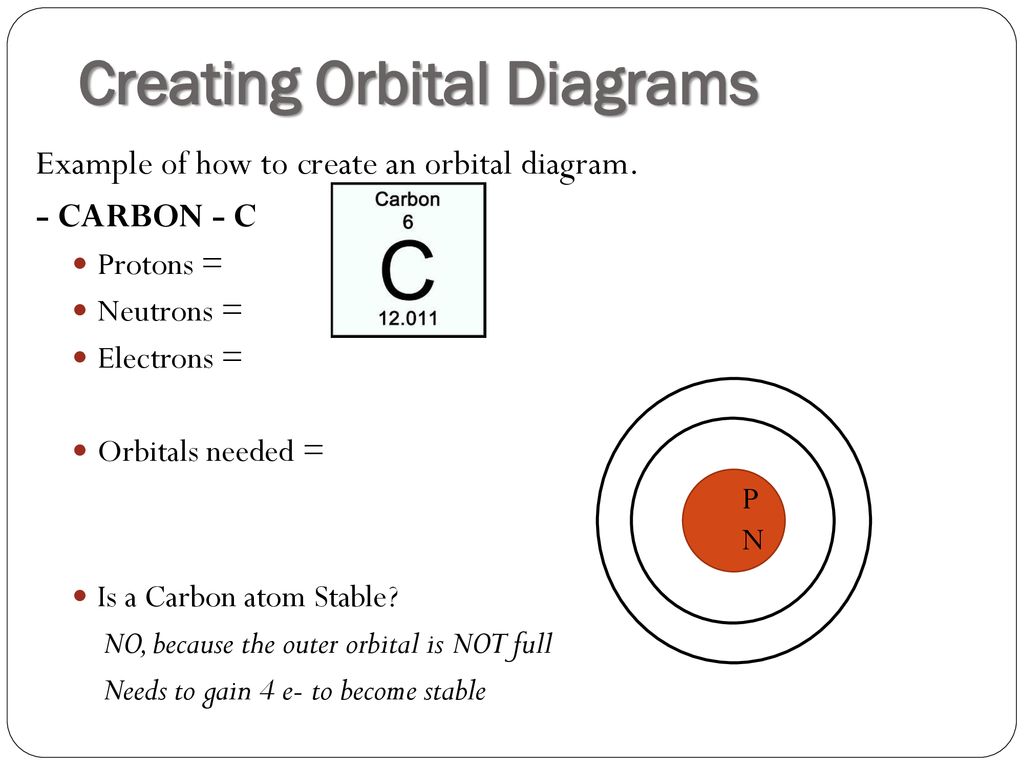
43 orbital diagram of carbon
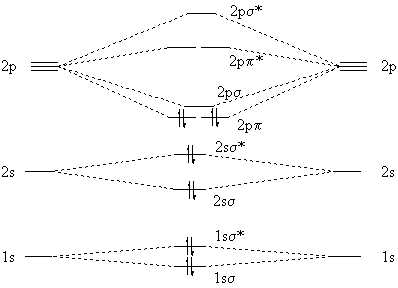
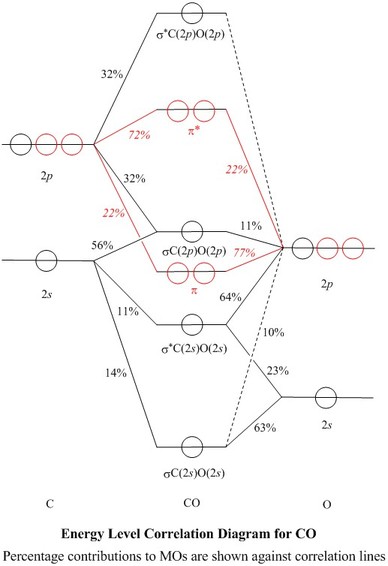
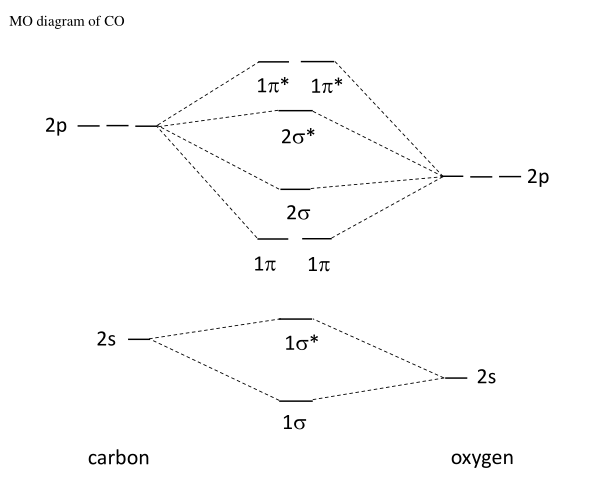
...energy of carbon orbital higher than oxygen it's actually the anitibonding molecular orbital whose potential energy which is higher than bonding The MO diagram for CO will be the same as that for N2, because CO has the same number of valence electrons as N2. There are some differences... 4) Occupy the orbitals according to a stick diagram. At this stage, we note that from our N pz orbitals we will obtain N π orbitals. Further, each carbon atom has one free valence electron to contribute, for a total of N electrons that will need to be accounted for (assuming the molecule is neutral). Accounting for spin, then, there will be N/2
Maximum multiplicity, when more than one orbital of equal energy is available, electrons will first occupy these orbitals singly with parallel spins. The pairing of electrons will start only after all the degenerate orbitals are singly occupied or half filled.
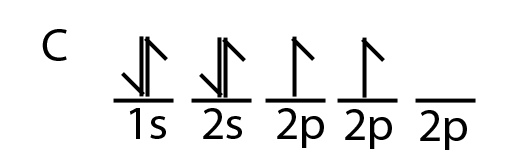
Orbital diagram of carbon
The global carbon cycle model describes the evolution of the mass of carbon in the mantle, Cm, in the combined reservoir consisting of ocean and atmosphere Figure 6.6 . The molecular orbital diagram for methane CH 4 illustrates how valence hydrogen and carbon atomic orbitals combine to form an... Carbon is the sixth element with a total of 6 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for carbon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for C goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining two electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. Thus, the two electrons in the carbon 2p orbitals have identical n, l, and ms quantum numbers and differ in their ml quantum number (in accord with the...
Orbital diagram of carbon. In this video we will draw the molecular orbital diagrams for diatomic nitrogen, carbon and boron. We will also calculate their bond order and determine if... The molecular orbital diagram shows that the third electron is shared equally by the end carbons, with none of the electron density on the middle carbon. This is in agreement with what the resonance contributors show: Only the end carbons have rad-ical character. The molecular orbital diagram carbon monoxide proposed by Coulson is given below. Carbon co Oxygen. Figure 9. The second molecular orbital diagram of carbonyl ligand. The MO diagram shown above is very useful in explaining the bonding between metal centre and carbonyl ligand. Carbon monoxide facts, formula, uses, bonding and properties Hybridization, molecular orbital diagram, production and chemical reaction carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colurless, odourless, poisonous gas produced by burning carbon in insufficient oxygen.
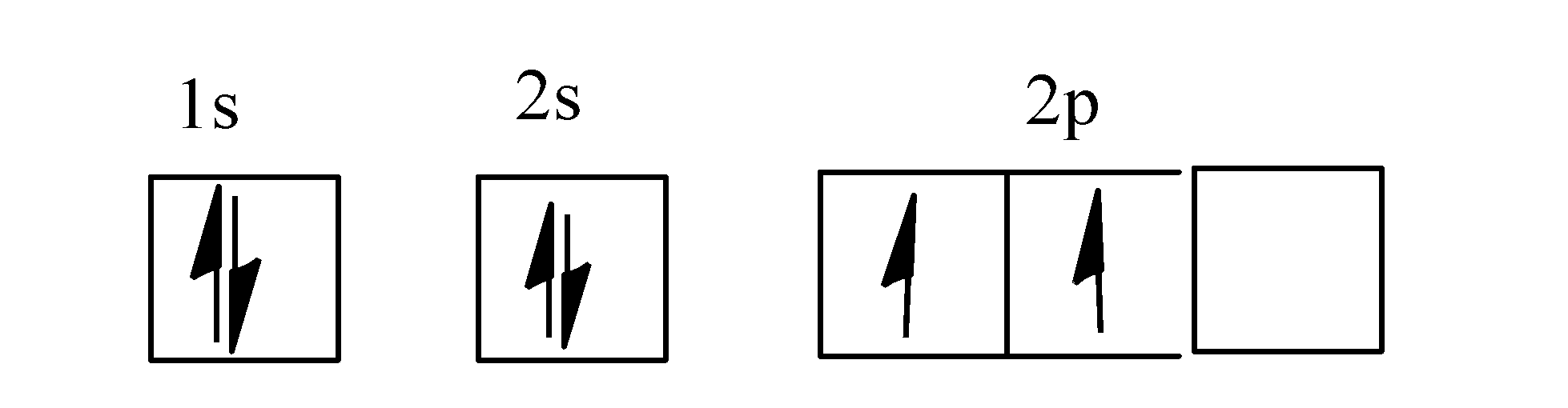
Carbon is a p-block element. The s-sublevel can only accommodate two maximum electrons because it has one orbital. This is why both 1s and 2s contains just two electrons each. Group orbital 2 also has an energy too low for strong interaction with the carbon pz (a difference of 21.72 eV), so the final molecular orbital diagram in Figure 5.25 shows only a slight interaction with The 2py orbital of carbon has B2u symmetry and interacts with group orbital 5 (Figure 5.23). The orbital diagram can be derived from the elemental carbon's (C) electron (e-) configuration. C is configured as a helium (He) core as [He]2s^2 2p^2, 2, 4. A Lewis dot structure would have a C with one dot, representing a valence electron over each of four sides. A C bonded to 4-hydrogens (H) is CH4... Solution · The atomic number of carbon is 6, which is also the number of positively charged protons its atomic nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the ...
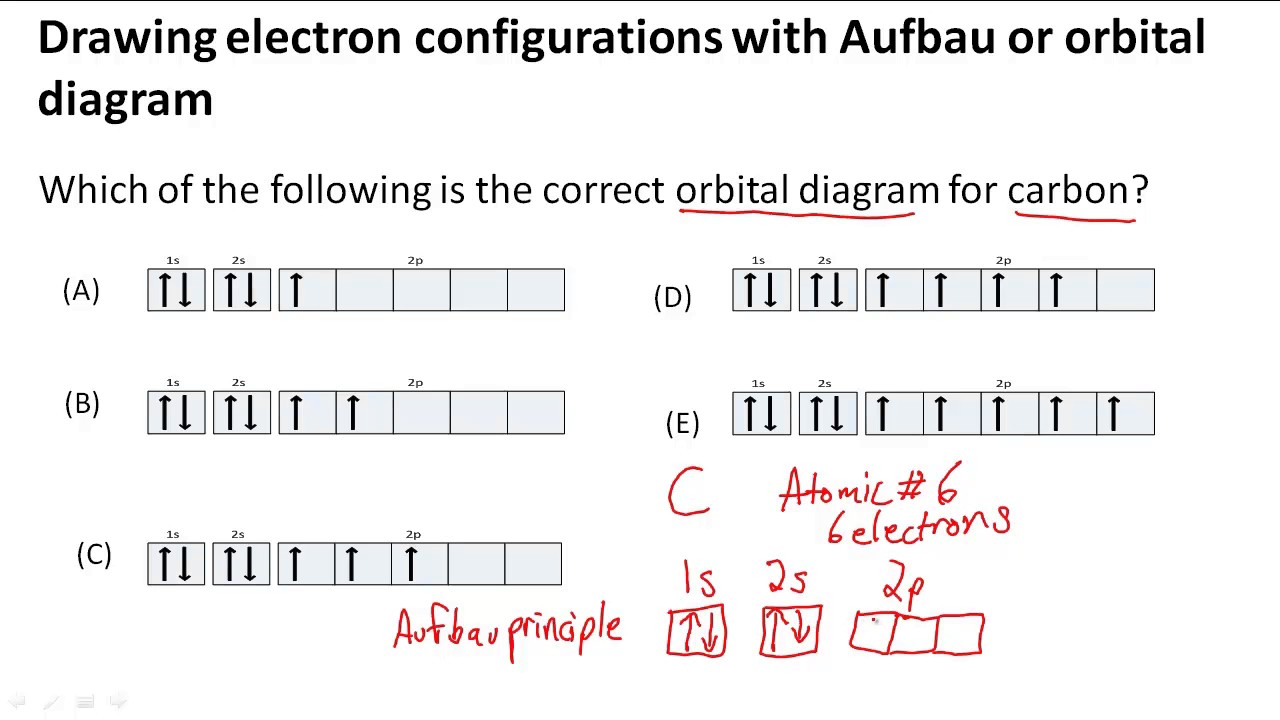
The four valence electrons on carbon can be added to the energy diagram ( ). Each of the hydrogens has one valence electron in its 1 s orbital ( ). These will pair up with the carbon electrons to form four s (sigma) bonds. These are called sigma bonds (Greek for s) because they are formed from hybridized orbitals, which result from s orbitals. 28.3.2018 · Orbital diagrams are like the configuration notation just introduced, except with the spins of electrons indicated. Use the Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule to work out how to fill shells. The exclusion principle states that no two electrons can share the same four quantum numbers, which basically results in pairs of states containing electrons with opposite spins. The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of showing how chemical bonding is taking place within a molecule. It determines how pi and sigma bonds have been formed within the shared covalent bond, along with the intensity in terms of strength. The oxygen is more... 23.2.2016 · The orbital filling diagram for carbon. Again, we start with the electron configuration, which is 1s²2s²2p². As we’ve seen, this means that there are 2 electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and two electrons in the 2p orbitals. This is shown like this:
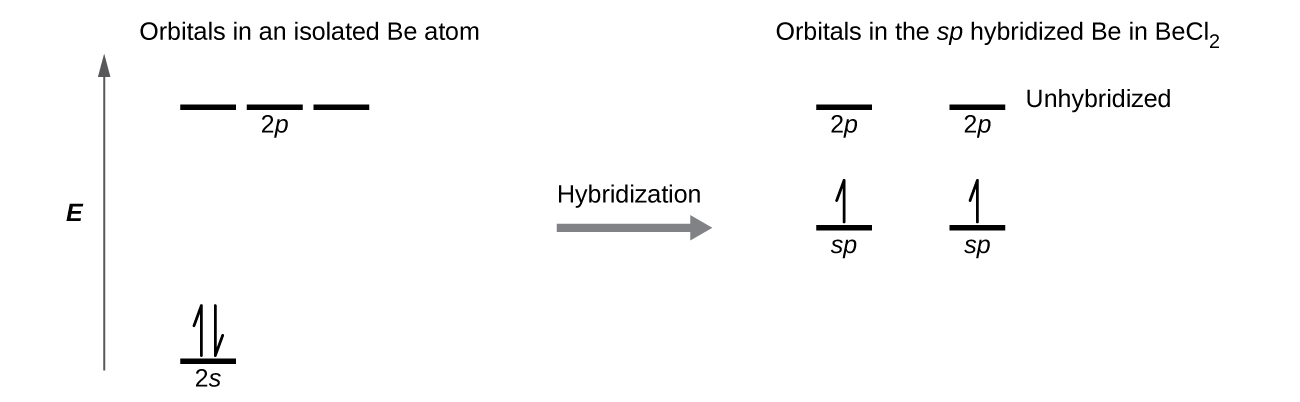
Carbon is making 2 s and 2 p bonds to the oxygen atoms. The 2 s bonds indicate that there are 2 equivalent molecular orbitals formed. To form 2 hybrid molecular orbitals, we need to mix 2 atomic orbitals, an s orbital and a p orbital. The resulting hybrid orbitals are called sp hybrids. sp 3 Hybridization.
Electron configuration of carbon (C) atom through orbital diagram Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O2. From the molecular orbital diagram of N2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic.
3.2.2019 · Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation and the nitrosyl anion 1 Order of filling of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear diatomic molecules such as CO. Molecular Orbital Theory – Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure.
Orbital Diagram For Carbon (C) - Carbon Electron. Just Now The element carbon has 6 electrons in total and one of the main things that many users might not know is the symbol 3 hours ago Answer to write orbital diagrams to represent the electron configuration of carbon before sp3 hybridization.
The atomic number of carbon is 6, which is also the number of The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. rule, each orbital must contain one electron each with the same spin, before.
5.4 Drawing Orbital Diagrams and Writing Electron Configurations. In the orbital diagram of carbon, two electrons occupy the 1s orbital, two electrons occupy the 2s orbital, and two electrons each occupy a 2p orbital in the 2p sublevel. 15 Basic Chemistry. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
English: Orbital diagram for carbon, showing the correct application of Hund's Rule. Date. The following other wikis use this file: Usage on en.wikibooks.org. High School Chemistry/Orbital Configurations.
What is the orbital diagram for carbon? With beryllium (Z = 4), the 2s sublevel is complete and the 2p sublevel begins with boron (Z = 5). Since there are three 2 p orbitals and each orbital holds two electrons, the 2p sublevel is filled after six elements….Second Period Elements.
The sp orbitals of carbon in carbon dioxide can be seen in Fig. 9.15, and the corresponding orbital energy-level diagram for their formation is given in Fig. 9.16. These sp hybrid orbitals are used to form the bonds between the carbon and the oxygen atoms. Note that two 2p orbitals remain unchanged...
The second diagram corrects this by realizing there are two unused p orbitals on the carbon. The valence electron configuration of "O" is ["He"] 2s^2 2p^4. To accommodate the two lone pairs and the bonding pair, it will also form three equivalent sp^2 hybrid orbitals.
C (Carbon) is an element with position number 6 in the periodic table. Located in the II period. Melting point: 3550 ℃. Density: 3.51 g/cm3. Below is the electronic diagram of the Carbon atom. Distribution of electrons over energy levels in the C atom 1-st level (K): 2 2-st level (L): 4.
The orbital diagrams may also look similar. A major difference is that the more electronegative atom will have orbitals at a lower energy level. Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements.
Download scientific diagram | Qualitative molecular orbital diagram for MoC. 8 There are several possibilities for the ground state. If the bonding interaction between the metal and carbon atoms becomes great enough at Zr, ZrC may be forced into the 10 2 11 2 5 4 , 1 ⌺ ϩ ground term.
And what orbital here is a new hybridized. This is um, hi brie diced mm pick. So so this is a orbital diagram of carbon in so to an indication of carbon atoms explanation for the given California, all of you to in tiger Ron of carbon in co. two and indication of carbon atoms electrons in each orbital and...
12.8.2018 · carbon with sp^2 hybridized atomic orbital is formed by mixing one s and two p atomic orbitals. An example of carbon with sp^2 hybridized atomic orbital is alkene, specifically the two carbons involved in the C=C. Each of that carbon has 3 sigma bonds and 1 pi bond. Carbon is tetravalent (forms 4 bond) and the ground state electron configuration cannot …
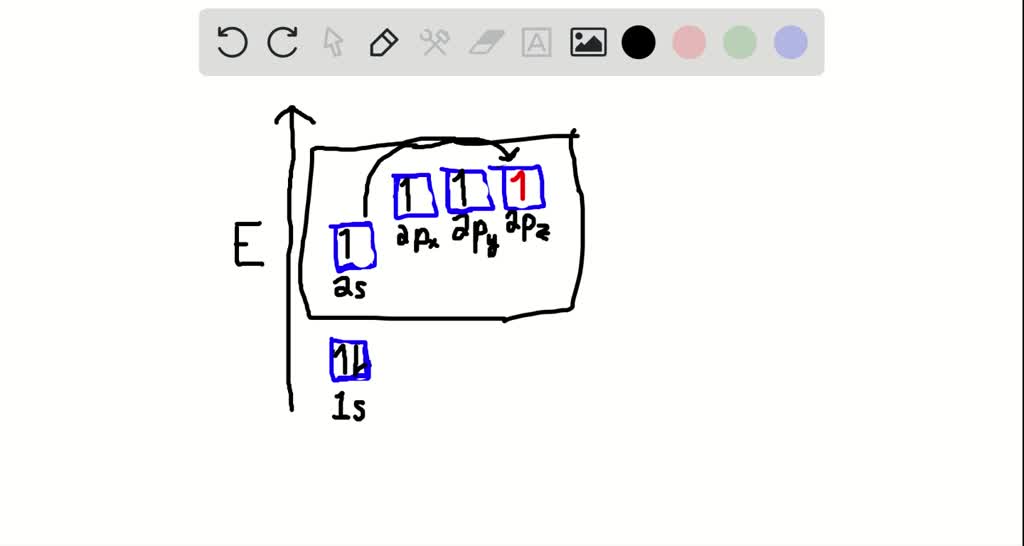
write orbital diagrams boxes with arrows in them to represent the electron configuration of carbon b
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine …
Carbon orbital diagram. With the next element, carbon, a complication arises. In which orbital should the sixth electron go It could go in the same orbital as the other 2p electron, in which case it would have to have the opposite Considering the molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide (Fig.
Orbital Diagrams Chemistry Tutorial. Key Concepts. An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence...
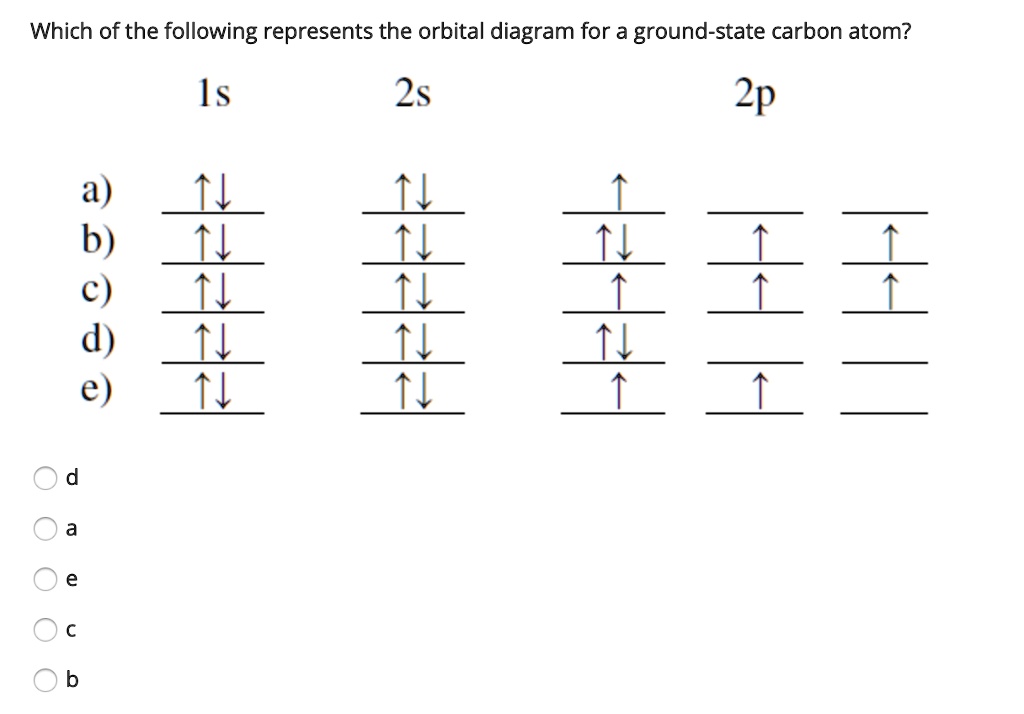
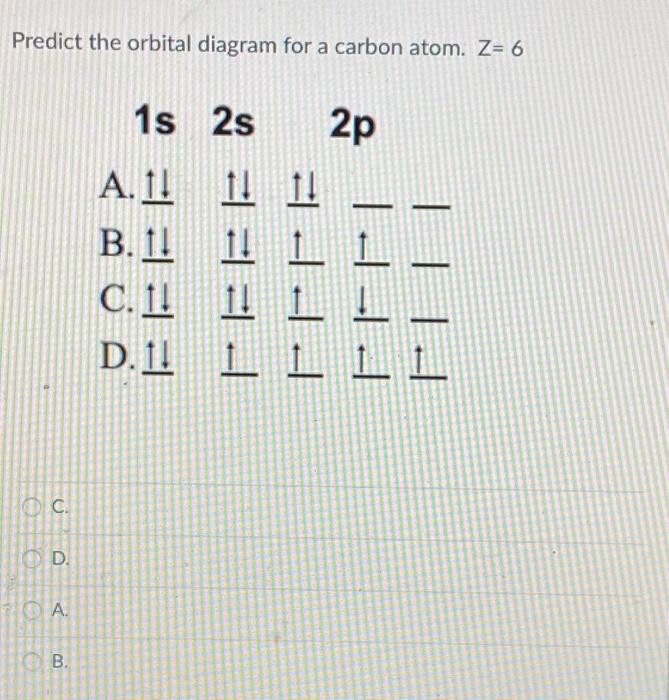
8 May 2021 — By Hund's rule, the electron configuration of carbon, which is 1s2 2s2 2p2, is understood to correspond to the orbital diagram shown in c.
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
The above diagram is for a symmetric diatomic molecule with no s-p mixing. This is true for the The atomic orbitals that are closer to the energy of the molecular orbital will have a larger coefficient. From this deductive chain one can reasonably explain, that the HOMO of carbon monoxide must be...
Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13 ...
Orbits and orbitals sound similar, but they have quite different meanings. The diagram (not to scale) summarises the energies of the various orbitals in the first and second levels. The electronic structure of carbon. Carbon has six electrons. Two of them will be found in the 1s orbital close to the nucleus.
The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is #2# , each with opposite spins (Pauli's exclusion principle). In a neutral carbon atom, the #"1s"# sublevel has one orbital with two electrons with opposite spins, represented by the arrows pointing in opposite ...
The element carbon has 6 electrons in total and one of the main things that many users might not know is the symbol by which it is represented. The symbol of carbon is written as 6. Carbon Electron Dot Diagram. If we talked about the electronic configuration of the element then, carbon is an element whose electronic configuration is given as 1s ...
For the ethene orbital energy diagram these are shown as pCC for the HOMO, and p*CC for the LUMO. In all cyclic polyenes (CnHn), the p-molecular orbitals occur in degenerate pairs, except for the lowest p-orbital, and for the cyclic polyenes with even numbers of carbon atoms, the highest...
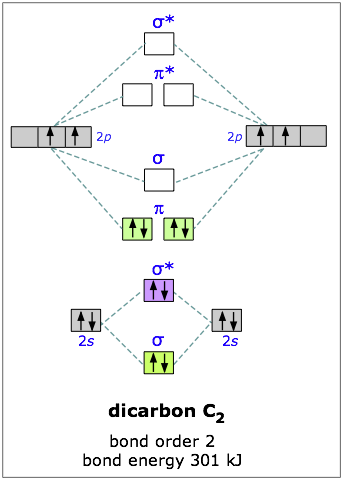
2.12.2016 · Here's what I got. The problem provides you with the MO diagram for the "C"_2 molecule, so all you really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. You need to add an electron and not remove one because of the overall negative charge that exists on the molecule. As you know, a neutral carbon atom has a total of 6 electrons.
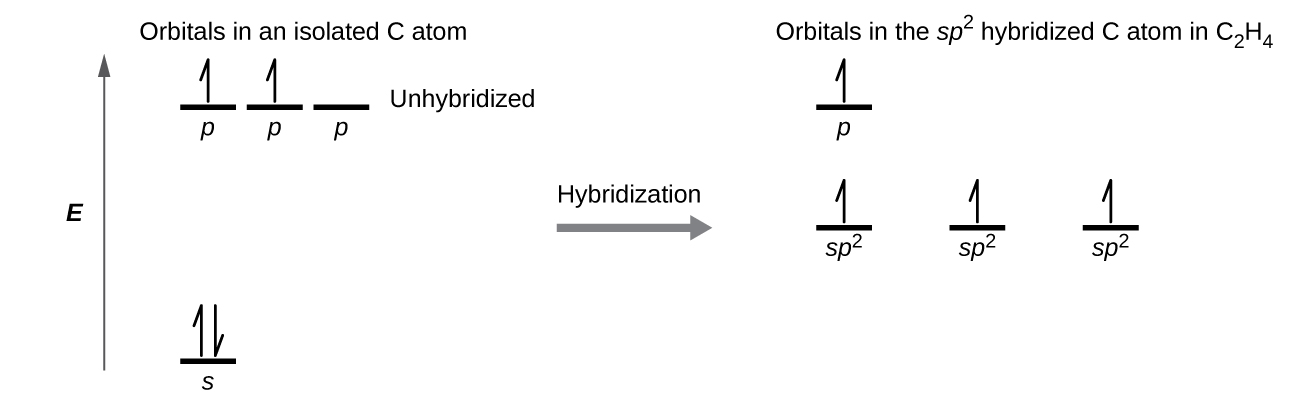
Other carbon compounds and other molecules may be explained in a similar way. For example, ethene (C 2 H 4) has a double bond between the carbons. For this molecule, carbon sp 2 hybridises, because one π (pi) bond is required for the double bond between the carbons and only three σ bonds are formed per carbon atom. In sp 2 hybridisation the 2s orbital is mixed …
Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. Thus, the two electrons in the carbon 2p orbitals have identical n, l, and ms quantum numbers and differ in their ml quantum number (in accord with the...
Carbon is the sixth element with a total of 6 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for carbon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for C goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining two electrons will go in the 2p orbital.
The global carbon cycle model describes the evolution of the mass of carbon in the mantle, Cm, in the combined reservoir consisting of ocean and atmosphere Figure 6.6 . The molecular orbital diagram for methane CH 4 illustrates how valence hydrogen and carbon atomic orbitals combine to form an...
















0 Response to "43 orbital diagram of carbon"
Post a Comment