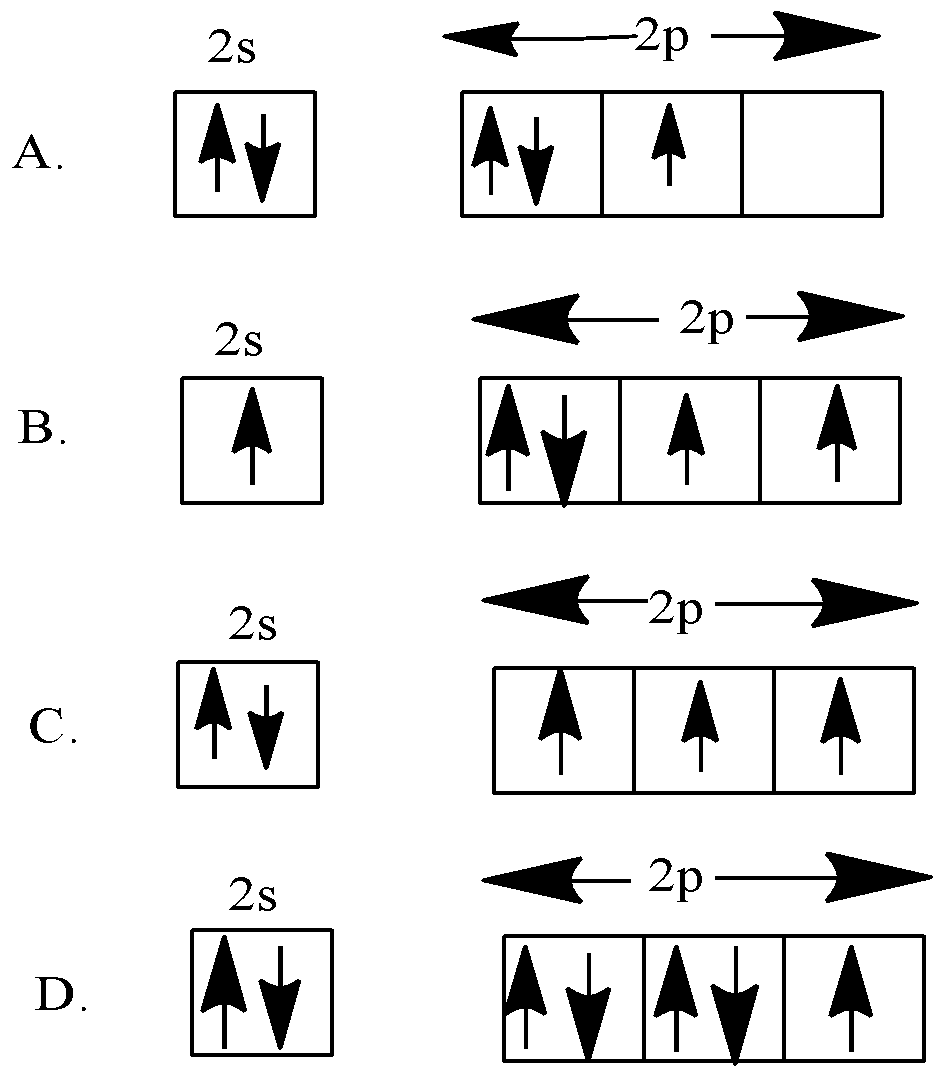
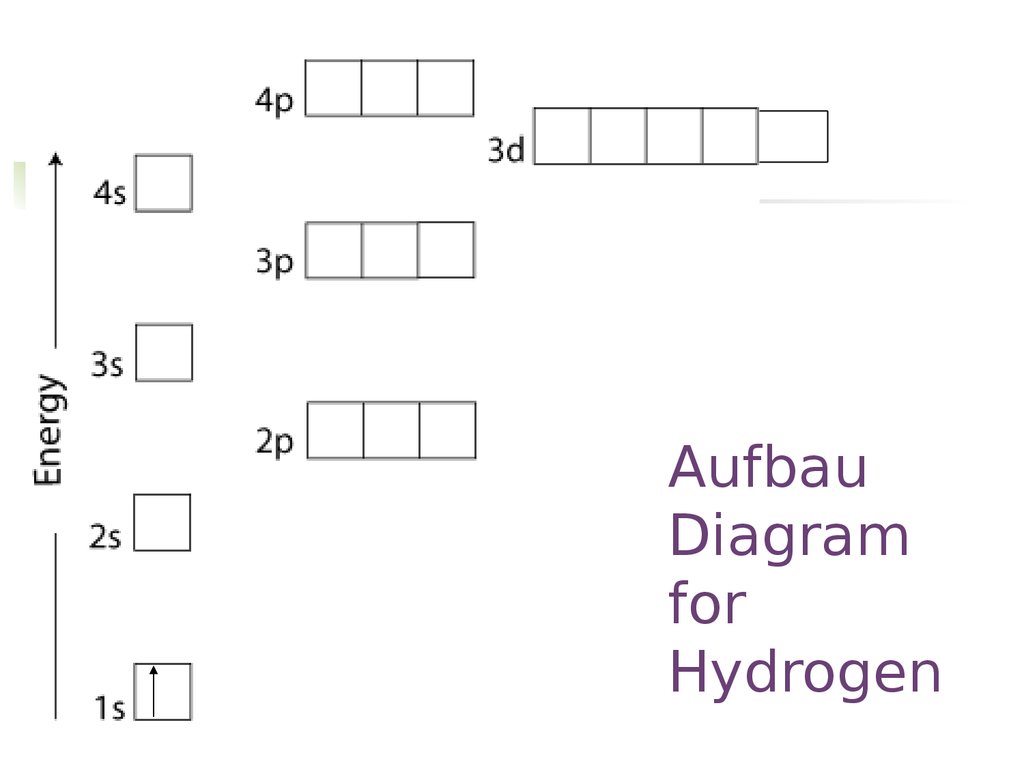
Pauli, Aufbau, Hund - ChemistNate Pauli Exclusion Principle, Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule ... Which of the rules do each of the following electron energy diagrams violate?Jul 26, 2020 · Uploaded by chemistNATE
Pauli exclusion principle diagram
Definition of the Pauli Exclusion Principle - Chemistry Dictionary The Pauli exclusion principle says that every electron must be in its own unique state. In other words, no electrons in an atom are permitted to have an identical The Pauli exclusion principle sits at the heart of chemistry, helping to explain the electron arrangements in atoms and molecules, and helping... PDF Pauli exclusion principle Pauli Exclusion Principle. of two-particle scattering amplitude with parallel spins must be zero. Similar rela-tionship can also be proven for two quasiparticles interaction function fσσ′ (p, p′) in terms of Eqs. Fig. 1. Scattering diagrams to illustrate Pauli exclusion principle. Pauli Exclusion Principle - Meaning, Applications, and FAQs Learn about pauli exclusion principle topic of physics in details explained by subject experts on vedantu.com. Register free for online tutoring The distributions can be clearly understood if we draw the diagram as given below. These are a few examples of how Pauli's exclusion principle is used.
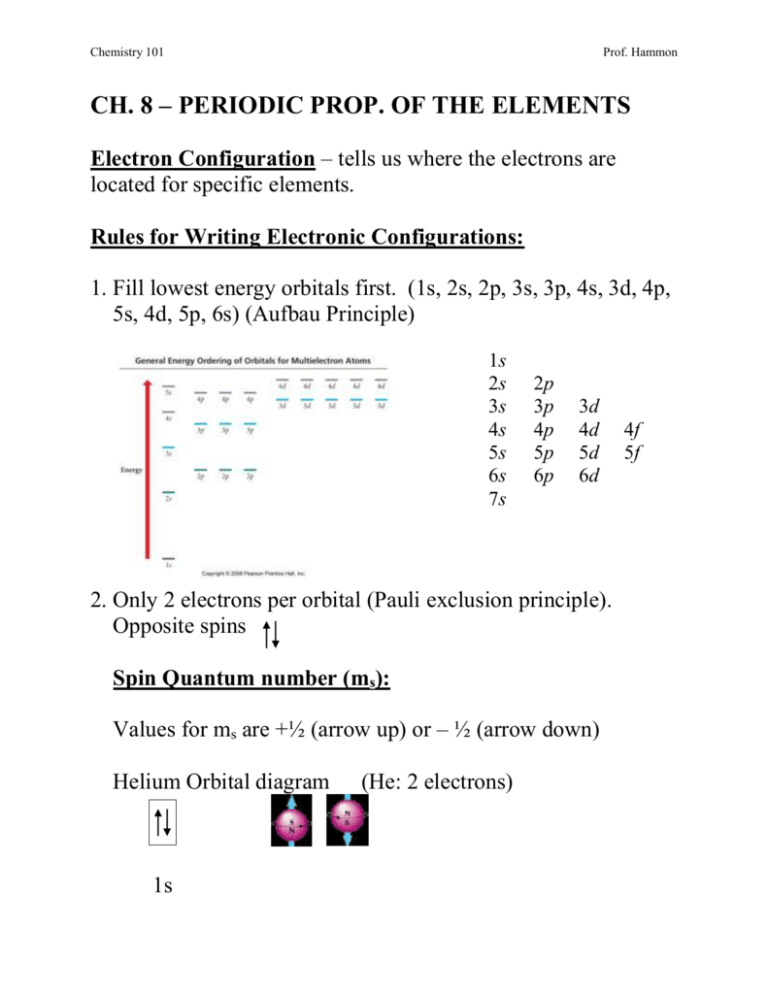
Pauli exclusion principle diagram. Bohr model - Wikipedia In atomic physics, the Bohr model or Rutherford–Bohr model, presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913, is a system consisting of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons—similar to the structure of the Solar System, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces in place of gravity.After the solar system Joseph Larmor model (1897), the cubical model … PDF The pauli principle The pauli principle, representation theory, and geometry of flag varieties. a dissertation submitted to the department of mathematics July, 2008 According to the Pauli exclusion principle, discovered in 1925, no two identical electrons may occupy the same quantum state. Pauli Exclusion Principle ( Read ) | Chemistry | CK-12 Foundation Pauli Exclusion Principle. Spin differentiates electrons within the same orbital. This concept states the Pauli exclusion principle and describes how the spin quantum number can allow us to differentiate between two otherwise identical electrons. Pauli formulated the exclusion principle which states that As we know that the spin quantum number can have only two values +½ and -½, only two electrons can be accommodated in a given orbital in accordance with Pauli exclusion principle. Let us understand this by writing all the four quantum numbers for the eight electron in L shell.
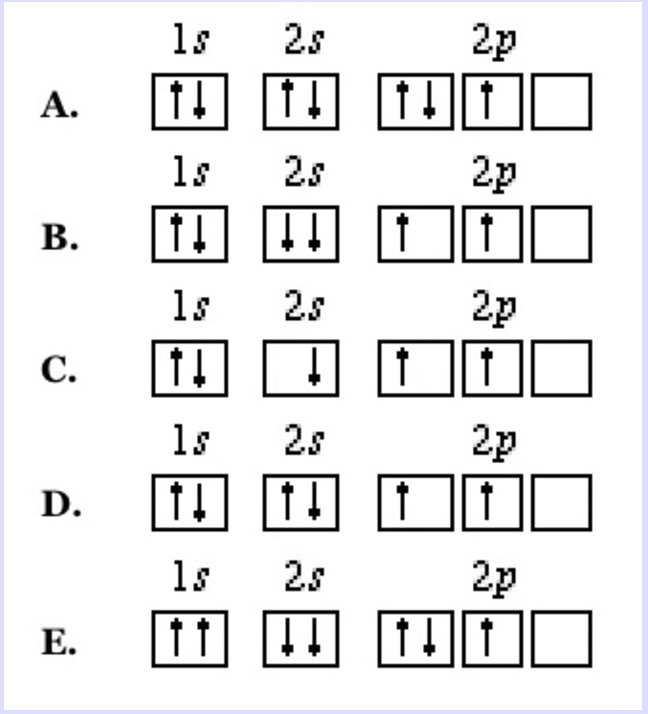
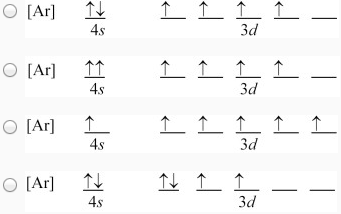
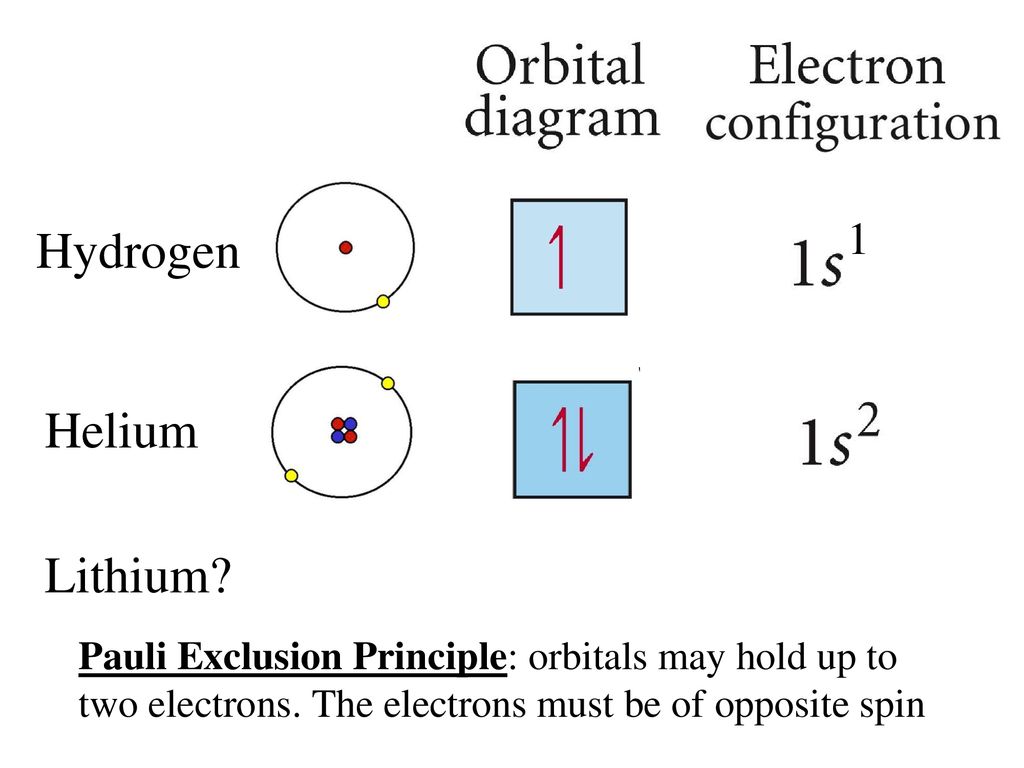
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle? + Example The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers. The fourth quantum number is the electron spin quantum number m_s=+-1/2. In the diagram below, notice that hydrogen's single electron is represented by an up arrow. Helium has two 1"s". electrons. Pauli Exclusion Principle | definition and example According to Pauli Exclusion Principle, No two electrons can have samples values of the quantum numbers n, l,ml and ms or they can not have all these quantum numbers similar; at least one of the four numbers which are strictly required to Specify the state of an electron should be different from the... Aufbau's Principle, Hund's Rule & Pauli's Exclusion Principle... This chemistry video explains what is the aufbau's principle, hund's rule, and pauli's exclusion principle and how it relates to orbital diagrams, electron... Pauli Exclusion Principle The Pauli Exclusion Principle allows for the distinction between different elements. Furthermore, the Principle also effects the way molecules form in the bonding of atoms, for the way molecules interact to form gases, liquids, or solids, and/or how the molecules aggregate themselves in living organisms.
Pauli Exclusion Principle: Definition, Application, Explanation and... Pauli exclusion principle is a fundamental principle along with Aufbau's Principle and Hund's Rule in chemistry. In the year 1925, the Austrian physicist Wolfgang Pauli proposed Pauli's exclusion principle. It states that no two electrons in the same atom can possess identical values for all four of... C2H6 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... 2 days ago · According to Pauli’s exclusion principle, one atomic orbital can have a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. The same is also true for molecular orbitals. The pairing of electrons in the degenerate molecular orbitals will take place only when all the degenerate molecular orbitals are singly occupied. Exclusion Principle, Pauli | Encyclopedia.com Exclusion Principle, Pauli Historical background The exclusion principle Electronic configurations Rationalizing the periodic law Resources Source for information on Exclusion Principle, Pauli: The Gale Encyclopedia of Science dictionary. What are Hund's Rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle, and Aufbau ... Dec 10, 2016 — Pauli Exclusion Principle: no two electrons can be identified by the ... do a lot of work with electron configurations and energy diagrams.1 answer · • Aufbau Principle: lower energy orbitals fill before higher energy orbitals. • Hund's Rule: one electron goes into each until all of them are half ...
Pauli Exclusion Principle - Chemistry LibreTexts The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that, in an atom or molecule, no two electrons can have the same four electronic quantum numbers. As an orbital can contain a maximum of only two electrons, the two electrons must have opposing spins. This means if one electron is assigned as a spin up (+1/2)...
Electronic band structure - Pauli Exclusion principle and perturbation... The exclusion principle can dictate how those bands get filled (and, if the particles interact, even through a mean-field description, the filling can then Well, the first thing that will happen is that we need to choose where we put them, and the Pauli exclusion principle is going to be very stringent...
VSEPR Theory: Introduction - YouTube To see all my Chemistry videos, check outhttp://socratic.org/chemistryThis is an introduction to the basics of VSEPR Theory. VSEPR theory is a set of rules f...
Pauli exclusion principle - Wikipedia Part of a series of articles about. Quantum mechanics. Schrödinger equation. Introduction. Glossary. History. v. t. e. The Pauli exclusion principle is the quantum mechanical principle which states that two or more identical fermions (particles with half-integer spin)...
What is the explanation of the Pauli exclusion principle for a layman? The Pauli exclusion principle is an example of a quantum principle that states that no two particles can have the same quantum numbers. Pauli exclusion principle Each state (point) on the diagram can be occupied by no more than one electron. which means that these bands "fill" up.
Pauli Exclusion Principle The Pauli exclusion principle is part of one of our most basic observations of nature: particles of half-integer spin must have antisymmetric wavefunctions, and particles of integer spin must have symmetric wavefunctions.
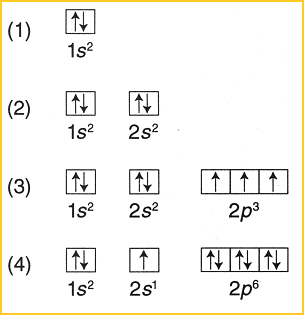
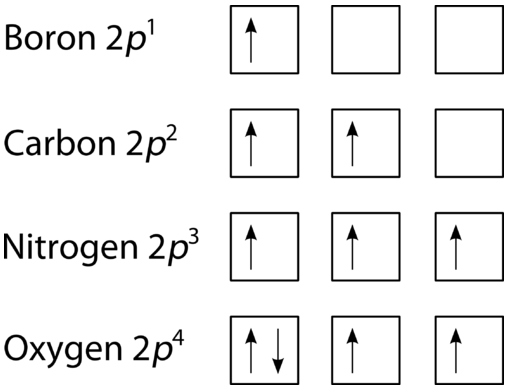
Oxygen(O) electron configuration and orbital diagram To create an orbital diagram of an atom, you first need to know Hund’s principle and Pauli’s exclusion principle. Hund’s principle is that electrons in different orbitals with the same energy would be positioned in such a way that they could be in the unpaired state of maximum number and the spin of the unpaired electrons will be one-way.
PDF Paulis Exclusion Principle: The Origin and Validation of a Scientific... 4 How Pauli's rule became the exclusion principle: from Fermi-Dirac statistics to the spin-statistics theorem. There is hardly another principle in physics with wider scope of applicability and more far-reaching consequences than Pauli's exclusion principle.
Electron configuration - Wikipedia Electron configuration was first conceived under the Bohr model of the atom, and it is still common to speak of shells and subshells despite the advances in understanding of the quantum-mechanical nature of electrons.. An electron shell is the set of allowed states that share the same principal quantum number, n (the number before the letter in the orbital label), that electrons …
Pauli Exclusion Principle | Open Science Wiki | Fandom Pauli exclusion principle states that in a single atom no two electrons will have an identical set or the same quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms). To put it in simple terms, every electron should have or be in its own unique state (singlet state). It states that:-. Only two electrons can occupy the same orbital.
Pauli Exclusion Principle Pauli Exclusion Principle Electrons in a single atom occupy discrete levels of energy. Band Diagram: Fermi-Dirac "Filling" Function The Fermi-Dirac function gives the fraction of allowed states, fFD(E), at an energy level E, that are populated at a given temperature.
The Pauli Exclusion Principle | Physics The Pauli Exclusion Principle. Learning Objectives. By the end of this section, you will be able... Explain the Pauli exclusion principle and its application to the atom. Specify the shell and subshell symbols and their positions.
Pauli Exclusion Principle ~ ChemistryGod The Pauli exclusion principle states no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of the quantum numbers (principal, azimuthal As we can see from the above diagram, all paired electrons in an orbital have opposite spins. It is the violation of the principle to place parallel spins in an orbital.
The Pauli Exclusion Principle - Big Chemical Encyclopedia The Pauli principle states that a maximum of two electrons can reside in each orbital, and we We can also represent the arrangement of electrons in an atom using orbital diagrams, in which each We have already discussed the Pauli exclusion principle in Chapter 5. In its most general form, this...
Pauli Exclusion Principle: Statement, Examples, and Diagrams Pauli exclusion principle applies to a set of fundamental particles called Fermions that have half-integer spin (S = 1/2, 3/2, 5/2 …). These particles do not violate the principle. On the other hand, it does not apply to Bosons that have integer-spin (S = 1,2,3…).
Pauli Exclusion Principle Definition The Pauli exclusion principle states no two electrons (or other fermions) can have the identical quantum mechanical state in the same atom or molecule. In chemistry, the Pauli exclusion principle is used to determine the electron shell structure of atoms.
PDF Pauli Exclusion Principle and its theoretical foundation Pauli Exclusion Principle; Spin-Statistics connection; Indistinguishability principle; Permutation symmetry. Wolfgang Pauli formulated his principle before the creation of the contemporary quantum mechanics. a Young diagram with N boxes. The symmetry postulate demands that the basis vectors.
Hunds Rule - Aufbau Principle | Pauli's Exclusion Principle 1. Pauli's exclusion principle. 2. Aufbau principle. 3. Hund's rule. Pauli's Exclusion Principle. According to this law, an orbital cannot have both the electrons in the same spin motion (half-integer spin); electrons will be in either positive half spin (+1/2) or negative half spin (-1/2) For example, argon's electron configuration: 1s² 2s² ...
Pauli Exclusion Principle Electrons: study guides and answers on... Pauli Exclusion Principle Electrons. Quizlet is the easiest way to study, practise and master what you're learning. Create your own flashcards or choose from millions created by other students. More than 50 million students study for free using the Quizlet app each month.
Pauli exclusion principle in nLab In physics, the Pauli exclusion principle (Pauli 25) states that no two spinors may inhabit the same quantum state. This is a consequence of the spin-statistics theorem, which states that spinors must be fermions. The Pauli exclusion principle implies that fermions, as opposed to bosons, may form...
Pauli Exclusion Principle - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The Pauli exclusion principle requires that the bare scattering rate given by Eqn. A2.4 Electrons and Magnetism. Pauli's Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in the same atom can have identical values for all four of their quantum numbers.
Fermi Dirac Distribution:Energy Band Diagram, Boltzmann ... Fermi-Dirac statistics is the branch of quantum statistics, that describes the distribution of particles in energy states that contains identical particles obeying Pauli-Exclusion Principle. Since F-D statistics is applied to particles with half-integer spin, these are called fermions.
Pauli Exclusion Principle - Meaning, Applications, and FAQs Learn about pauli exclusion principle topic of physics in details explained by subject experts on vedantu.com. Register free for online tutoring The distributions can be clearly understood if we draw the diagram as given below. These are a few examples of how Pauli's exclusion principle is used.
PDF Pauli exclusion principle Pauli Exclusion Principle. of two-particle scattering amplitude with parallel spins must be zero. Similar rela-tionship can also be proven for two quasiparticles interaction function fσσ′ (p, p′) in terms of Eqs. Fig. 1. Scattering diagrams to illustrate Pauli exclusion principle.
Definition of the Pauli Exclusion Principle - Chemistry Dictionary The Pauli exclusion principle says that every electron must be in its own unique state. In other words, no electrons in an atom are permitted to have an identical The Pauli exclusion principle sits at the heart of chemistry, helping to explain the electron arrangements in atoms and molecules, and helping...

























0 Response to "42 pauli exclusion principle diagram"
Post a Comment