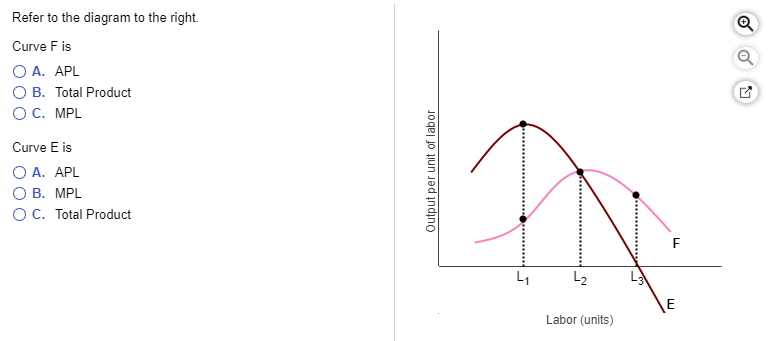
45 refer to the diagram to the right. identify the curves in the diagram.
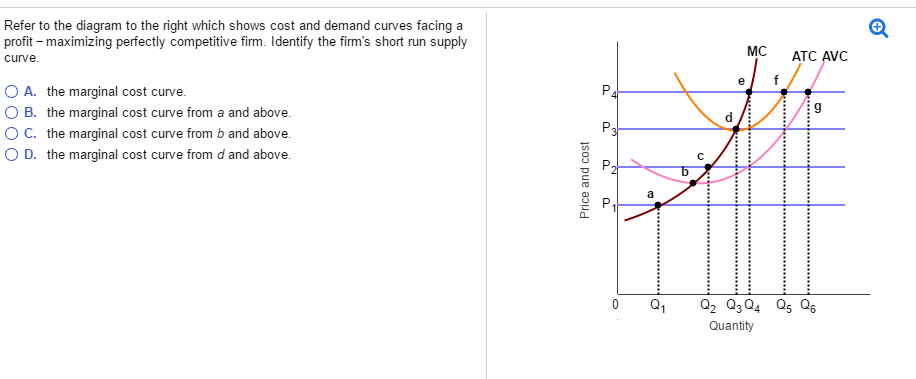
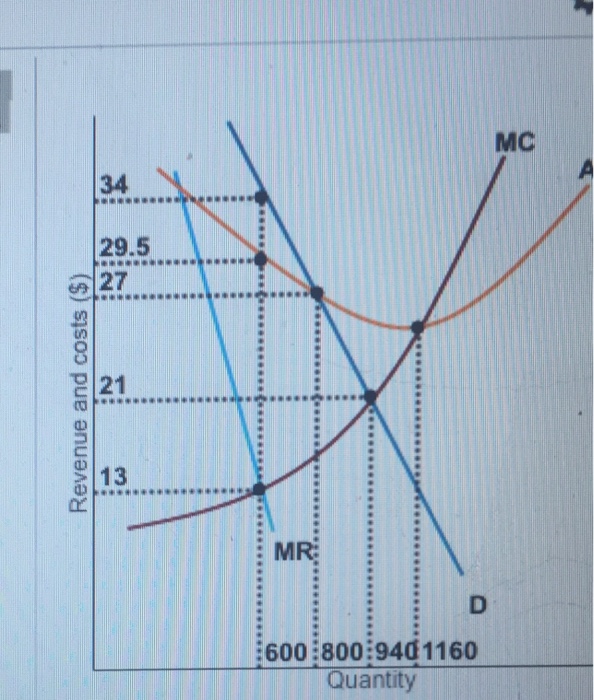
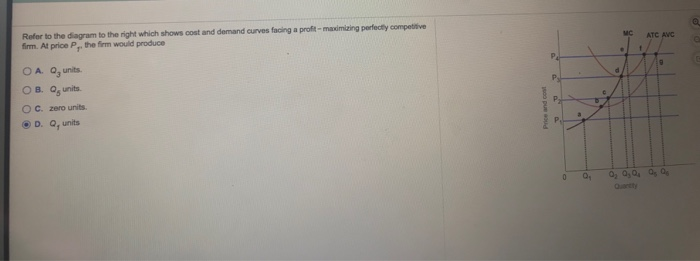
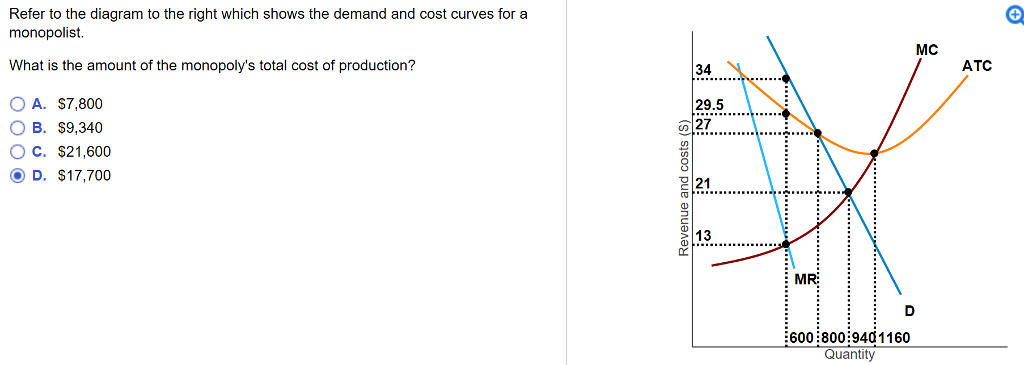
See Page 1. 18) Refer to Figure 11 - 5. Identify the curves in the diagram. A) E = marginal cost curve; F = average total cost curve; G = average variable cost curve; average fixed cost curve. B) E = average fixed cost curve; F = variable cost curve; G = total cost curve, H = marginal cost curve C) E = average fixed cost curve; F = average ... the typical firm earns zero profit. Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the cost and demand curves for a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $30, the firm's profit maximizing output level is 180 Producing where marginal revenue equals marginal cost is equivalent to producing where
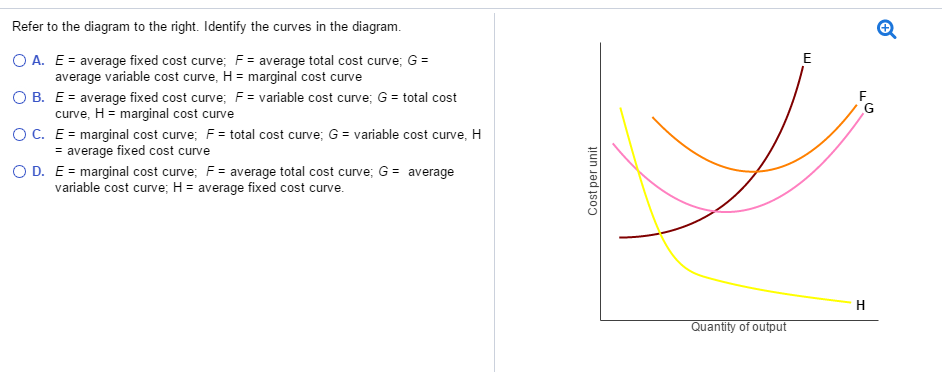
Jun 08, 2017 · Answer is D) E represents marginal cost as it increases with increase in output due to diminishing returns (when the marginal cost cur …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. E=average fixed cost curve, F=average total cost curve, G= average variable cost curve, H ...
Refer to the diagram to the right. identify the curves in the diagram.
This can be made clear with the help of diagram 13. In the diagram 13 output has been measured on OX- axis while costs on OY-axis. Here, we see that AC = MC and both are parallel to X-axis. Relationship of Different Cost Curves in Short Period: In Figure, the relationship between different cost curves can be explained with the help of figure 14. Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. additional cost of producing an additional unit or output. Marginal cost is the. $340. Vipsana's Gyros House sells gyros. The cost of ingredients (pita, meat, spices, etc.) to make a gyro is $2.00. Vipsana pays her employees $60 per day. Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the demand and supply curves for the almond market. The government believes that the equilibrium price is too low and tries to help almond growers by setting a price floor at Pf.
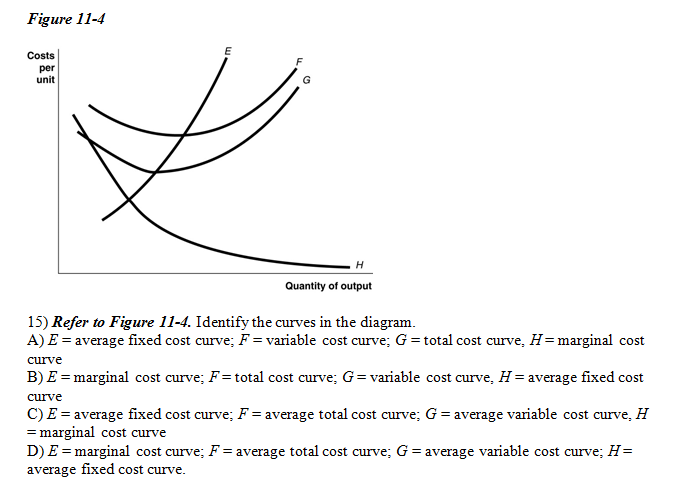
Refer to the diagram to the right. identify the curves in the diagram.. Transcribed image text: Identify the curves in the diagram. E = marginal cost curve; F = total cost curve; G = variable cost curve, H = average fixed cost curve E = average fixed cost curve; F = variable cost curve; G = total cost curve, H = marginal cost curve E = marginal cost curve; F = average total cost curve; G = average variable cost curve; H = average fixed cost curve. Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. ... Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the minimum efficient scale of production. Qb(very bottom point of the diagram) If 11 workers can produce a total of 54 units of a product and a 12th worker has a marginal product of 6 units, then the average product of 12 ... We can use the phase diagram to identify the physical state of a sample of water under specified conditions of pressure and temperature. For example, a pressure of 50 kPa and a temperature of −10 °C correspond to the region of the diagram labeled “ice.”. Under these conditions, water exists only as a solid (ice). Phase Diagram Worksheet Name: A phase diagram is a graphical way to depict the effects of pressure and temperature on the phase of a substance: The CURVES indicate the conditions of temperature and pressure under which "equilibrium" between different phases of a substance can exist. BOTH phases exist on these lines: Sohd Liqtnd Nihon
A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. Venn Diagram: A Venn’s diagram may be a commonly used diagram vogue that shows the relation between sets.Venn Diagrams area unit introduced by English logician John Venn \(\left( {1834 – 1883} \right).\)The Venn Diagrams area unit accustomed teach pure elementary mathematics, and as an instance, easy set relationship in chance, logic, statistics, linguistics, and engineering. Refer to the diagram to the right which shows cost and demand curves facing a typical firm in a constant-cost perfectly competitive industry. If the market price is $20, what is the amount of the firm's profit? $6,750 In a perfectly competitive industry, in the long-run equilibrium the typical firm earns zero profit. Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the demand and supply curves for the almond market. The government believes that the equilibrium price is too low and tries to help almond growers by setting a price floor at Pf.
Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. additional cost of producing an additional unit or output. Marginal cost is the. $340. Vipsana's Gyros House sells gyros. The cost of ingredients (pita, meat, spices, etc.) to make a gyro is $2.00. Vipsana pays her employees $60 per day. This can be made clear with the help of diagram 13. In the diagram 13 output has been measured on OX- axis while costs on OY-axis. Here, we see that AC = MC and both are parallel to X-axis. Relationship of Different Cost Curves in Short Period: In Figure, the relationship between different cost curves can be explained with the help of figure 14.

Image from page 162 of "Practical mathematics : an elementary treatise covering the fundamental processes of arithmetic, algebra, and geometry, with a practical presentation of logarithms and curve plotting" (1915)

Grid plan...Benefits and criticisms.. The nature of the city: the living environment is a social and artistically dedicated being


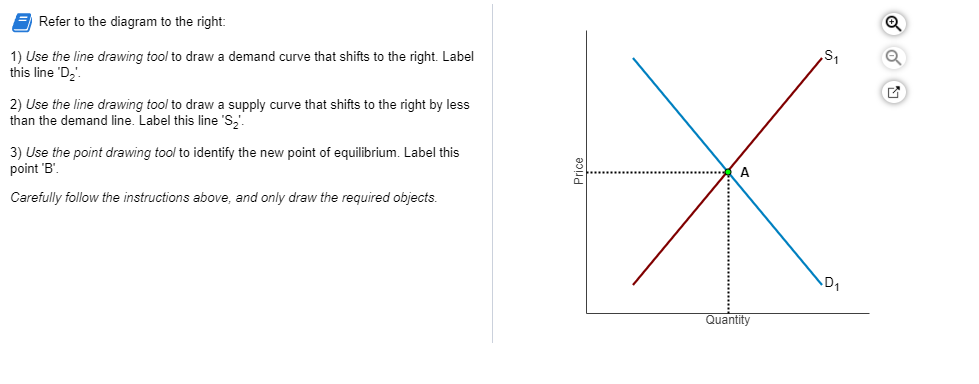

























0 Response to "45 refer to the diagram to the right. identify the curves in the diagram."
Post a Comment