43 draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens
a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. Subject: Physics Price: 2.85 Bought 3. Share With. a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The a) ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. EOF
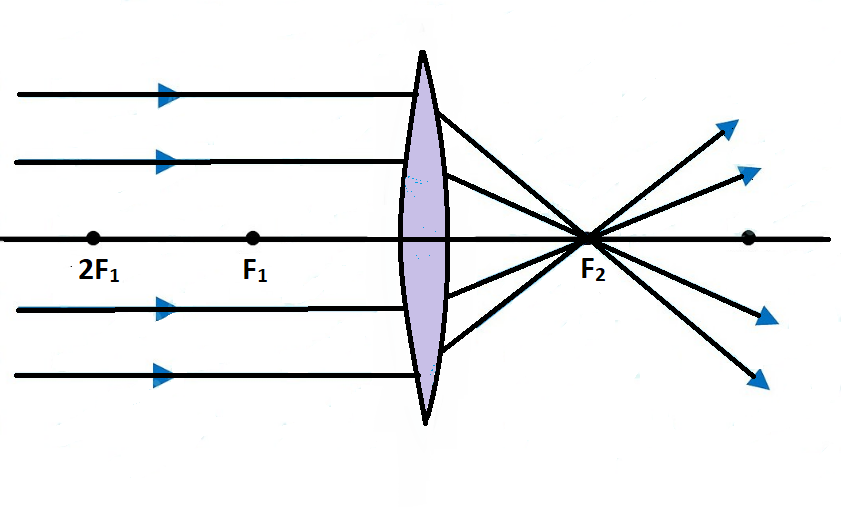
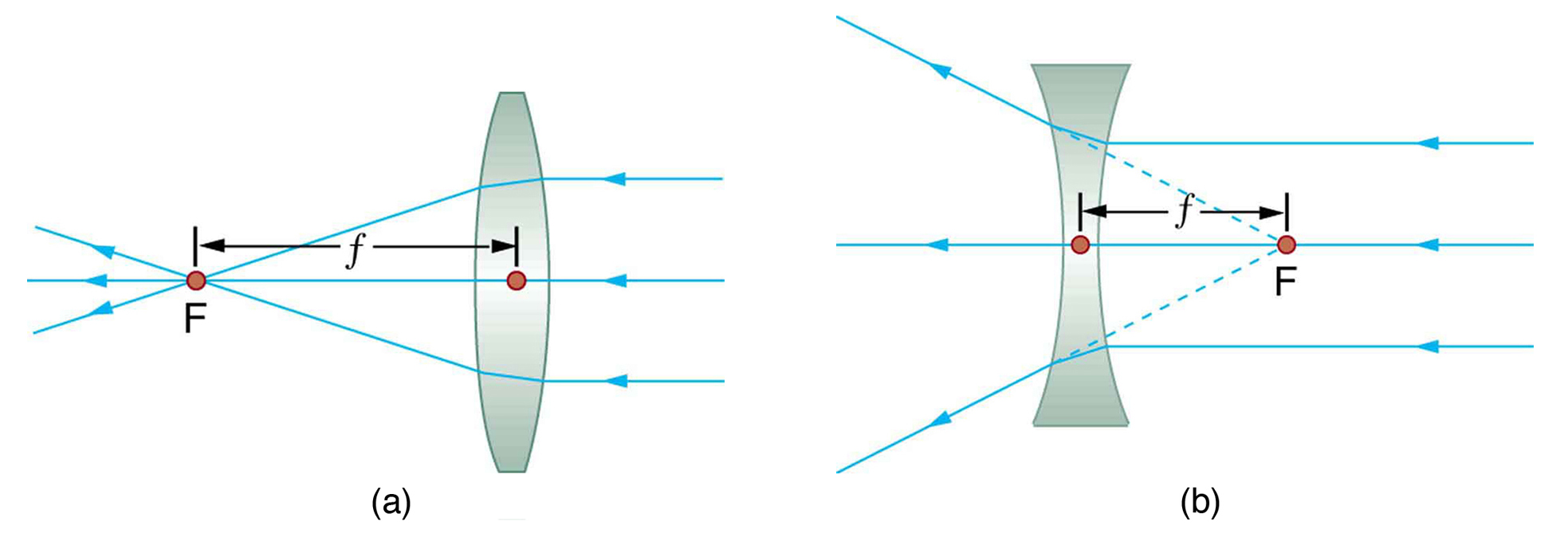
Converging Lenses - Ray Diagrams - Physics Classroom The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the lens.

Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens
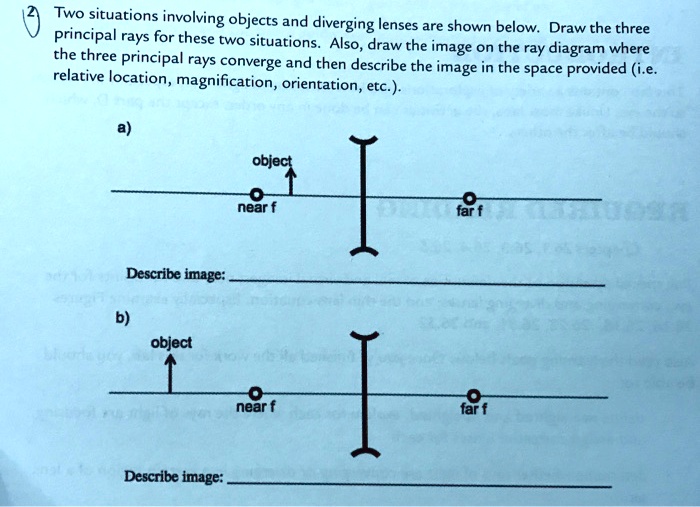
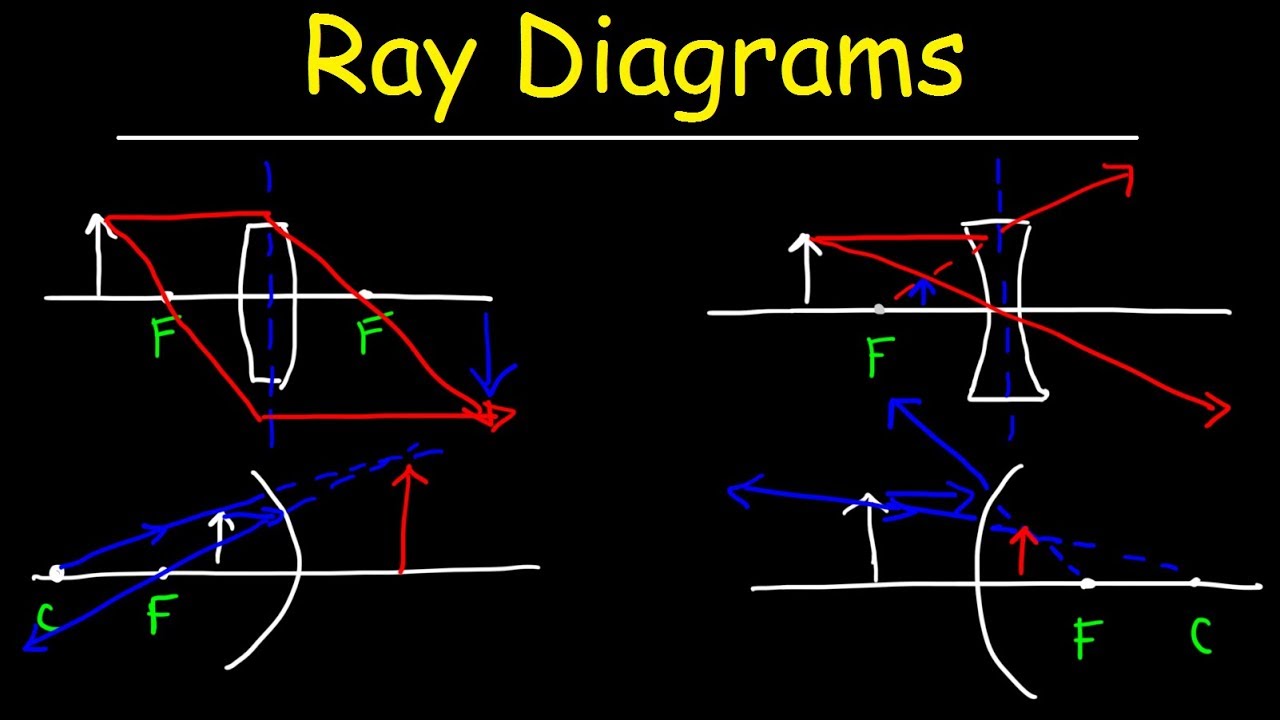
Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray ... Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. A) Draw a ray diagram for the following si... | Clutch Prep A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ( an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation. Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of a three times ... Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of a three times magnified (i) real image (ii) virtual image of an object kept in front of a converging lens. Mark the positions of object, F, 2F, O and position of image clearly in the diagram.
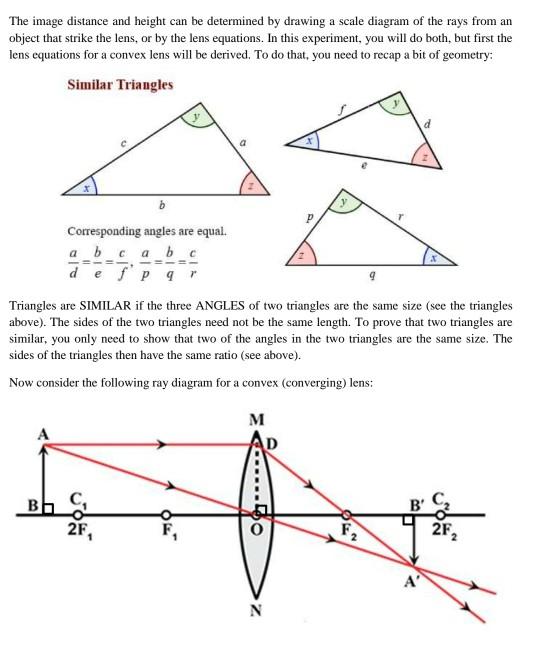
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the mirror. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly ... Draw ray diagram showing the image formation by a convex ... Draw ray diagram showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed at infinity. - Hint: The property of a convex lens is that it converges the light rays passing through them. The nature of image formed by the lens depends on the distance of the object from the lens. Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table - teachoo First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it passes through focus after refraction. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2. We can say that. A) Draw a ray diagram for the following si... | Clutch Prep Problem: A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) where the three principle waves converge.B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation. 1.
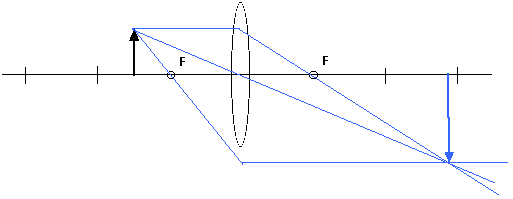
Solved 2.) a) Draw a ray diagram for the following ... a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The a) ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays r Use a ruler to measure the ... OneClass: (a) Draw a ray diagram for the following ... (a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray-tracing needs to have three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. (b) Use the ruler to measures the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths of the ray diagram. then, verify that your ... Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University Ray Diagrams for Lenses The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: Solved a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ... a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. b) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram.
Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of a three times ... Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of a three times magnified (i) real image (ii) virtual image of an object kept in front of a converging lens. Mark the positions of object, F, 2F, O and position of image clearly in the diagram. A) Draw a ray diagram for the following si... | Clutch Prep A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ( an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation. Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray ... Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.

























0 Response to "43 draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens"
Post a Comment