40 reaction coordinate diagram organic chemistry
The research group of R. Grubbs (Cal. Tech.) has produced a family of easily handled ruthenium catalysts that have proven effective and valuable tools in the field of synthetic organic chemistry. By further clicking on the diagram examples of some applications of metathesis reactions will be presented in two additional pages. The ROMP reaction ... This video introduces the energetics of organic reactions and covers thermodynamics versus kinetics.
The free energy diagrams for these reactions are as follows: The transition state is closer to the products when H20 is the nucleophile. The energy barrier is smaller, so the reaction is faster, and H2S is the stronger nucleophile. 1 H20 H2S H 20 Reaction coordinate Both reactions are endergonic because two new charges are produced. Both sets of
Reaction coordinate diagram organic chemistry
Organic chemistry students struggle with understanding the energetics of chemical reactions. Reaction coordinate diagrams are one tool that is widely used in organic chemistry classrooms to assist students with visualizing and explaining the energy changes that take place throughout a reaction. Reaction coordinate diagrams are derived from the corresponding potential energy surface (PES), which are used in computational chemistry to model chemical reactions by relating the energy of a molecule(s) to its structure (within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation). energy diagram (or reaction energy diagram): a graph of the energy of a reaction against the progress of the reaction. enthalpy: a thermodynamic state function, generally measured in kilojoules per mole. In chemical reactions the enthalpy change (deltaH) is related to changes in the free energy (deltaG) and entropy (deltaS) by the equation:
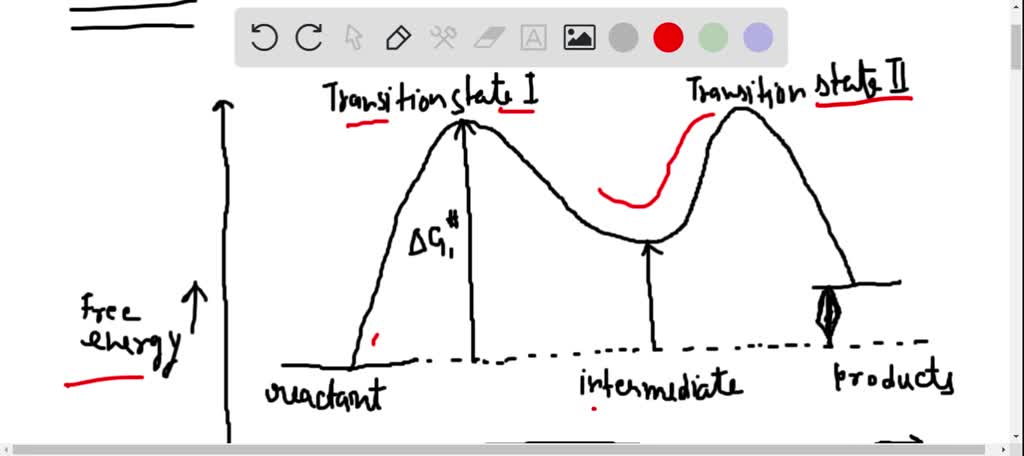
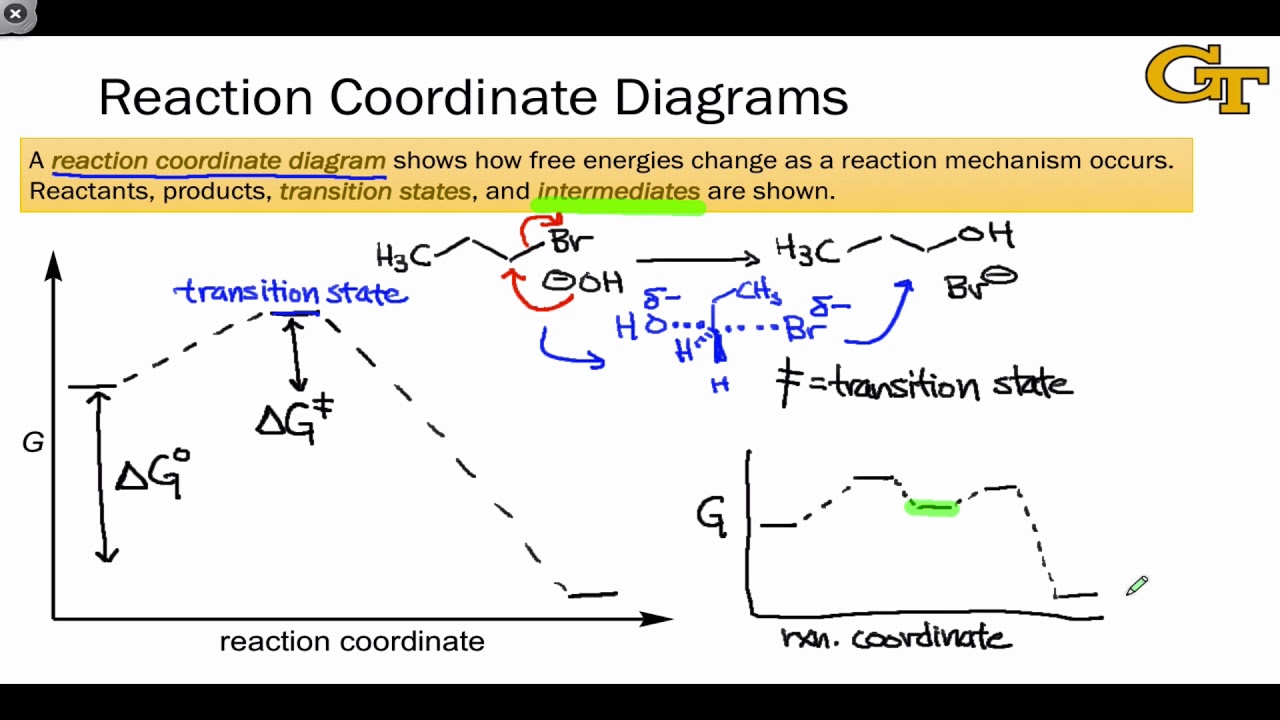
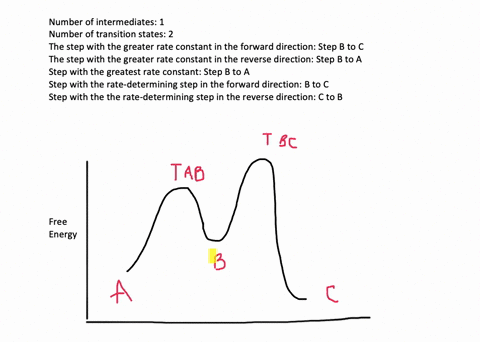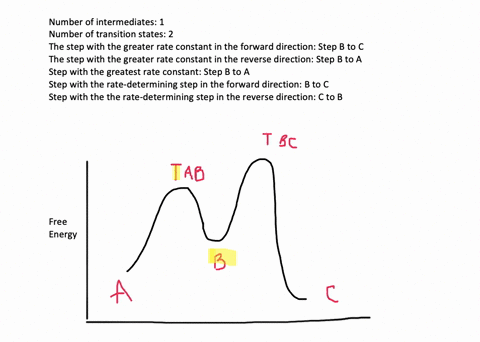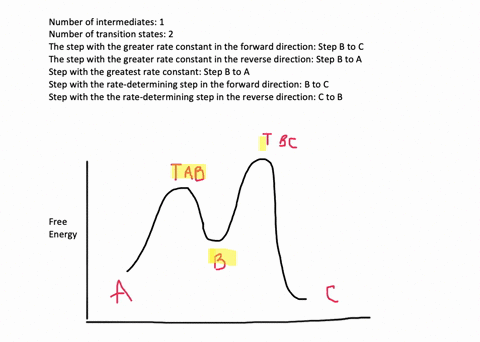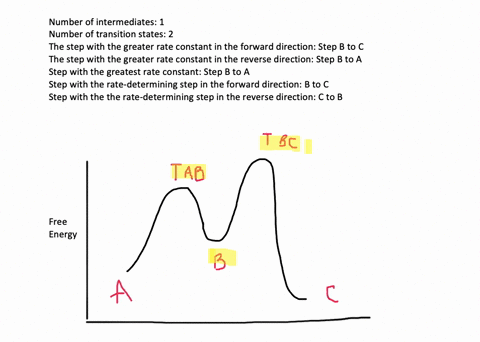
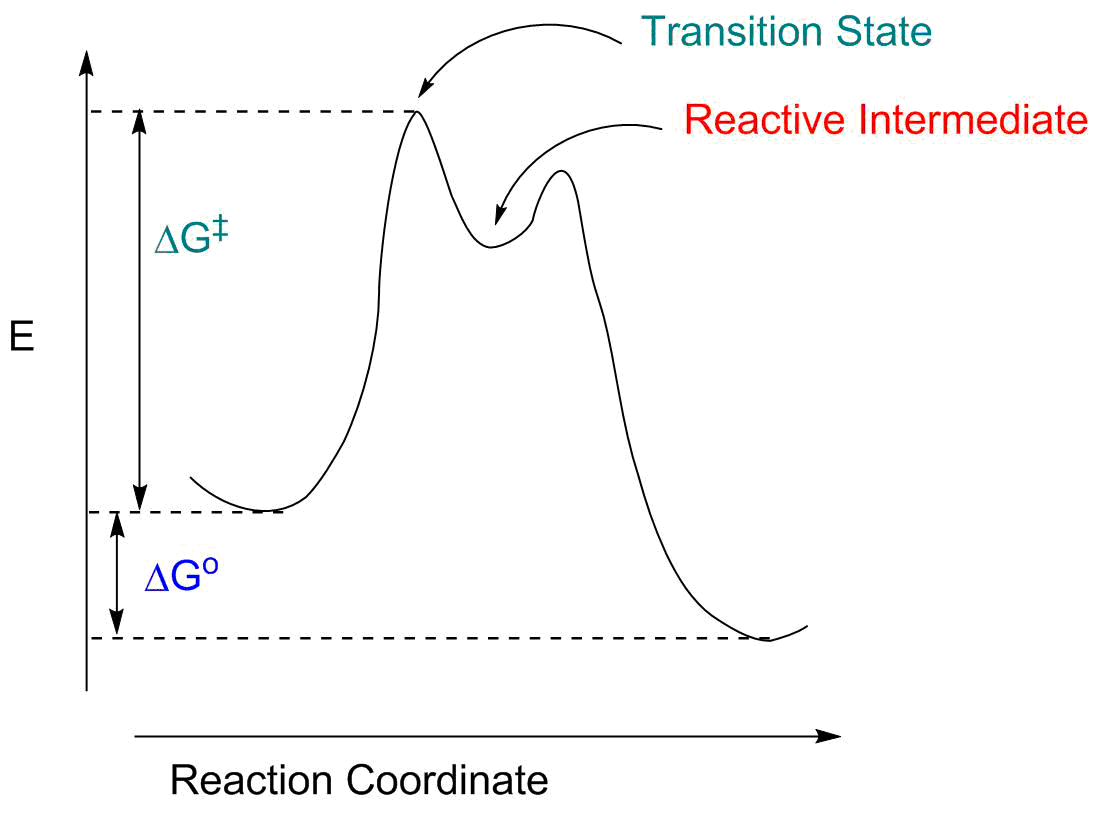
Reaction coordinate diagram organic chemistry. Basic Parabola Analysis: Single-Electron Transfer Step 1: Draw parabolas for reactant and product states on the reaction coordinate Anslyn, E. V.; Dougherty, D. A. Modern Physical Organic Chemistry, 1st ed.; University Science Books: Sausalito, 2006. reaction coordinate December 1, 2015 - Ace Your Next Organic Chemistry Exam. The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction(heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. The energy difference between A and B is E in the diagram. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Reaction coordinate diagrams show the energies of transition states, intermediates, reactants and products Reaction Coordinate G transition state reactant product intermediate intermediateany chemical structure that lasts longer than the time of a typical bond vibration, 10-13to 10-14s rate-determining step (rds)
A unified description of chemical reactivity is made possible with valence bond (VB) diagrams, such as those shown for the a simple case (only reactants and products must be considered) and a more complex system (an intermediate state also plays an important role; RC = reaction coordinate). Analysis … Dec 20, 2021 · The cover art illustrates the molecular structure of the first iron-carbene complex with a square-planar coordination environment. This geometry induces an unprecedented intermediate-spin configuration for the iron-carbene unit. The orbitally near-degenerate paramagnetic ground state exhibits large unquenched orbital momentum, manifesting in … An elementary reaction coordinate almost everyone learns in sophomore organic chemistry 1. Draw, and carefully label, a relaxed butane rotational reaction coordinate. 2. On that same drawing, overlay the expected energy if you were to hold all degrees of freedom other than the reaction coordinate fixed at the values of the trans conformer. 3. Professor Patricia Shapley, University of Illinois, 2012
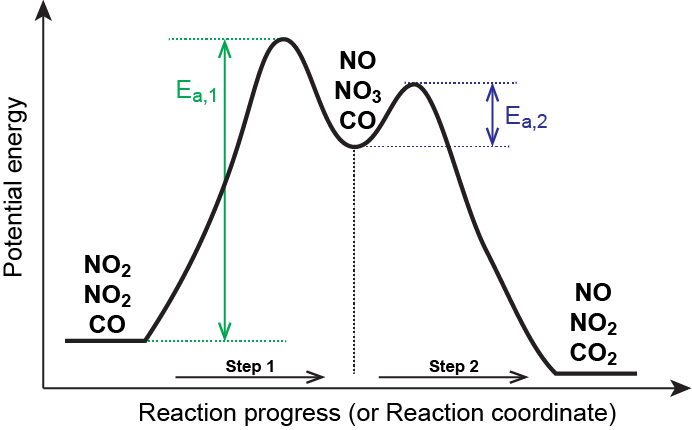
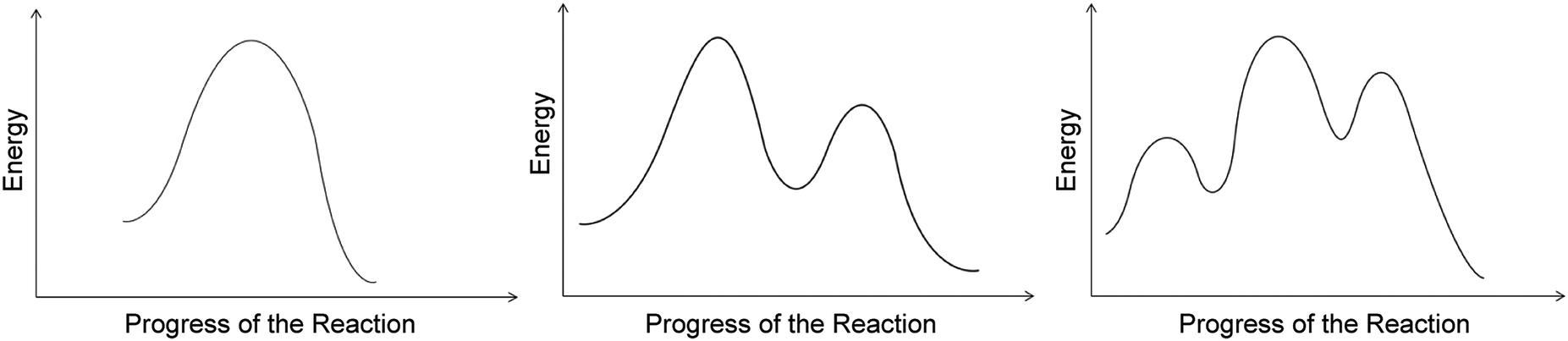
As chemists we want to know the mechanism of this reaction! (or how does the energy diagram appear)! What we know:! Reaction does not proceed in the dark or in the cold! Reaction occurs with wavelengths corresponding to Cl 2 absorption! Quantum yield is greater than 1! (therefore more moles of product are obtained than moles of photons of light ... a maximum (a peak) in an energy diagram. Consider , for example, an energy diagram sho wing the reaction betw een a cyanide ion and methyl br omide (F igure 7.4). TABLE 7.2 EFFECT OF SUBSTITUENTS ON THE RATES OF S N 2 REACTIONS Br H 3 C Br Br 145 Br 1 1 0. 8 Structure Relative rate* Structure Relative rate* Effect of . The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, which is the energy barrier that must be overcome in order for the reactants to form products. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants. Report an Error Reaction Progress Reaction Progress 6. Draw hypothetical reaction coordinate diagrams for: (a) An endergonic, two-step reaction with the first step being the rate-determining step. (b) A reaction with three transition states and DG > 0. (c) A three-step reaction where K > 1, and the third step is faster than the first step,
See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. Given the following reaction, determine the correct reaction coordinate diagram and draw the major organic product.Which of the following reaction coordinate diagrams corresponds to the reaction?Draw product B. Expert Answer.
Understanding the Reaction Coordinate Diagram. Major product at low temperatures- 1, 2 Bromobutene: The main product at low temperatures is Kinetically controlled. This means that there is not enough energy to overcome the Activation Energy of the Thermodynamic product even though it is the more stable product.; 98% product: At a low temperature the amount of …
AboutPressCopyrightContact usCreatorsAdvertiseDevelopersImpressumNetzDG TransparenzberichtNetzDG ComplaintsTermsPrivacyPolicy & SafetyHow YouTube worksTest new features · © 2021 Google LLC
The coordinate covalent N–O function is polar, with the oxygen being a powerful hydrogen bond acceptor. If one of the alkyl substituents consists of a long chain, such as C 12 H 25 , the resulting amine oxide is an amphoteric surfactant and finds use in …
draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two step reaction in which the first step is endergonic the
Read in chemical files from over 30 formats created by other chemistry software. More than just the molecules are recovered, including reactions, spectra, arrows, shapes and more. Thorough support for MDL, SMILES, CDX, CDXML files and more.
Let's consider a general reaction where a reactant or set of reactants, A, is transformed into a product or set of products, B. The diagram below is called a ...
Hammond's postulate (or alternatively the Hammond–Leffler postulate), is a hypothesis in physical organic chemistry.which describes the geometric structure of the transition state in an organic chemical reaction. First proposed by George Hammond in 1955, the postulate states that:. If two states, as, for example, a transition state and an unstable intermediate, occur …
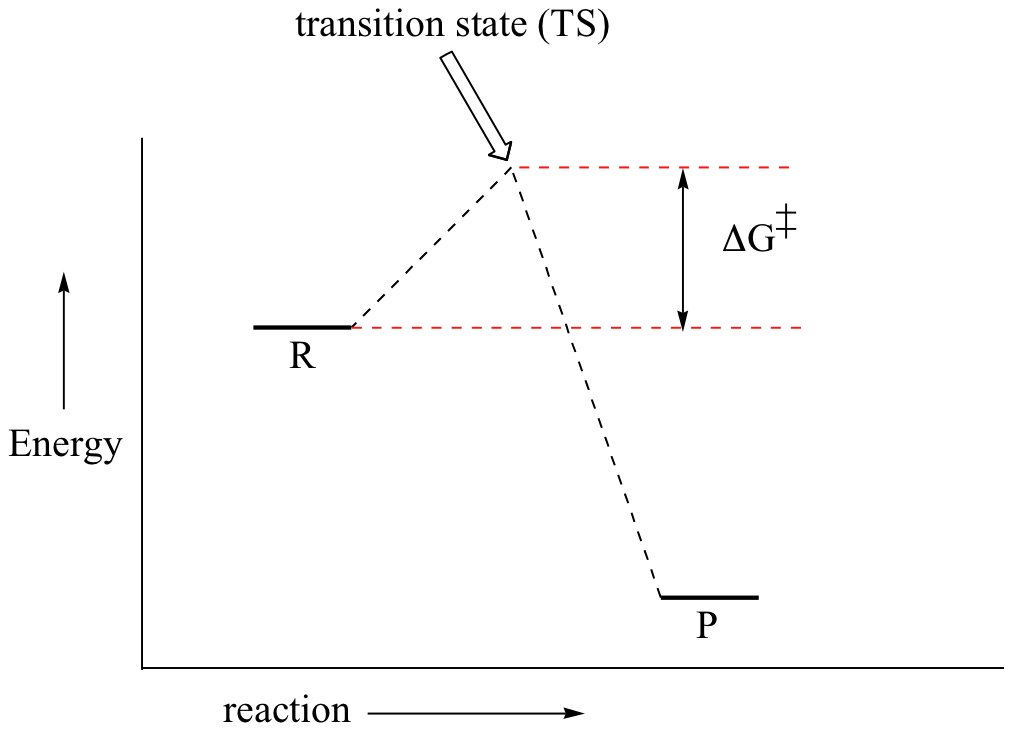
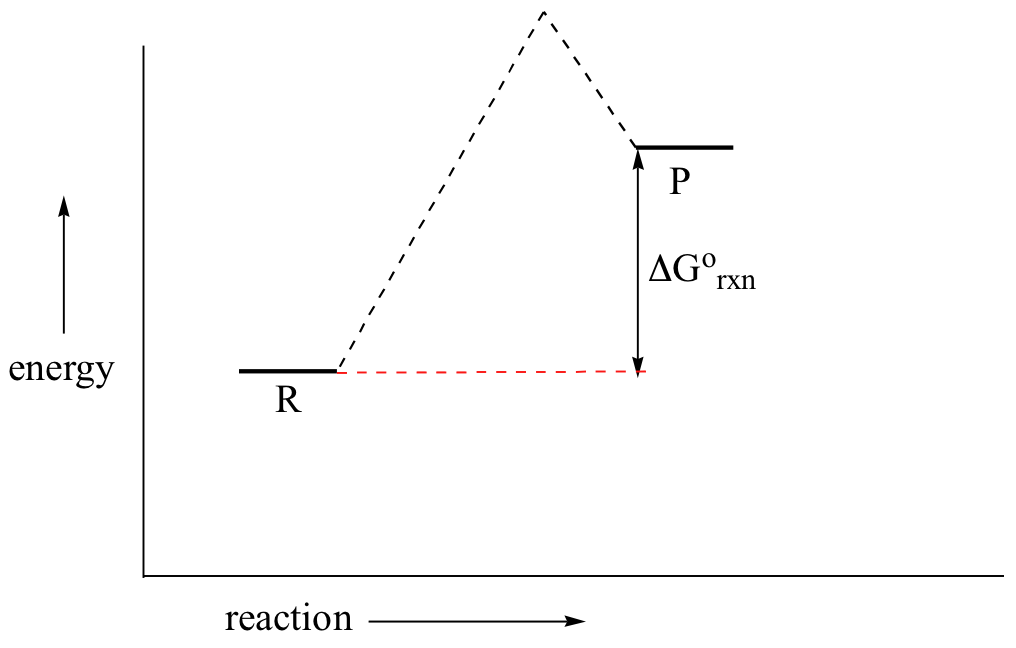
You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ‘reaction coordinate’, tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products.
Feb 05, 2022 · Reaction Coordinate Diagram of Ozone Photolysis The reaction coordinate diagram for the ozone photolysis reaction is a little different from those above because this is an endothermic reaction . Together, the products O 2 and atomic O, have a higher energy than the reactant O 3 and energy must be added to the system for this reaction.
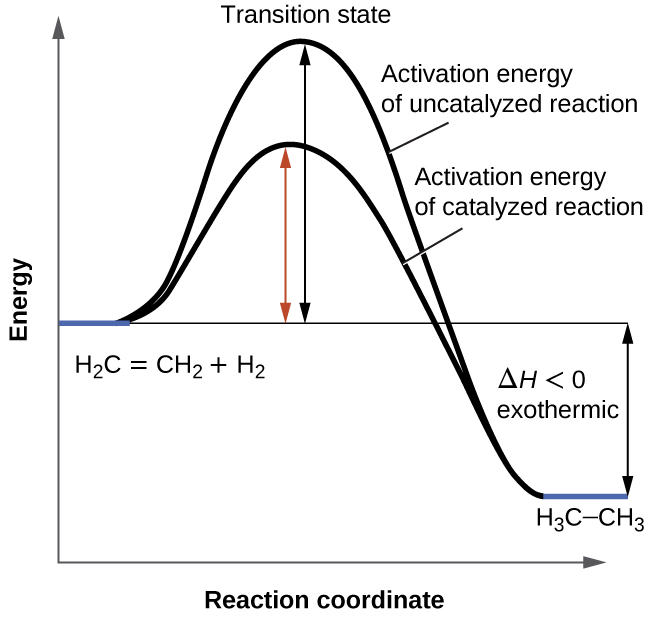
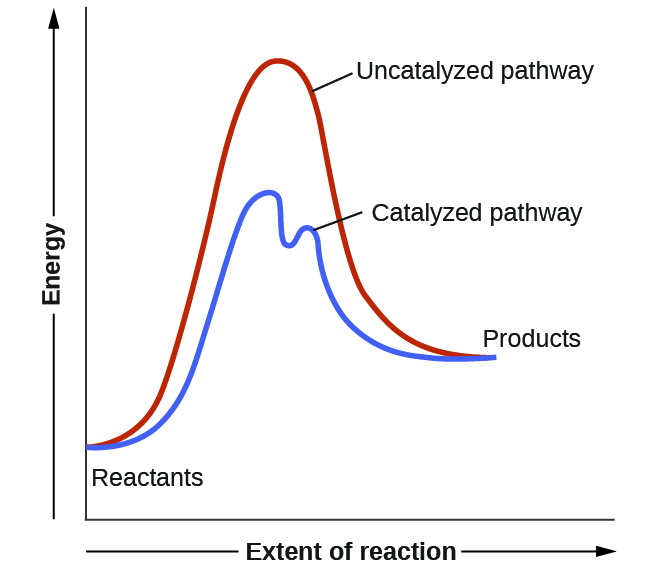
reaction coordinate diagram shows that the energy of activation for the reverse reaction is lowered by the catalyst as well. Enzymatic catalysis The ability of enzymes to catalyze reactions depends on their ability to interact directly and specifically with
March 28, 2021 - Last week Diana left this comment: I recently had my first orgo exam and one of the concepts that I have trouble visceralizing is Hammond’s
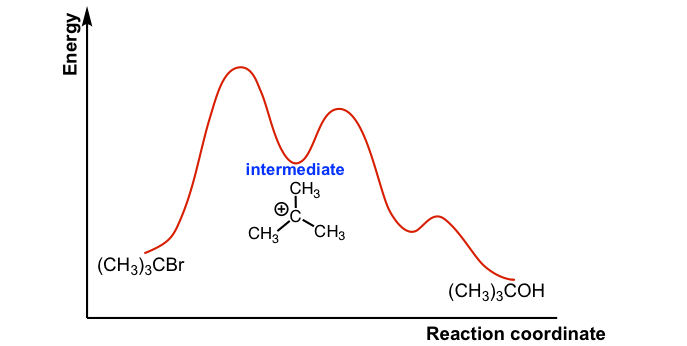
the x-axis that is a reaction coordinate: a loosely defined term meaning the reaction progress in the general direction from the starting materials or reagents (SM) to the products (Pr). the energy curve describing the energy states of the components at a certain point in the reaction. the transition states (TS) and an intermediate (I).
In chemistry, a reaction coordinate is an abstract one-dimensional coordinate which represents progress along a reaction pathway. It is usually a geometric parameter that changes during the conversion of one or more molecular entities. In molecular dynamics simulations, a reaction coordinate ...
Feb 07, 2015 · If you balance the first reaction as a standard reduction reaction in acidic solution, you get: O 2 + 4H + + 4e- ---> 2H 2 O. If you balance the second reaction as a standard reduction reaction in basic solution you get: O 2 + 2H 2 O + 4e- ---> 4 OH-In a cell diagram, the anode is always on the left of the double lines and the cathode is on the ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Free practice questions for College Chemistry - Reaction Coordinate Diagrams. Includes full solutions and score reporting.
reaction with sodium or potassium chloride and sodium or potassium nitrate. • Identification and Tests for both dilute and concentrated sulphuric acid. 9. Organic Chemistry (i) Introduction to Organic compounds. • Unique nature of Carbon atom – tetra valency, catenation. • Formation of single, double and triple bonds, straight chain ...
Mar 12, 2016 · *Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Organic Reactions *Electrophiles *Nucleophiles *Organic Reaction Mechanisms in General *Electrophilic Addition *Nucleophilic Substitution *Free Energy of Activation vs Activation Energy *Complex Reaction Coordinate Diagrams *Names and Structures of Organic Molecules *Alkanes *Cycloalkanes *Alkenes
Organic chemistry students' challenges with coherence formation between reactions and reaction coordinate diagrams. Chemistry Education Research and Practice 2018, 19 (3) , 732-745.
In this video, Dr. Norris goes over practice problems in interpreting reaction energy coordinate diagrams.
Chemistry questions and answers Please help me with drawing reaction coordinate diagram for each reaction from Organic chemistry below : 2-methylbutane with bromine/heat 1- propene with HBr in ROOR 1-methylcyclbutene with Br2 in light cyclobutane with chlorine/light 3-methylbut-ene with HCl cyclopentene with H20/H2SO4 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with
Arizona State University in Tempe, AZ is a public research university ranked #1 in the U.S. for innovation, dedicated to accessibility and academic excellence.
PRACTICE: The reaction coordinate diagram below is an example of the application of Hammond postulate to carbocation formation in an SN1 reaction. Based on the reaction coordinate diagram below, which of the following statements is FALSE? A. The relative stabilities of the carbocation decreases in the following order: 3 o > 2 o > 1 o B. The transition state shifts towards the reactant with ...
Reaction Coordinate G 2e) In mechanism 1 we assumed the first step is rate-determining. Provide a detailed reaction coordinate diagram consistent with this scenario; include as much detail as possible. 2f) Assume for the moment that it is not known which step of Mechanism 1 is rate-determining. Consider an
The purpose of this study was to elucidate and describe students’ thinking when making connections between substitution and elimination reactions and their corresponding reaction coordinate diagrams. Thirty-six students enrolled in organic chemistry II participated in individual, semi-structured interviews.
The energy changes that accompany each step of a reaction mechanism are represented on a reaction coordinate diagram. The reaction pathway on this plot is t...
Consequently, most potential energy surfaces in organic chemistry are not drawn with any single, numerical coordinate, but with a generalized reaction coordinate that reflects the geometry changes in the reaction. Instead of numerical labels on the axis, the positions are labeled with their ...
Lecture notes in General and Inorganic Chemistry provides an introduction to the chemistry of inorganic molecules. The emphasis is on basic principles of atomic and molecular structure, thermodynamics, chemical kinetics and catalysis, properties of
This Concept Map, created with IHMC CmapTools, has information related to: CHEM232Fa12, Halogenation of the Carbonyl alpha-Carbon The Michael Reaction, [E2] [Ebeta] & [DE] - Elementary Steps for Elimination The [E2] Elimination Mechanism, Structure-Reactivity Relationships Bond Energy Changes, Conventions & Terms in Writing Chemical Equations Classes of Chemical Transformations, The Elements ...
In organic chemistry parlance, this is what is meant by "identify the symmetry elements that are preserved throughout the reaction". In organic chemistry, it is "conventional to be less formal with the notation" (Atkins's words; Molecular Quantum Mechanics 4ed, p 400), and so the irrep symbols are replaced with a series of S's (for a character ...
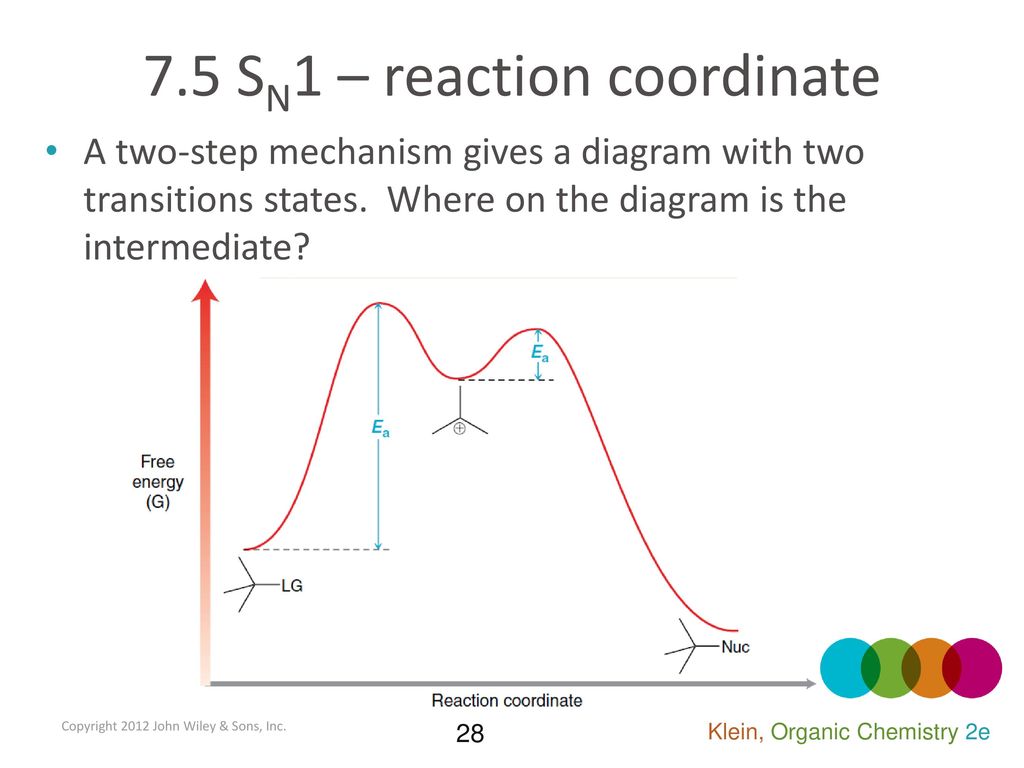
Potential energy diagrams. In a potential energy diagram (see illustration), the reaction coordinate is intended to represent the progress of the reaction, and it may or may not correlate with an easily observed or measurable feature.In reaction (), the reaction coordinate could be considered to be the increasing bond length of the carbon-bromine (C-Br) bond as it is broken, or the decreasing ...
In this section, we will review some fundamentals of organic and biological chemistry that are helpful in understanding enzyme reaction mechanisms. Definition of an Enzyme Recall from Chapter 6, that enzymes are biological catalysts that reduce the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed in the forward direction (Figure 7.1).
You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ‘reaction coordinate’, tracing from left to right ...
This is illustrated by the energy diagram, where the activation energy for the first step is higher than that for the second step. Also recall that an SN1 reaction has first order kinetics, because the rate determining step involves one molecule splitting apart, not two molecules colliding. Organic Chemistry ...
energy diagram (or reaction energy diagram): a graph of the energy of a reaction against the progress of the reaction. enthalpy: a thermodynamic state function, generally measured in kilojoules per mole. In chemical reactions the enthalpy change (deltaH) is related to changes in the free energy (deltaG) and entropy (deltaS) by the equation:
Reaction coordinate diagrams are derived from the corresponding potential energy surface (PES), which are used in computational chemistry to model chemical reactions by relating the energy of a molecule(s) to its structure (within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation).
Organic chemistry students struggle with understanding the energetics of chemical reactions. Reaction coordinate diagrams are one tool that is widely used in organic chemistry classrooms to assist students with visualizing and explaining the energy changes that take place throughout a reaction.










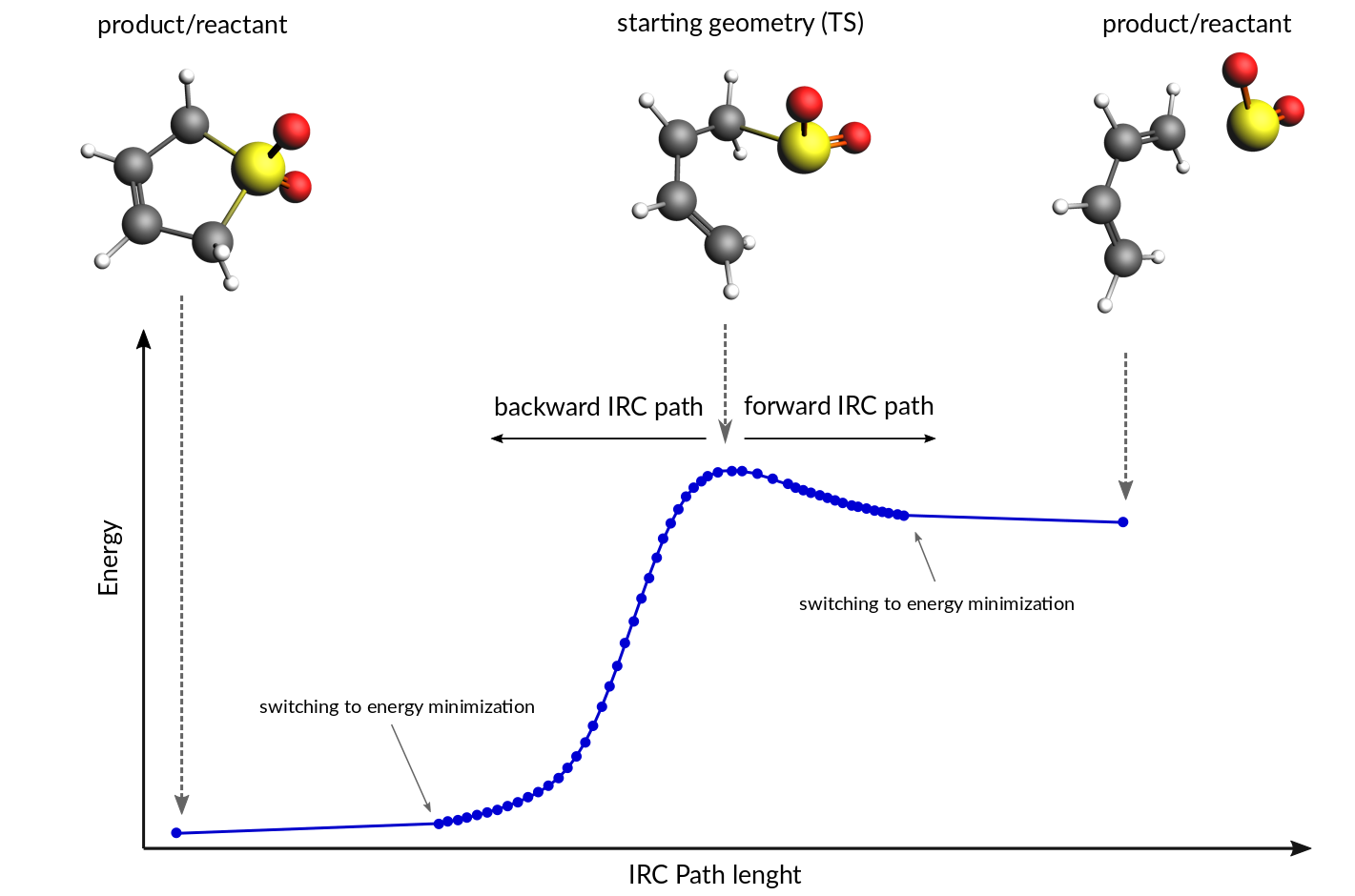
![Solved] Draw a hypothetical free-energy diagram for the SN2 ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.question.images/image/images11/877-C-O-S(403).png)





0 Response to "40 reaction coordinate diagram organic chemistry"
Post a Comment