41 pathophysiology of stroke diagram
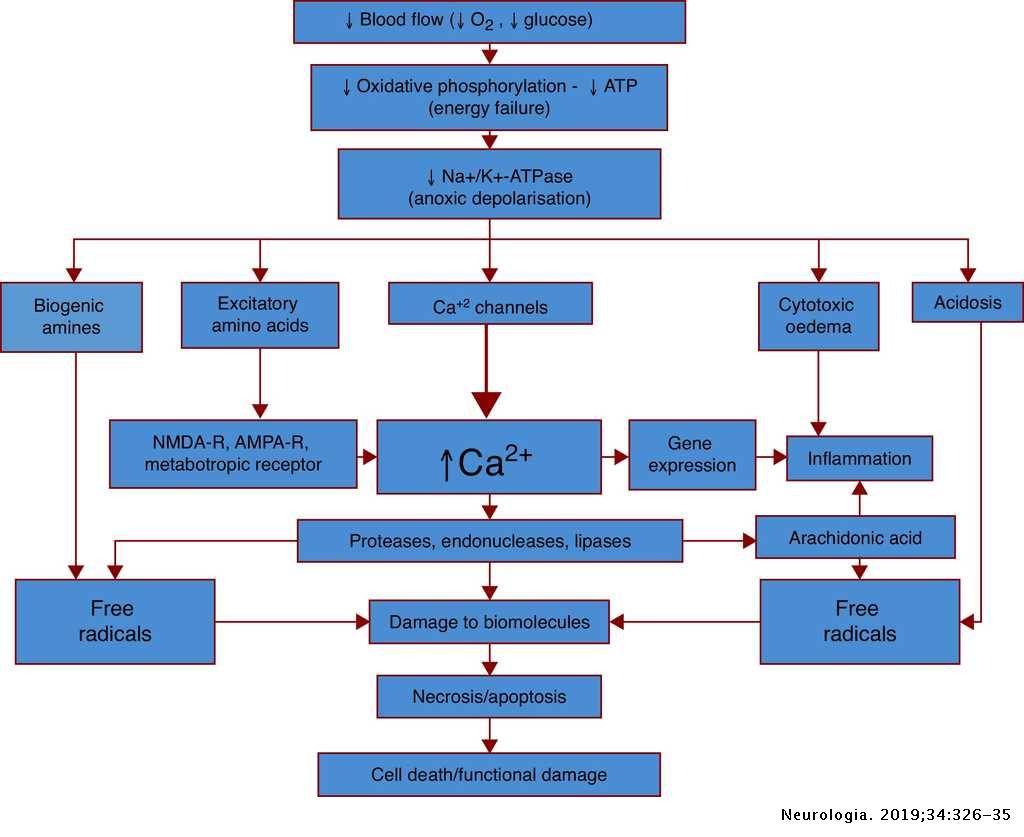
Pathophysiology and Treatment of Stroke: Present Status and Future ... Clots form in the brain and interrupt blood flow, clogging arteries and causing blood vessels to break, leading to bleeding. Rupture of the ... Pathophysiology, treatment, and animal and cellular models ... - NCBI Major cellular patho-physiological mechanisms of ischemic stroke. Ischemia-induced energy failure leads to the depolarization of neurons.
Stroke Pathophysiology - StuDocu Pathophysiology of Stroke 31 the pathophysiology of ischaemic stroke: considerations for emergency department advanced practice nursing yvonne tan year student.

Pathophysiology of stroke diagram
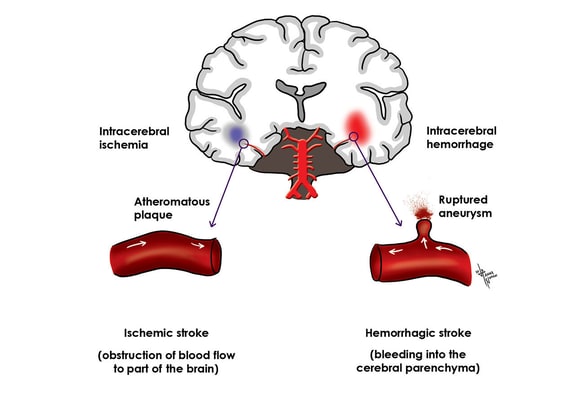
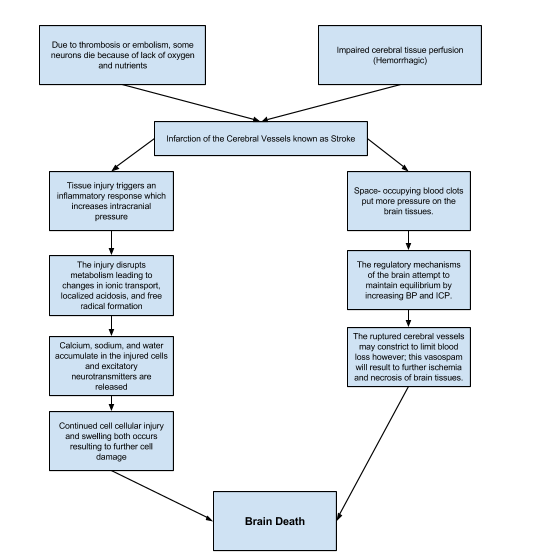
The Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke Studied by Radionuclide... Ischemic stroke is caused by interruption or significant impairment of blood supply to the brain, which leads to a cascade of metabolic and molecular alterations resulting in functional disturbance and morphological damage. Serial observations on the pathophysiology of acute stroke. Pathophysiology of Hemorrhagic Stroke - Health Guide Info The pathophysiology of cerebrovascular accident is different for these two types of stroke. An ischemic stroke may be caused by a blood clot that occurs in the affected artery (thrombosis), a blood clot that traveled from another part of the body (embolism), or a blockage due to damage to the... Stroke patho physiology - SlideShare Mechanisms and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke. ... Schematic Pathophysiology Cva 1233470514641540 2. Edward Patrick Lasquite. Cns path congenital, edema.
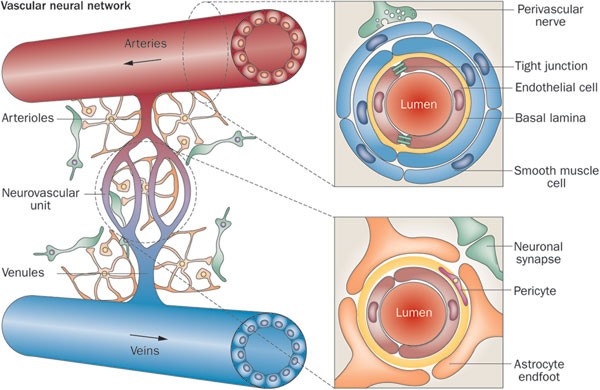
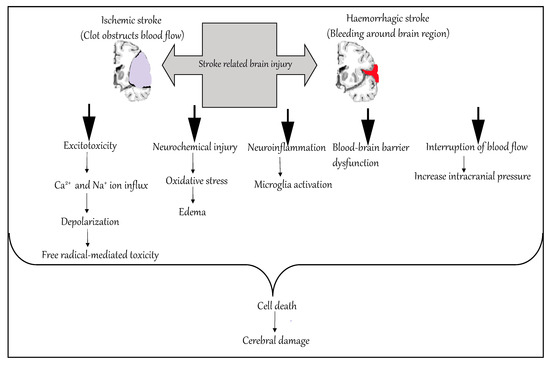
Pathophysiology of stroke diagram. pathophysiology of stroke because of atherosclerosis diagrammatic... Download scientific diagram | Schematic diagram illustrating the main contributory factors involved in the pathophysiology of the ischemic stroke. The ischemic injury leads to the BBB disruption, inflammation and oxidative stress. Pathology, anatomy, and pathophysiology of stroke (Chapter 2) In a small fraction of patients with strokes, the veins are the main or initiating site of pathophysiology. Venous hypertension may cause both ischemia and ... Ischemic Stroke: Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy 27 May 2020 — Acute ischemic strokes result from vascular occlusion secondary to thromboembolic disease (see Etiology). Ischemia causes cell hypoxia and ... PDF Occupation №1 | GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY SUBJECT OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Objectives of pathophysiology. Purpose of Pathophysiology. Methods of patho-logical physiology. Acute and chronic experiments. What thrombus localization leads to? Pulmonary artery emboli. Stroke. Infarctum myocardium.
Ischemic Stroke Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of stroke is complex and involves numerous processes, including: energy failure, loss of cell ion homeostasis, acidosis, increased In contrast, the pathophysiological significance of lymphocyte recruitment into the brain after ischemic stroke remains uncertain. Stroke pathophysiology - YouTube 25 Dec 2013 — This video series explains stroke, its cause, the pathophysilogy and treatment of stroke.For more information, log on ... PDF Microsoft Word - Lectures on the course of pathophysiology Part 1.doc Department of pathophysiology and clinical pathophysiology. Lectures on the course. Introduction in course of pathophysiology. Pathology literally is the study of suffering. It likes a bridging between theo-retical disciplines: anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, histology and clinical prac-tice. [PDF] Stroke Pathophysiology | Semantic Scholar Semantic Scholar extracted view of "Stroke Pathophysiology" by Siddarth N. Shah. Globally, stroke is the second largest cause of death. Stroke can also lead to permenant disability. Stroke can impact individuals in various ways including an individual's physical, psychological
Stroke Pathophysiology Diagram : Detailed Login Instructions Stroke Pathophysiology & Schematic Diagram. Stroke or otherwise known as cerebrovascular accident (CVA), or sometimes called as cerebrovascular disease (CVD) is the infarction of a specific portion of the brain brought about by insufficient blood supply. PDF Pathophysiology_Cover Pathophysiology is the study of the disturbance of normal mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions, either caused by a disease, or resulting At the end of this chapter the students will be able to:-- Discuss the different types of body defense mechanisms - Describe Pathophysiologic events of... (PDF) Pathophysiology of Strokes - ResearchGate pathophysiology of stroke is complex, and involves excitotoxicity mecha nisms, inflammatory p athways, oxidative damage, ionic imbalances, apoptosis, angiogenesis and neuroprotection. T he ultimate result of. ischemic cascade initiated by acute stroke is neuronal death along with an... CE: Acute Stroke: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Stroke, a neurologic event due to altered cerebral circulation, is the third leading cause of death in the United States. Risk factors for stroke include hypertension, family history, and diabetes mellitus. The subtypes of stroke are ischemia, infarction, and hemorrhage.
PDF The Science of Ischemic Stroke: Pathophysiology & Pharmacological... ISSN: 2278-6074. Review Article. The Science of Ischemic Stroke: Pathophysiology & Pharmacological Treatment. *Neema Kanyal. Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shri Guru Ram Rai Institute of Technology & Science, Patel Nagar, Dehradun 248001, Uttarakhand, India.
Chapter 2 - Pathology, anatomy, and pathophysiology of stroke Introduction and perspective. Chapter 2. Pathology, anatomy, and pathophysiology of stroke. Mokri, B: Cervicocephalic arterial dissections. In Bogousslavsky, J, Caplan, LR (eds): Uncommon Causes of Stroke.
Pathophysiology of stroke Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Pathophysiology of stroke. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Type of stroke. Caused by bleeding into brain tissue from a ruptured cerebral vessel. Fast, sudden event. Usually occurs as result of rupture of blood vessel from hypertension...
Pathophysiology Diagram - Stroke | PDF Pathophysiology Diagram- Stroke. Copyright: © All Rights Reserved. Pathophysiology Diagram- Stroke. Uploaded by. misstheatricality130. Description: Pathophysiology Diagram- Stroke.
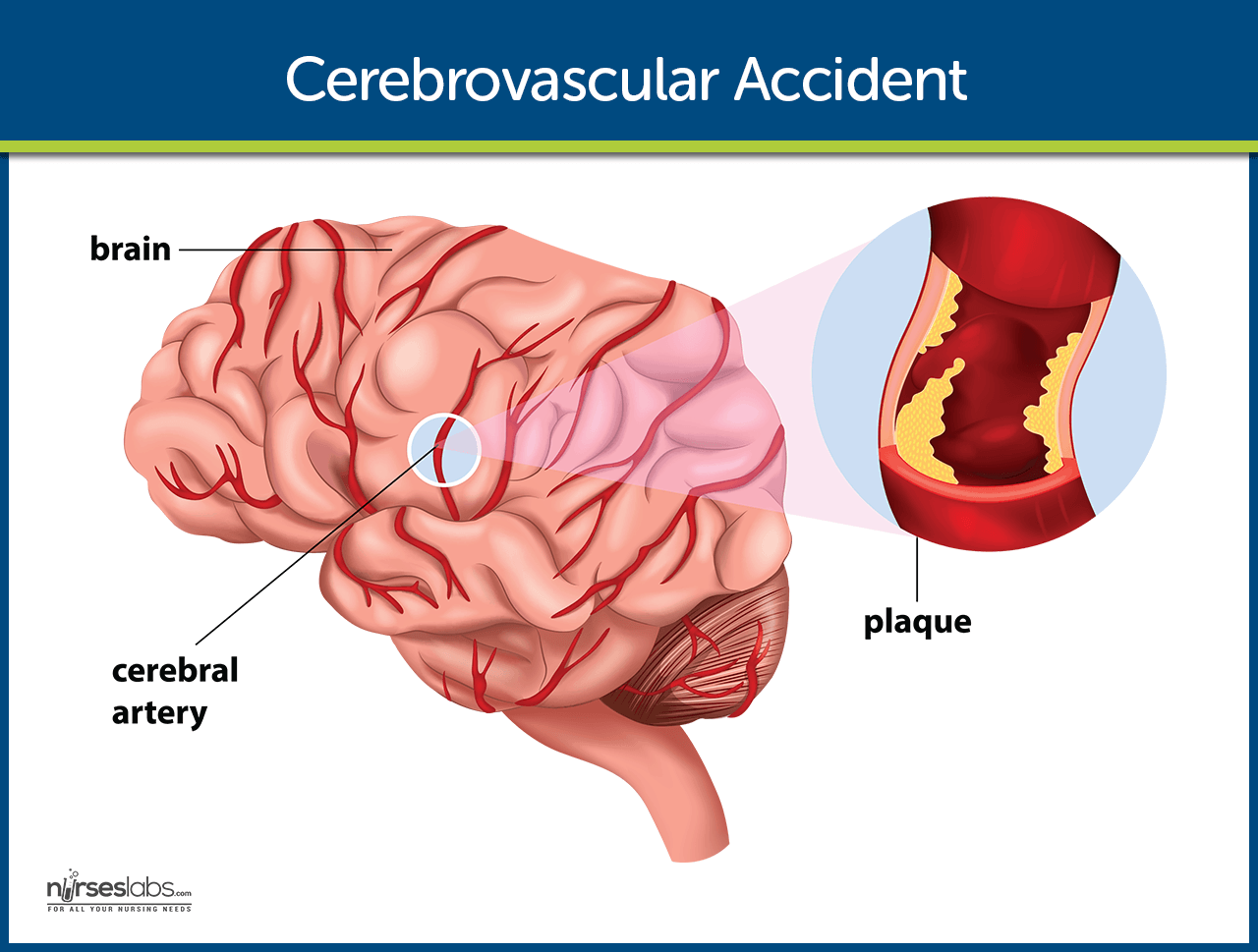
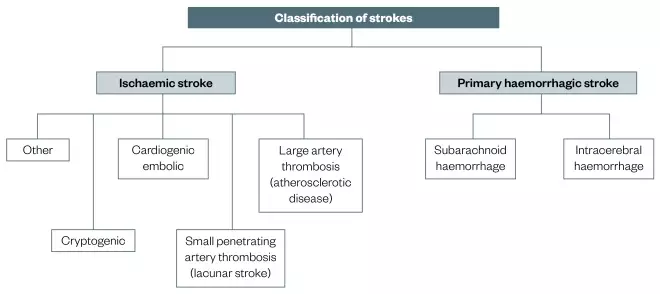
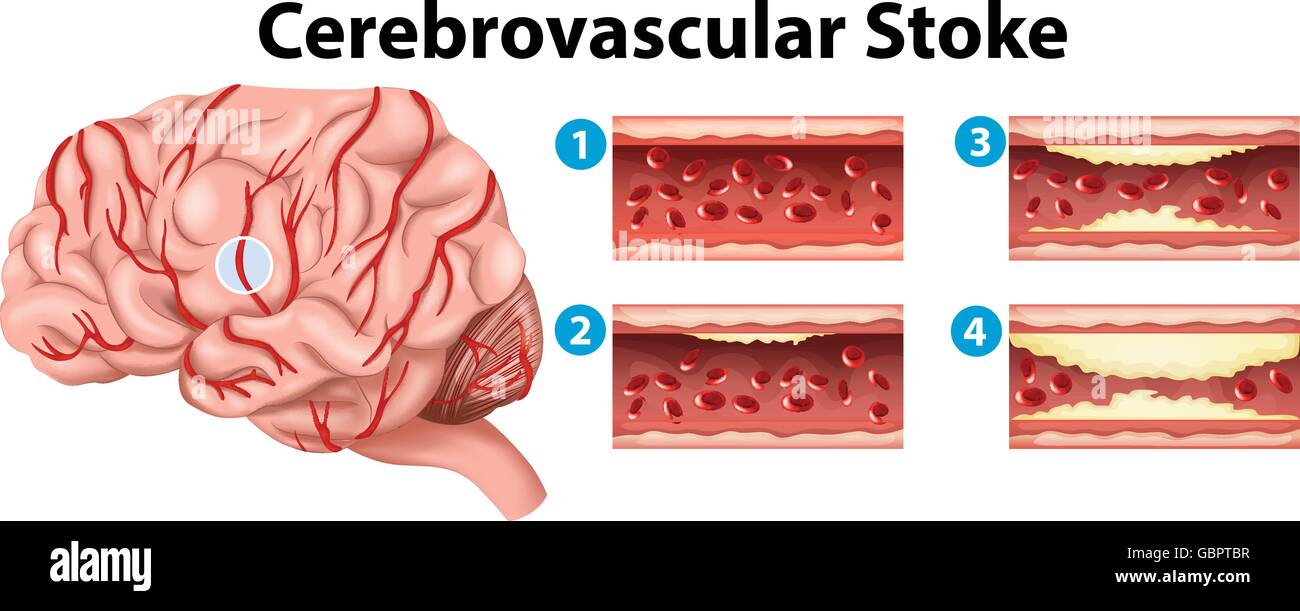
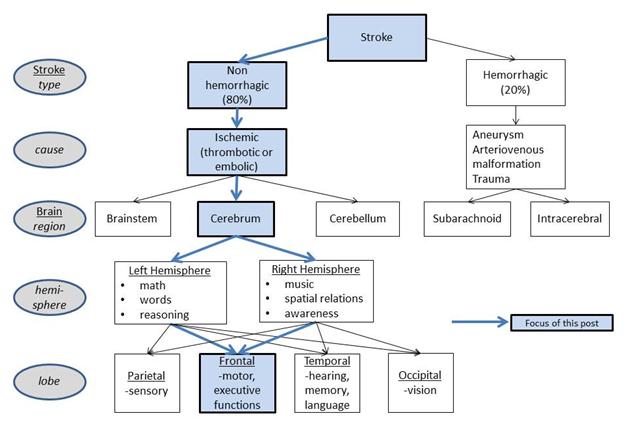
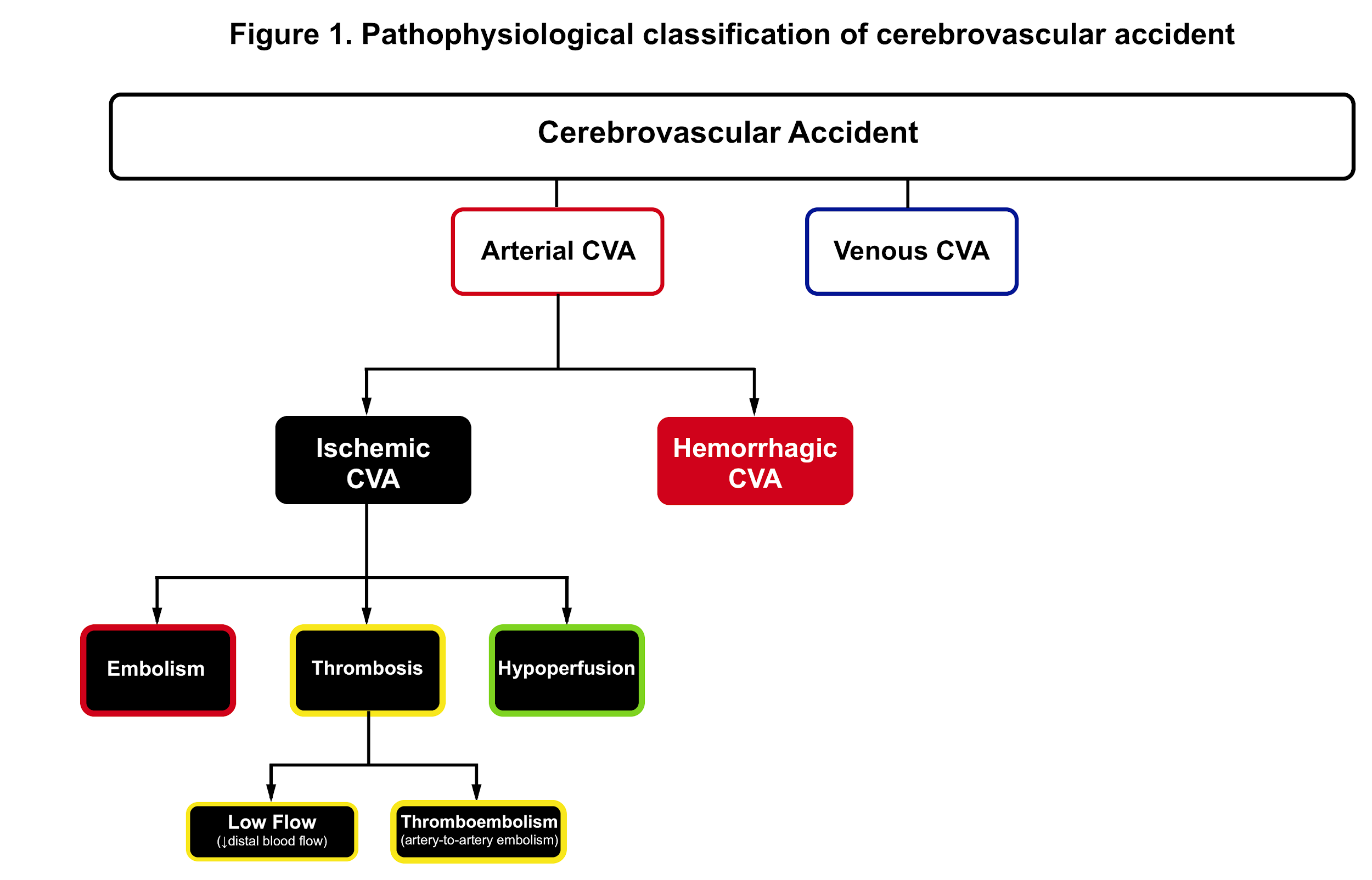
Full revision for pathophysiology of stroke by occlusion of... Schematic diagram of stroke. 6. • Ischemic strokes are due to a reduction or complete blockage of blood flow • This reduction can be due to decreased systemic perfusion, severe stenosis or occlusion of a blood vessel • Ischemic strokes represent about 80 percent of all strokes Caplan LR.
Stroke Pathophysiology & Schematic Diagram - RNspeak Stroke Pathophysiology & Schematic Diagram. Signs and Symptoms that may precede stroke are: Paresthesia. Hemiplegia. Hypokalemia Pathophysiology and Schematic Diagram. LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply. Please enter your comment!
Pathophysiology of stroke | strokeforum.com Pathophysiology. A stroke occurs when the blood flow to an area of the brain is interrupted, resulting in some degree of permanent neurological damage. Stroke of determined aetiology - such as inherited diseases, metabolic disorders, and coagulopathies. Stroke of undetermined aetiology - after...
Stroke Pathophysiology, Etiology and Risk Factors - YouTube Created by world-class clinical faculty, Learning in 10 (LIT) Reviews covers topics in the United States Medical Licensing Exam (USMLE) Step 2CK examination.
Pathophysiology of Stroke Sid M - ppt video online download Presentation on theme: "Pathophysiology of Stroke Sid M"— Presentation transcript 14 Thrombotic Stroke Atherosclerosis: the commonest pathology of vascular obstruction leading to thrombosis Other pathological causes: Fibro muscular dysplasia Arteritis (Giant Cell & Takayasu)...
PDF Section I - To draw graphs and diagrams on the basis of experimental protocols da-ta (tab. 1-2) and illustrative material for the topic presented in tables showing basic experimental results. - To answer questions and formulate conclusions on the basis of experi-mental results presented as graphs and diagrams.
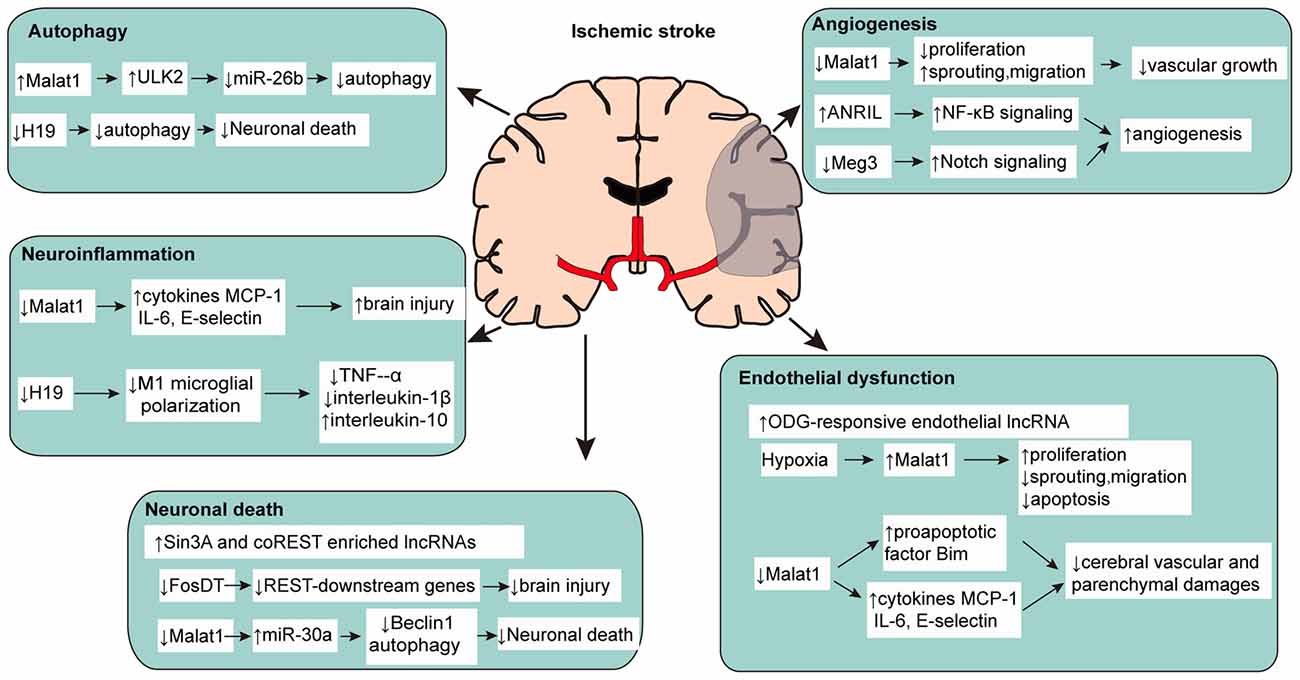
Roles of lncRNAs in Post-Stroke Pathophysiology The underlying pathophysiologic processes of ischemic stroke include oxidative stress, toxicity of excitatory amino acids, excess calcium ions, increased apoptosis and inflammation. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) may participate in the regulation of the pathophysiologic processes of ischemic...
Stroke (summary) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org Stroke is a clinical diagnosis where an acute neurological deficit follows a cerebrovascular insult. pathophysiology. brain parenchyma is deprived of blood flow and therefore oxygen. ischemic. Figure 1: diagram of cerebral vascular territories Figure 1: diagram of cerebral vascular territories.
Hemorrhagic stroke pathophysiology - wikidoc Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. ; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mehrsefat, M.D. A hemorrhagic stroke, or cerebral hemorrhage, is a form of stroke that occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or bleeds.
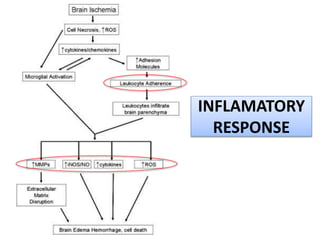
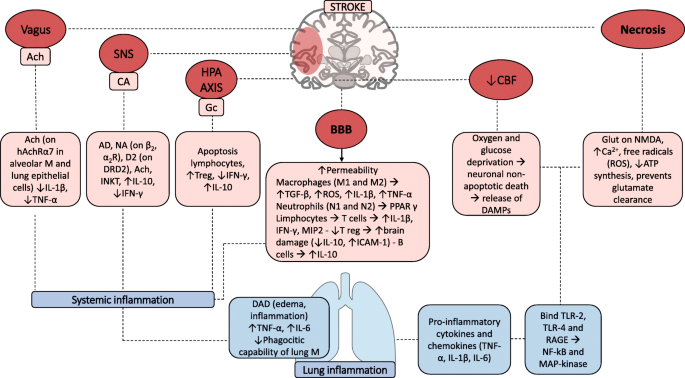
Beyond the Brain: The Systemic Pathophysiological Response to... Each pathophysiology then facilitates development of the detrimental clinical complications observed beyond the stroke-affected brain (Venn diagram). Though much overlap exists between influential pathophysiologies and the ensuing complications, this figure presents a simplified overview of how...
PDF Клиничкская патофизиология: осоновы=Clinical pathophysiology... Pathophysiology of the cardiovascular system 1. Heart failure 2. Atherosclerosis. Ischemic heart disease 3. Disorders of regulation of vascular tone. Cardiac output depends on stroke volume and heart rate. Hypox-ia during anemia stimulates sympathetic activity thus leading to the tachycardia.
Stroke Pathophysiology Aka: Stroke Pathophysiology, CVA Causes, Transient Ischemic Attack Causes, TIA Risk Factors, Cerebrovascular Accident Risk Factors, CVA Risk Strokes happen when blood flow to your brain stops. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. There are two kinds of stroke. The more common kind...
Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke. Inadequate blood flow in a single brain artery can often be compensated for by an efficient collateral system, particularly between the carotid and vertebral arteries via anastomoses at the circle of Willis and, to a lesser extent, between major arteries supplying the...
Understanding stroke:Pathophysiology, presentation, and investigation Strokes may either be haemorrhagic or ischaemic. Eighty eight per cent of all strokes are ischaemic, 9% are due to intracerebral haemorrhage, and 3% are due K A L Carroll fifth year medical student, J Chataway consultant neurologist. Carroll K A L, Chataway J. Understanding stroke:Pathophysiology...
Stroke patho physiology - SlideShare Mechanisms and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke. ... Schematic Pathophysiology Cva 1233470514641540 2. Edward Patrick Lasquite. Cns path congenital, edema.
Pathophysiology of Hemorrhagic Stroke - Health Guide Info The pathophysiology of cerebrovascular accident is different for these two types of stroke. An ischemic stroke may be caused by a blood clot that occurs in the affected artery (thrombosis), a blood clot that traveled from another part of the body (embolism), or a blockage due to damage to the...
The Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke Studied by Radionuclide... Ischemic stroke is caused by interruption or significant impairment of blood supply to the brain, which leads to a cascade of metabolic and molecular alterations resulting in functional disturbance and morphological damage. Serial observations on the pathophysiology of acute stroke.























0 Response to "41 pathophysiology of stroke diagram"
Post a Comment