41 virtual image lens diagram
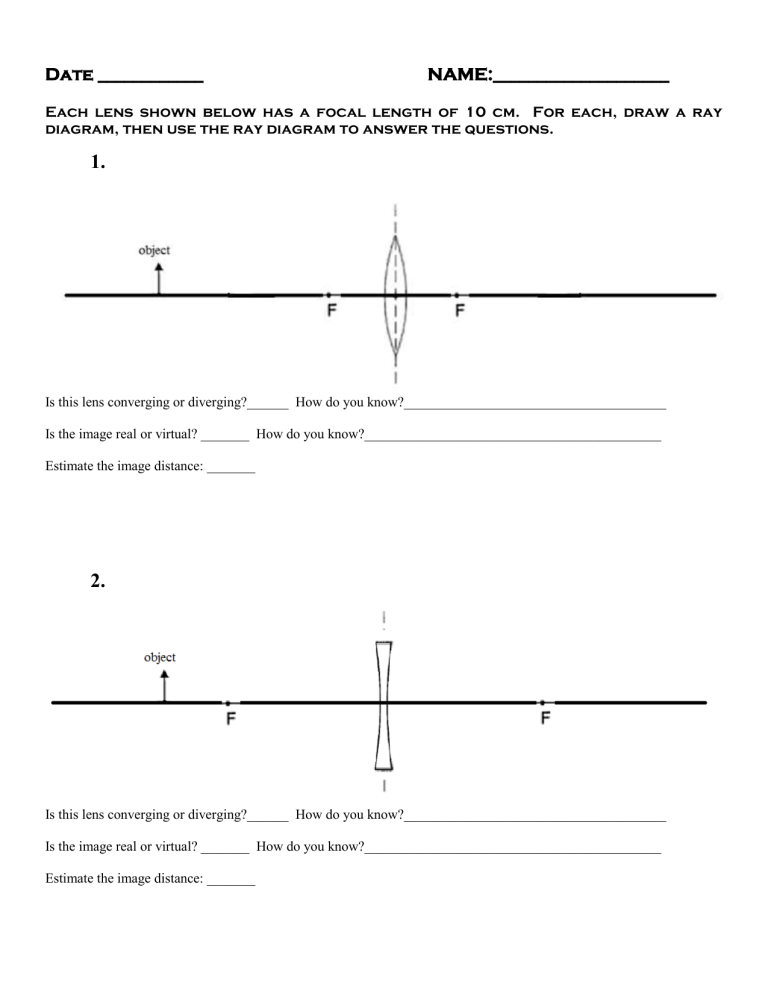
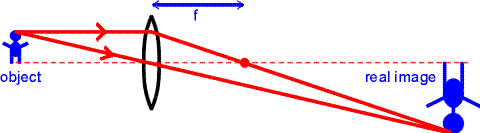
Converging lens - interactive simulations - eduMedia Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray. The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and ... A lens forms an erect, magnified and virtual image of an object. (a) Name the type of lens. (b) Where is the object placed in relation to the lens? (c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image. (d) Name the device which uses this principle.
What are Real and Virtual Images? | Definition, Examples ... A virtual image is defined as the opposite of a real image, therefore an image that cannot be obtained on a screen is referred to as a virtual image. The explanation for this is the fact that the rays of light that form a virtual image never converge therefore a virtual image can never be projected onto a screen. The best example of a virtual image is your reflection in the mirror.

Virtual image lens diagram
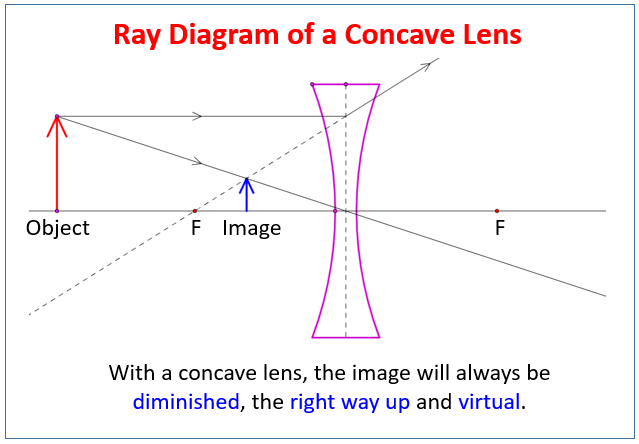
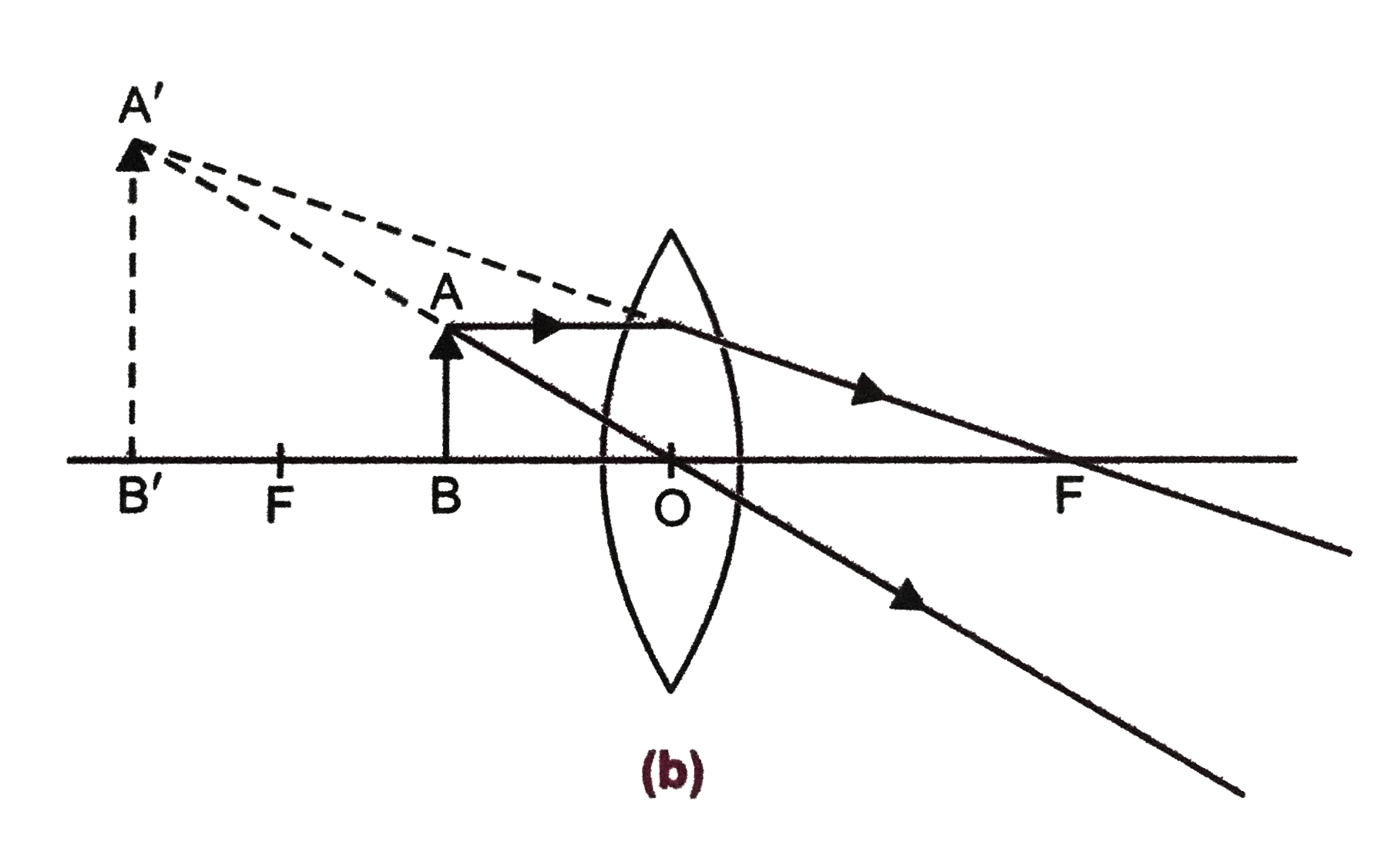
Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the … Concave Lens - Ray diagram, Images Formed - with Steps ... 26.04.2020 · Concave Lens - Ray diagram You are here Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens ... Image is virtual (left side of the lens) Image is Erect Image is Smaller than the Object (Highly Diminished) Case 2 - Object is between Infinity and Optical Center Here, Object AB kept anywhere on the principal axis - between Infinity and … PDF 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 VIRTUAL IMAGES - Pomona Figure 7.3: Using a ray diagram to locate the virtual image formed by a diverging lens. The dotted lines show the trajectories that the photons appear to follow, according to the observer. The gray lines indicate the relationships between the second and third principal rays and the focal points of the diverging lens. object image eye second ...
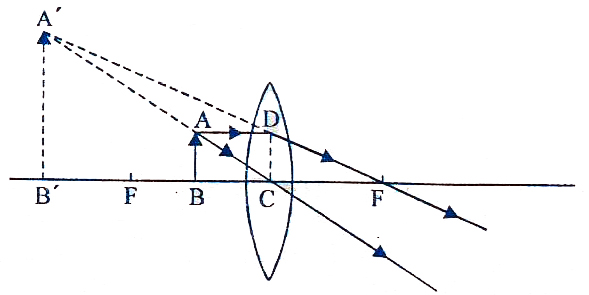
Virtual image lens diagram. Real and virtual images - Lenses - AQA - GCSE Physics ... A virtual image appears to come from behind the lens. To draw a ray diagram: Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. Once through the lens, the ray should... Image Formation by Lenses | Physics - Lumen Learning Virtual images are always upright and cannot be projected. Virtual images are larger than the object only in case 2, where a convex lens is used. The virtual image produced by a concave lens is always smaller than the object—a case 3 image. We can see and photograph virtual images only by using an additional lens to form a real image. PDF Imaging with two lenses - lpc1.clpccd.cc.ca.us - object can be real or virtual (virtual in this case) - object can be real even if image from lens 1 is virtual • Trace any two of the three rays shown through tip of object to find tip of final image - Final image may be real or virtual (real in this case) L2 F2 F2' Object (virtual) Image (real) Virtual image - Wikipedia In diagrams of optical systems, virtual rays are conventionally represented by dotted lines, to contrast with the solid lines of real rays. Because the rays never really converge, a virtual image cannot be projected onto a screen. In contrast, a real image can be projected on the screen as it is formed by rays that converge on a real location.
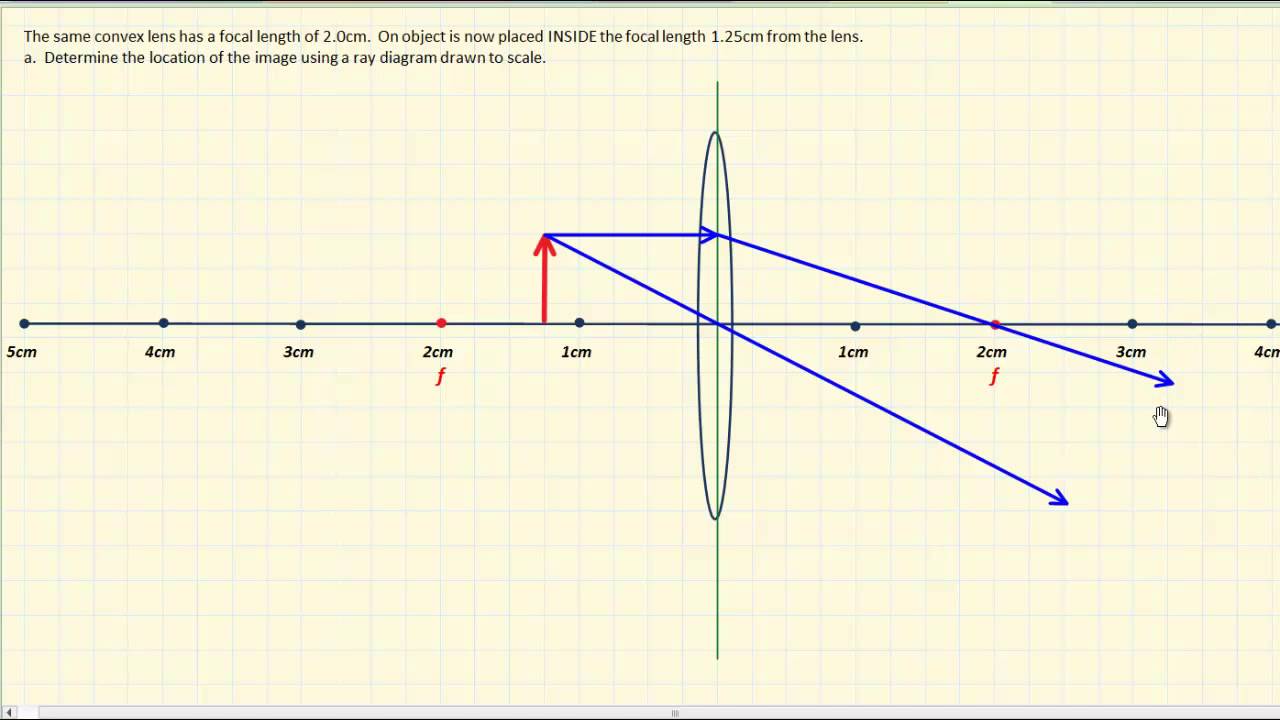
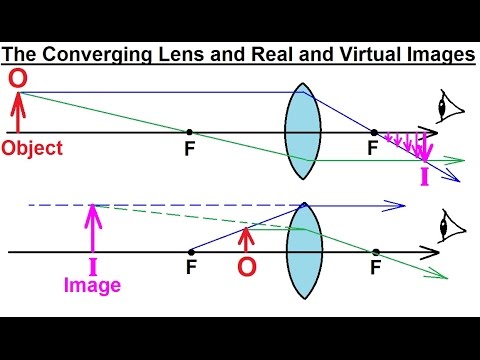
Ray diagram for diverging lens with both object and image ... 2 The top diagram shows the formation of the virtual object where converging rays are prevented from meeting by the diverging lens. Then those converging rays are made to diverge by the lens and so a virtual image is formed. Update as a result of a comment from @Floris. Real and virtual images - Lenses and ray diagrams - OCR ... virtual (cannot be produced on a screen) Ray diagram for an object placed less than one focal length from a convex lens Only the person using the magnifying glass can see the image. The image... Images, real and virtual - Michigan State University Virtual images are formed by diverging lenses or by placing an object inside the focal length of a converging lens. The ray-tracing exercise is repeated for the case of a virtual image. In this case the virtual image is upright and shrunken. The same formula for the image and object distances used above applies again here. Rules for identifying sign in Convex and Concave Lens ... 15.05.2020 · Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for ... If a virtual image is formed, image is formed on left side, so image distance is negative Since object is always above the principal axis, object height will be positive If image is above the principal axis, image height will be positive. It means that image is erect If image is below the …
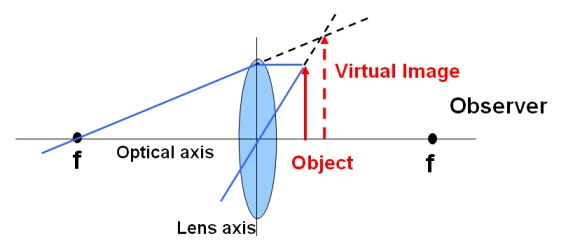
Converging Lenses - Ray Diagrams - Physics Classroom A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. To see why this is so, a ray diagram can be used. A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right. Convex Lens Ray Diagram - Virtual Image - YouTube Convex Lens Ray Diagram with Virtual Image. Convex Lens Ray Diagram with Virtual Image. Real and virtual images - Lenses - CCEA - GCSE Physics ... A virtual image cannot be projected onto a screen. It appears to come from behind the lens and can only be seen by looking through the lens. Rays of light appear to come from a virtual image ... Concave and Convex Lenses - Image Formation | Curvature ... When an object is placed at a finite distance from the lens, a virtual image is formed between the pole and the focus of the convex lens. The size of the image is larger than that of the object. Summary of Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lens 14,248
Virtual Microscope - NCBioNetwork.org Lesson Description BioNetwork’s Virtual Microscope is the first fully interactive 3D scope - it’s a great practice tool to prepare you for working in a science lab. Explore topics on usage, care, terminology and then interact with a fully functional, virtual microscope. When you are ready, challenge your knowledge in the testing section to see what you have learned.
Convex & Concave Lens Ray Diagrams | How to Draw Ray ... The steps in drawing a convex lens ray diagram are as follows: Step 1 Draw the first incident ray (Ray 1) from the tip of the object parallel to the principal axis. The refracted ray should pass...
Difference Between Real Image and Virtual Image with ... A virtual image is an upright image that is achieved where the rays seem to diverge. A virtual image is produced with the help of a diverging lens or a convex mirror. A virtual image is found by tracing real rays that emerge from an optical device backward to perceived or apparent origins of ray divergences.
7 Concave Lens Examples in Daily Life - StudiousGuy The concave lens forms a virtual and erect image in between its optical center and the focal point when the object is placed at a finite distance from the concave lens. The image formed is of a smaller size than that of the object. Uses of Concave Lens 1. Spectacles. Concave lenses are widely used in spectacles to correct near-sightedness or Myopia. People suffering from myopia …
PDF Thin Lenses and Virtual Images - Steffin combinations of lenses to produce a magnified image. OBJECTIVES In this experiment, you will Use ray diagrams to show the formation of virtual images by concave and convex lenses. Contrast characteristics of real and virtual images. Examine the conditions under which a convex lens acts like a magnifying glass.
Image Formation by Lenses: Formation of Convex and Concave ... 25.11.2021 · The image formation by concave lenses using ray diagram depiction can be briefly explained as follows, When the object is placed at infinity: When the object is placed at infinity, the image formed by the concave lens will be at the first focus, F1. The nature of the image obtained will be a virtual image and it will be in erect form. Also, the size of the image formed will be …
Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Wolfram Demonstrations Project This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both the object and the lens. You can change the focal length using a slider.
Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table - Teachoo Hence, we extend both rays behind the lens We see that the rays form an image behind the lens (on the left side). So, the image is virtual And image formed would be larger than the object We can say that Image is virtual (behind the lens) Image is erect Image is larger than the object (Magnified) To summarise
Cow's Eye Dissection - step 1 - Exploratorium Learn how to dissect a cow's eye in your classroom. This resource includes: a step-by-step, hints and tips, a cow eye primer, and a glossary of terms.
PDF 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 VIRTUAL IMAGES - Pomona Figure 7.3: Using a ray diagram to locate the virtual image formed by a diverging lens. The dotted lines show the trajectories that the photons appear to follow, according to the observer. The gray lines indicate the relationships between the second and third principal rays and the focal points of the diverging lens. object image eye second ...
Concave Lens - Ray diagram, Images Formed - with Steps ... 26.04.2020 · Concave Lens - Ray diagram You are here Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens ... Image is virtual (left side of the lens) Image is Erect Image is Smaller than the Object (Highly Diminished) Case 2 - Object is between Infinity and Optical Center Here, Object AB kept anywhere on the principal axis - between Infinity and …
Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the …
























0 Response to "41 virtual image lens diagram"
Post a Comment