45 molecular orbital diagram for o2 2-
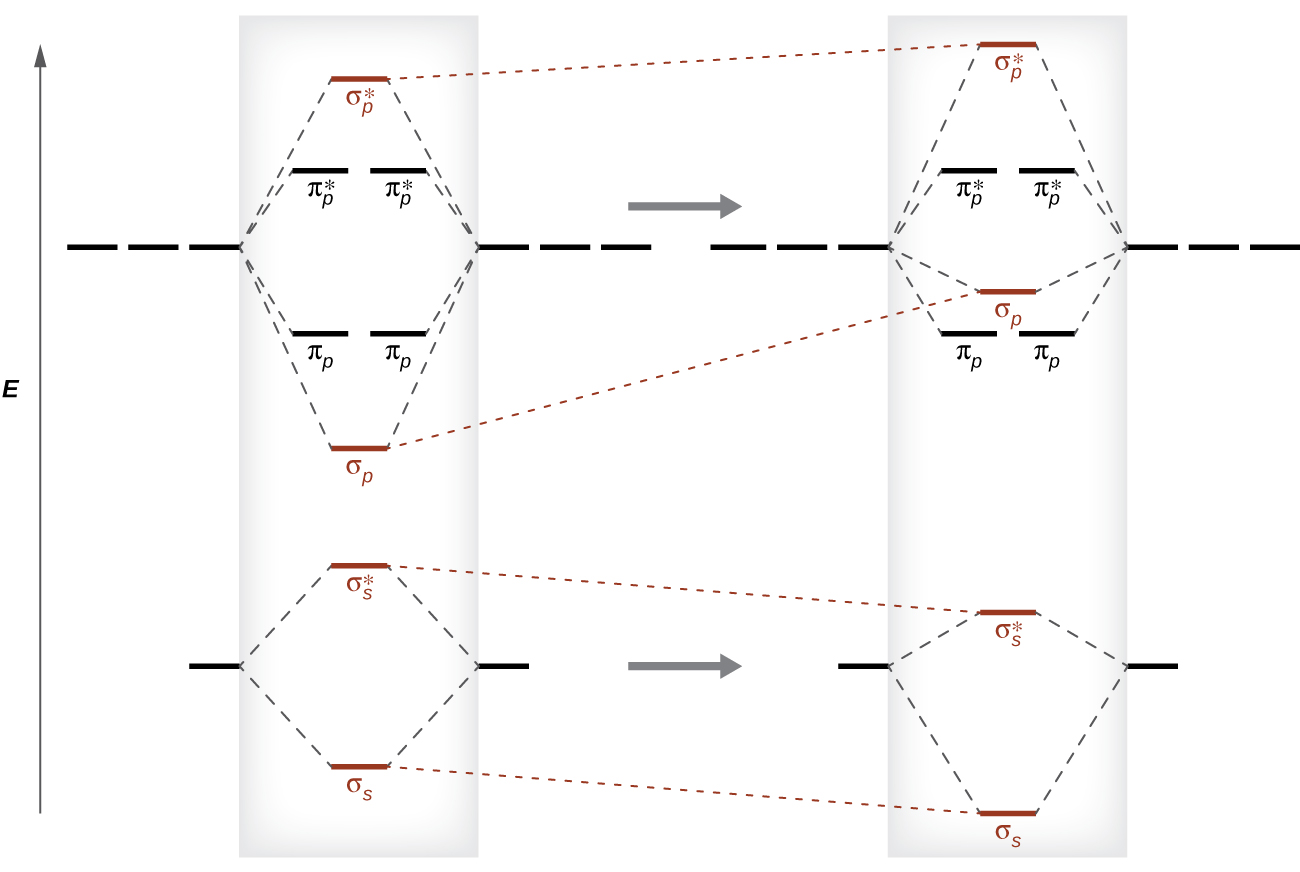
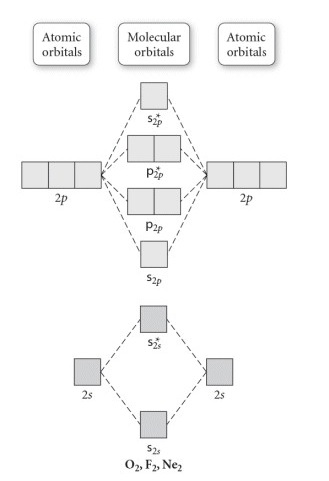
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... The molecular geometry of sulfur dioxide is a bent shape. Sulfur to the Oxygen ratio in Sulfur dioxide is 1:2. Sulfur dioxide molecule has two double bonds between the Sulfur atom and Oxygen atoms. There are 5 lone pairs of electrons in the molecule of SO2. Molar mass of sulfur dioxide = 64.066 g/mol.
The double bond in C 2 consist of both Pi bonds because the four electrons are present in the two pi molecular orbitals. 10) N 2. ... Diagram for O2+ is wrong because 2p atomic orbital of 2nd O atom will have only 3 e-. Reply. Mrs Shilpi Nagpal says. September 26, 2018 at 11:06 am.
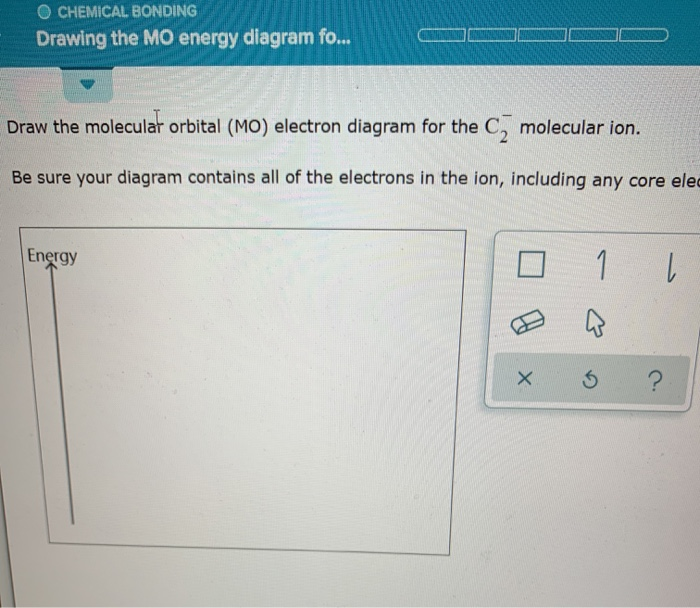
Molecular orbital diagram for o2 2-
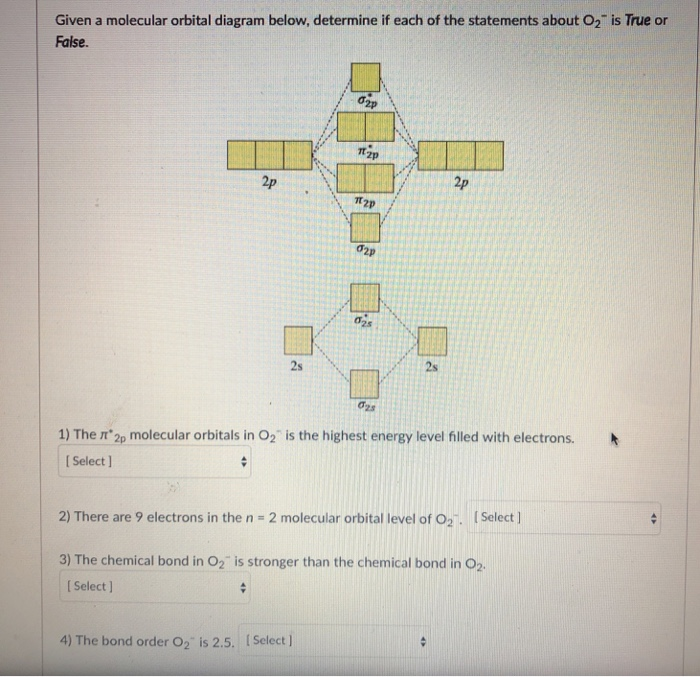
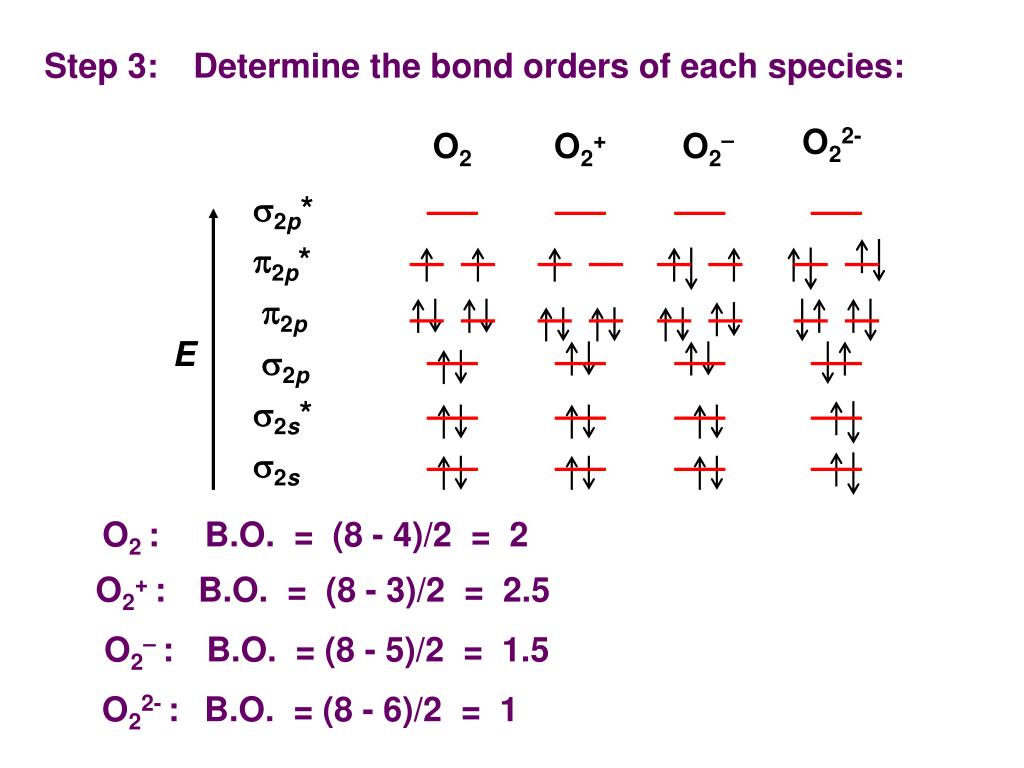
Below is a molecular orbital diagram for O2. Label the atomic and molecular orbitals and fill in the electrons. Sketch two bonding and two antibonding orbitals in the provided boxes and identify which MOs they correspond to in the MO diagram. (8) Is O2 diamagnetic or paramagnetic and is this consistent with the Lewis structure. O 2 2-. is 1. So, the correct order of bond order is O 2 2- O 2 − O 2 O 2 +. So, the correct answer is "Option B". Note: You should notice that bond order is indirectly proportional to the length of the bond. The higher the bond order, the shorter and stronger will be the bond. The addition of each electron in the antibonding molecular ... As it can be seen from the MOT of O 2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, the bond order can be calculated as [N b − N a ] / 2 = [1 0 − 6] / 2 = 2. Therefore there is a double bond present as O = O.
Molecular orbital diagram for o2 2-. molecular electron configuration for O2 σ2σ*2σ2π4π*2 We can also calculate the O-O bond order: BO 1 2 # bonding e # anti-bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 LCAO MO theory also predicts (correctly) that O2has two unpaired electrons. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - . Item 2: Part A Complete the MO energy diagram for the N2+ ion by dragging the electrons Electron with spin up., ↑, ↑↓, ↓ in the figure given below.M.O. diagram for N2+Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Show Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 7.7.12. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as ... Molecular Orbitals for Water (H 2 O). The five occupied and the lowest three unoccupied molecular orbitals of the isolated molecule (1a 1) 2 (2a 1) 2 (1b 2) 2 (3a 1) 2 (1b 1) 2 (4a 1) 0 (2b 2) 0 (3b 2) 0 were calculated using the Restricted Hartree-Fock wave function (RHF) using the 6-31G** basis set. b (experimental data is given in []).They are set out with the lowest energy (that is, most ...
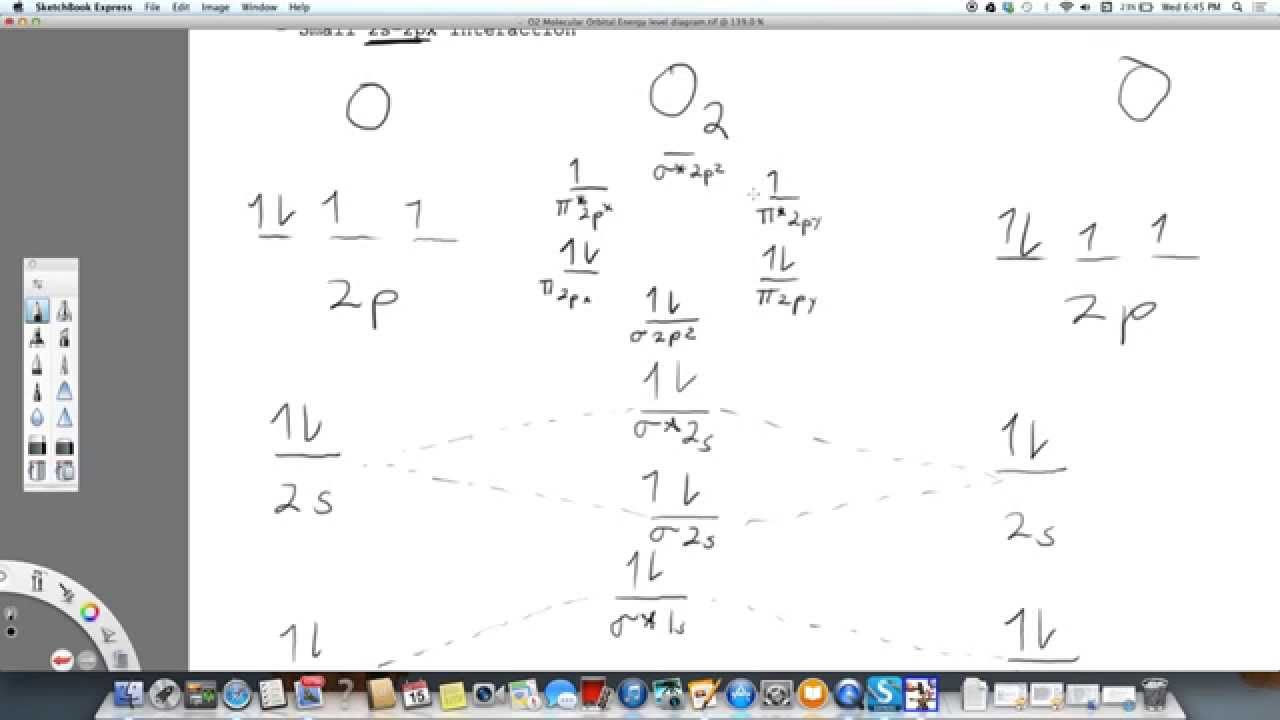
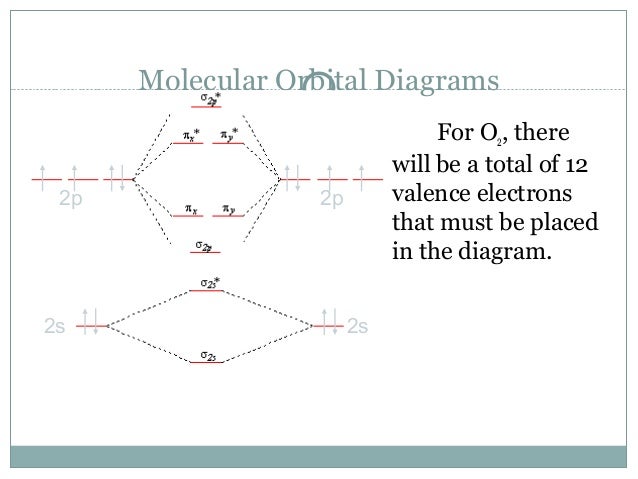
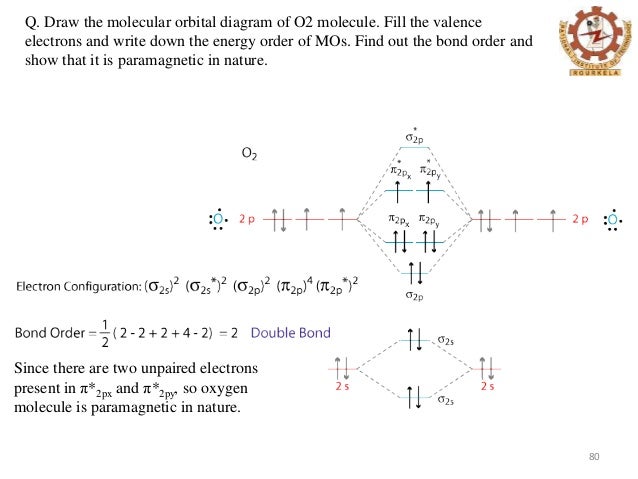
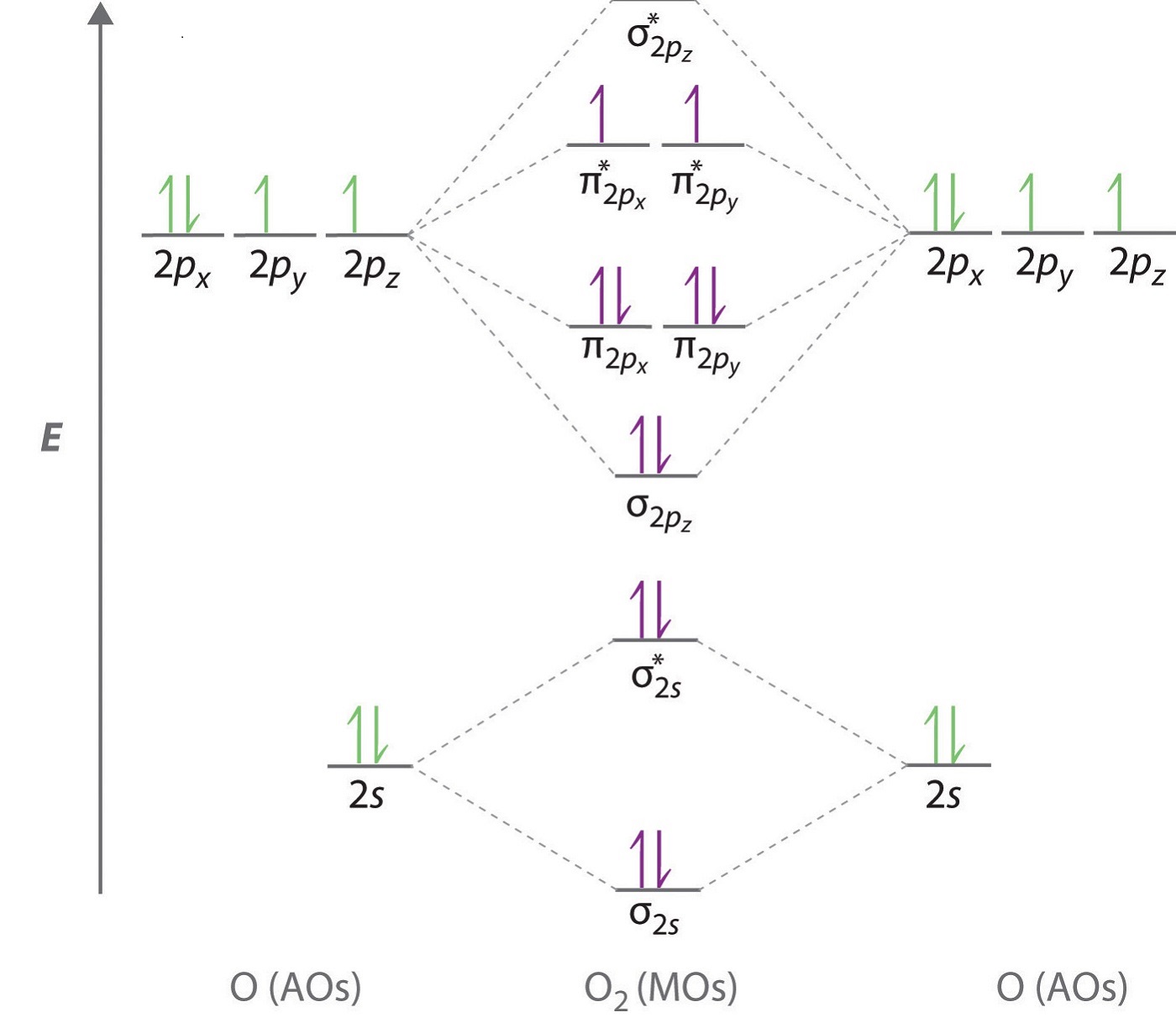
It is sigma2s(2)sigma2s*(2)sigma2p(2)pi2p(4)pi2p*(4)Bond order 1. It is stable. In fact, it's the perioxide ion.Check me out: http://www.chemistnate.com O2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Oxygen has a similar setup to H 2, but now we consider 2s and 2p orbitals. When creating the molecular orbitals from the p orbitals, notice the three atomic orbitals split into three molecular orbitals, a singly degenerate σ and a doubly degenerate π orbital. Relative energy levels of molecular orbitals of O 2 and ... Molecular orbitals of O2 1. Electronic configuration of O atom is 1s2 2s2 2p4 2. Electronic configuration of O, molecule is σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 σ2px2 π2py2 π2pz2 π*2py1 π*2pz1 3. Bond order = N b−N a 2 N b − N a 2 = 10−6 2 10 − 6 2 = 2 4. Molecule has two unpaired electrons, hence it is paramagnetic. ← Prev Question Next Question → The molecular orbital diagram shows the energy state at each level where the excited state increases from the bottom to the top. The left-hand side diagram is of O2 at ground level whereas the right-hand side diagram is of rearranged electrons as per the Lewis structure within the O2 molecule.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed. The Molecular orbital diagram for O2 O 2 is like this: As you can see the oxygen molecule has two unpaired electrons in the lower π π * ant-bonding states. For O2+2 O 22 + basically remove the two unpaired electrons in the π π * anti-bonding states, as they are the most easily removed. 26.2K views View upvotes Related Answer Amara Sehrish You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of O2. Begin with the atomic orbitals. Oxygen atom has 2s and 2p valence orbitals and 6 valence electrons: Each oxygen contributes 6, so we distribute 12 valence electrons into the molecule to get O2. Two 2s orbitals combine to give a σ2s bonding and σ* 2s antibonding MO. O2has a single bond, with four electrons in the π*orbitals canceling those in the π orbitals. O2 -has three electrons in the π* orbitals, and a bond order of 1.5. The Lewis structures have an unpaired electron and an average bond order of 1.5. O2has two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals,and a bond order of 2.
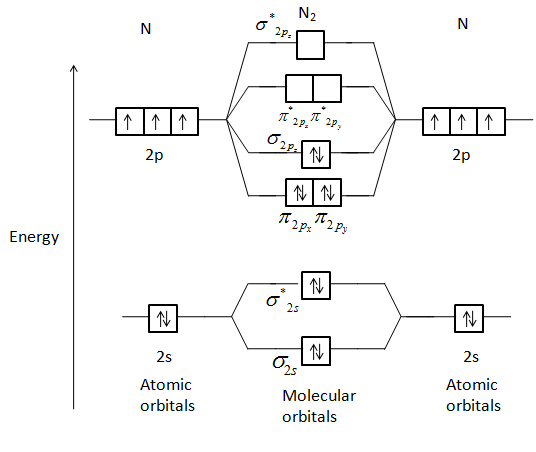
Oxygen's paramagnetism is explained by the presence of two unpaired electrons in the (π 2py, π 2pz)* molecular orbitals. Check Your Learning The main component of air is N 2. From the molecular orbital diagram of N 2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic.
For each Fluorine atom: Formal Charge = 7 - 0.5*2 - 6 = 7 - 1 -6 = 0. Since the elements are present in their least possible formal charge values, we have achieved our suitable Lewis Structure configuration. Let us see: Here, oxygen forms a single bond with each of the fluorine atoms (O-F). OF2 Molecular Geometry
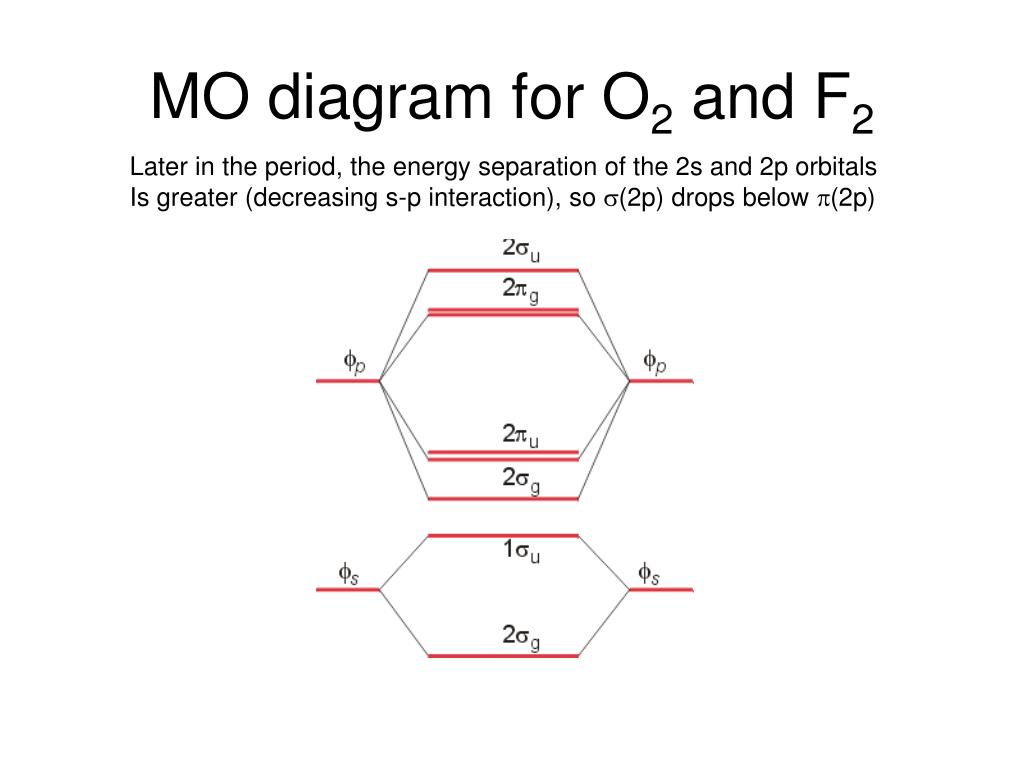
Answer (1 of 3): Here is the MO diagram for O₂: Whilst this is the MO diagram for N₂: If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on the Second Period (Li₂, Be₂, B₂, C₂, N₂, O₂, and F₂), the resulting pattern looks like this: When it comes to O₂ and N₂, I think there are two things ...
To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for (ce {O2}), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure (PageIndex {1}). We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy.
Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule. Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ . Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means.
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ...
O₂ has an infinite number of molecular orbitals, but only nine of them are occupied in the ground state. The molecular orbital diagram for O₂ is Each O atom contributes 8 electrons to the O₂ molecule. You use the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's Rule to add the 16 electrons to the molecular orbitals in an Aufbau process. The molecule then has 5 fully occupied bonding molecular ...
There are two lone pairs of electrons on each Oxygen atom; thus, there are four lone pairs of electrons for H2O2. As each Oxygen atom forms an sp3 hybrid orbital, H2O2 has sp3 hybridization. The bond angle for H2O2 in its gas phase is 94.8°and has a bond angle of 101.9°. It has tetrahedral electron geometry and a bent molecular shape.
Remember: When two oxygen atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals. They are flipped compare...
Aug 25, 2017 — In normal O2, there are 6 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, making the bond order 2. By removing the 2 highest electrons, which reside in ...3 answers · 7 votes: In O2 2+, there is 14 electrons. So, it’s MOT is comparable to N[code ]2[/code] & the MOT ...What is the electronic configuration O2^-2 molecule ...5 answersOct 6, 2015What is the bond order of o2^+2? - Quora4 answersOct 1, 2018What is the molecular orbital diagram for O2- and ...5 answersMar 27, 2017What is a bond order for 02-? - Quora11 answersMar 31, 2018More results from www.quora.com
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ...
As it can be seen from the MOT of O 2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, the bond order can be calculated as [N b − N a ] / 2 = [1 0 − 6] / 2 = 2. Therefore there is a double bond present as O = O.
O 2 2-. is 1. So, the correct order of bond order is O 2 2- O 2 − O 2 O 2 +. So, the correct answer is "Option B". Note: You should notice that bond order is indirectly proportional to the length of the bond. The higher the bond order, the shorter and stronger will be the bond. The addition of each electron in the antibonding molecular ...
Below is a molecular orbital diagram for O2. Label the atomic and molecular orbitals and fill in the electrons. Sketch two bonding and two antibonding orbitals in the provided boxes and identify which MOs they correspond to in the MO diagram. (8) Is O2 diamagnetic or paramagnetic and is this consistent with the Lewis structure.














.png)




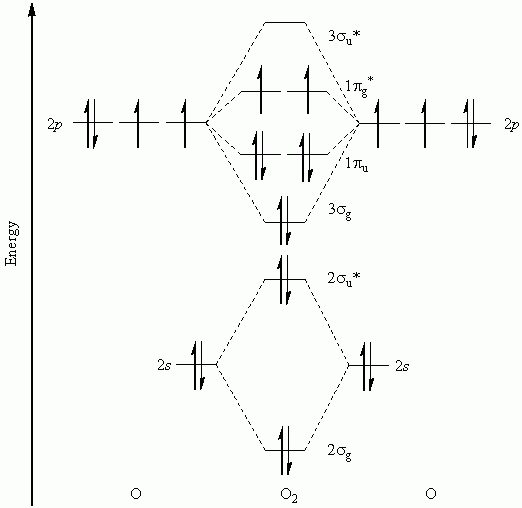






0 Response to "45 molecular orbital diagram for o2 2-"
Post a Comment