45 what kind of molecule is represented in the diagram
Sep 27, 2020 — Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ What kind of molecule is represented in the diagram? Fatty Acid Glycerol Fatty Acid ...2 answers · 48 votes: Hi! This is a triglyceride A tissue is a group of cells, in close proximity, organized to perform one or more specific functions. There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion of ions and ...
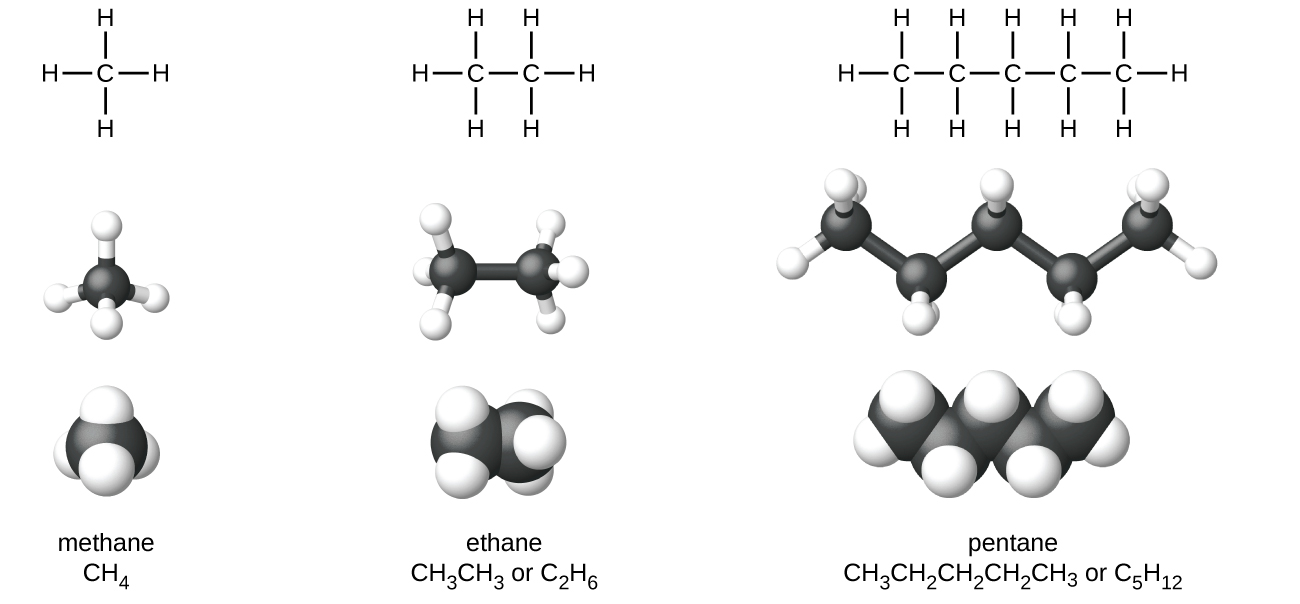
Determine the type and number of atoms in the molecule (C H H H H). Write the Lewis dot structure for each individual atom. Connect the atoms by electron pair bonds so that each atom has a full octet.
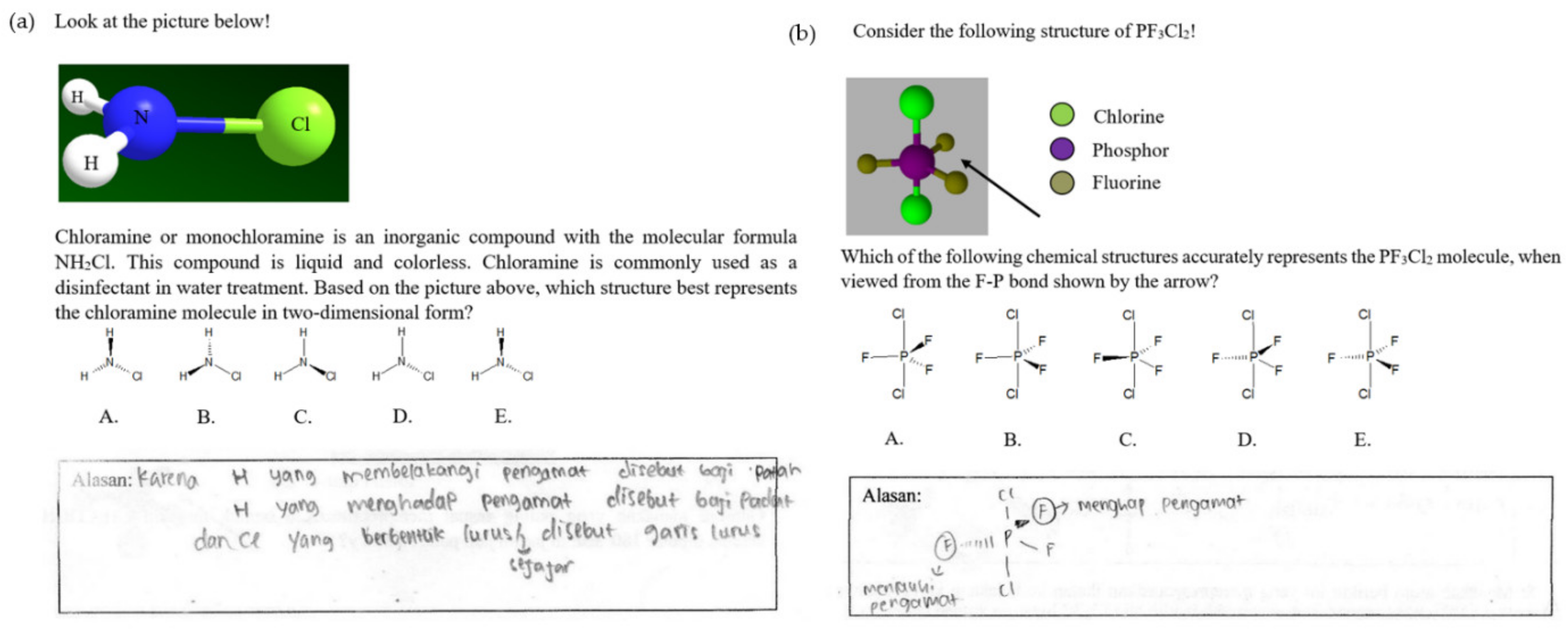
What kind of molecule is represented in the diagram
Regardless of the type of molecule, matter normally exists as either a solid, a liquid, or a gas. We call this property of matter the phase of the matter. The three normal phases of matter have unique characteristics which are listed on the slide. Solid. In the solid phase the molecules Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell. Graph Representation in Data Structure. Below are the two most common ways of representation of graph in data structure: 1. Adjacency Matrix. An Adjacency Matrix is the simplest way to represent a graph. It is a 2D array of V x V vertices with each row and column representing a vertex.
What kind of molecule is represented in the diagram. Apr 3, 2019 — The structure of nucleotide consists of a pentose sugar, nitrogenous bases and a phosphate group attached with the pentose sugar as depicted in ...2 answers · 11 votes: Answer:DExplanation:A nucleotide is made up of a 5-carbon ring. On the 1’ Carbon is where ... HCN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Shape, and Polarity. Hydrogen Cyanide is a colorless, flammable, and poisonous chemical liquid. Represented by the chemical formula, HCN is one of those molecules that has an interesting Lewis structure. This liquid is used in electroplating, mining, and as a precursor for several compounds. The diagram below shows an mRNA molecule that encodes a protein with 202 amino acids. The start and stop codons are highlighted, and a portion of the nucleotide sequence in the early part of the molecule is shown in detail. Let us draw a Lewis structure of ethane step by step. Step 1: Determining the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. The valence electron for carbon (1s22s22p2) and hydrogen (1s1) is 4 and 1, respectively. In ethane, we have two carbon atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms and hence, the total number of valence electron are (2 X 4) + (1 X 6 ...
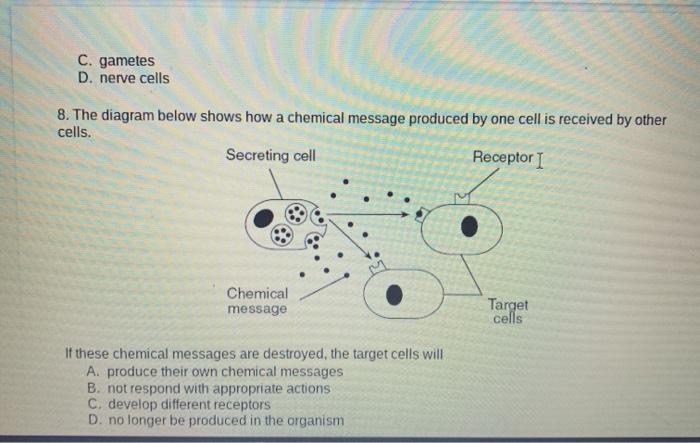
Jun 4, 2019 — What kind of molecule is represented in the diagram? O A. A fatty acid. O B. A nucleotide. O C. A lipid. OD. A carbohydrate.2 answers · 42 votes: Answer:B Explanation: The Lewis diagram of two hydrogen atoms sharing electrons looks like this: This depiction of molecules is simplified further by using a dash to represent a covalent bond. The hydrogen molecule is then represented as follows: Remember that the dash, also referred to as a single bond, represents a pair of electrons. (d) A perspective drawing (also called a wedge-and-dash representation) attempts to show the three-dimensional structure of the molecule. (e) The space-filling model shows the atoms in the molecule but not the bonds. (f) The condensed structural formula is by far the easiest and most common way to represent a molecule. Jun 11, 2018 — What kind of molecule is represented in the diagram? A,B,C or D Get the answers you need, now!2 answers · 6 votes: C. A nucleotide which contains a Phosphate group, a sugar, and a base
A hydroxyl group is composed of one hydrogen atom bonded to one oxygen atom. Its chemical formula is written as either -OH or HO-. The '-' represents the carbon to which the hydroxyl group is ... Two types of pentose are found in nucleotides, deoxyribose (found in DNA) and ribose (found in RNA). Deoxyribose is similar in structure to ribose, but it has an H instead of an OH at the 2′ position. Bases can be divided into two categories: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have a double ring structure, and pyrimidines have a single ring. Ans: The molecular formula represents the exact number and type of atoms present in a single molecule of a compound. The constituting elements of a compound are represented by their chemical symbols followed by numeric subscripts describing the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule. Look at the diagram below. phosphate base sugar what kind of molecule is represented in the diagram? o a. a fatty acid o b. a nucleotide o c. a lipid od. a carbohydrate
The different colors represent different types of atoms. Is sugar an element, just a molecule, or a molecule and. This structure shows how atoms make up sugar. The different colors represent different types of atoms. Is sugar an element, just a molecule, or a molecule and.
In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure. Chromosomes were first described by Strasburger (1815), and the term 'chromosome' was first used by Waldeyer in 1888.
The water molecule represented in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) contains polar covalent bonds. The attractive force between water molecules is a dipole interaction. The hydrogen atoms are bound to the highly electronegative oxygen atom (which also possesses two lone pair sets of electrons, making for a very polar bond.
the phenomenon as a result of which a molecule can be expressed in different forms none of which can explain all the properties of the molecule. The actual structure of the molecule is called resonance hybrid. Question 12. H 3 PO 3 can be represented by the structures 1 and 2 as shown below.
5) Divisional Structure. Within a divisional types of organizational charts has its own division which corresponds to either products or geographies. Each division contains the necessary resources and functions needed to support the product line and geography. Another form of divisional org chart structure is the multi-divisional structure.
Jan 17, 2017 · 4 answersA molecule is represented by a chemical formula. What is the diagram that shows a lipid? Lipid is a molecule and molecules are represented by ...
Jan 6, 2020 — What kind of molecule is represented in the diagram? Fatty Acid Glycerol Fatty Acid Fatty Acid A. A nucleic acid. B. A lipid. C. A nucleotide. D ...2 answers · 39 votes: B. Lipid because it contains Fatty Acid And Glycerol
The molecular geometry of POCl 3 is tetrahedral with asymmetric charge distribution around the central atom. Therefore this molecule is polar. The structure of this compound is tetrahedral and hybridisation of P is sp³. On the central atom P, there are 4 bonding electron clouds (1 P = O double bond and 3 P-Cl bonds) but no lone pair of electrons.
Jun 20, 2018 · 2 answersC. A lipid. It's because lipids include glycerol and fatty acids. jd3sp4o0y and 41 more users found this answer helpful. Thanks 25.
Dec 23, 2016 — A triglyceride is a molecule that contains a glycerol group and three fatty acids ... What kind of molecule is represented in the diagram?1 answer · 1 vote: Answer:It is a triglycerideExplanation:A triglyceride is a molecule that contains a glycerol group and three fatty acids linked by an ester linkage. ...
The diagram below represents an incomplete section of a DNA molecule. The boxes represent unidentified bases. When the boxes are filled in, the total number of bases represented by the letter A (both inside and outside the boxes) will be
Covalent Bond: Definition, Types, Properties, Solved Examples. Covalent Bond is a bond formed by the sharing of electrons present in the valence shell of the atoms. It holds the atoms within an individual molecule together. We are told not to touch electrical appliances with bare wet hands.
The anticlotting factor can then be extracted from the goat milk and used during surgery. To produce these genetically modified goats, scientists most likely: A. Injected the anticlotting factor into the milk-producing glands of the animals. B. added modified DNA into the milk of the animals. C. Inserted the human gene into the egg cells of goats.
SF4 Lewis Structure. Lewis structure is a pictorial representation of the bonds and valence electrons in the molecule. The bonds formed between two atoms are depicted using lines, whereas the valence electrons not forming any bonds are shown by dots. The valence electrons that participate in forming bonds are called bonding pairs of electrons ...
Feb 28, 2017 — Triglycerides are the fats that we get from the food we eat and it is carried in our blood. The fat we eat in a diet are butter, oils etc all ...2 answers · 36 votes: The correct answer should be D. a triglyceride. The picture shows a lipid (fatty acid) and ...
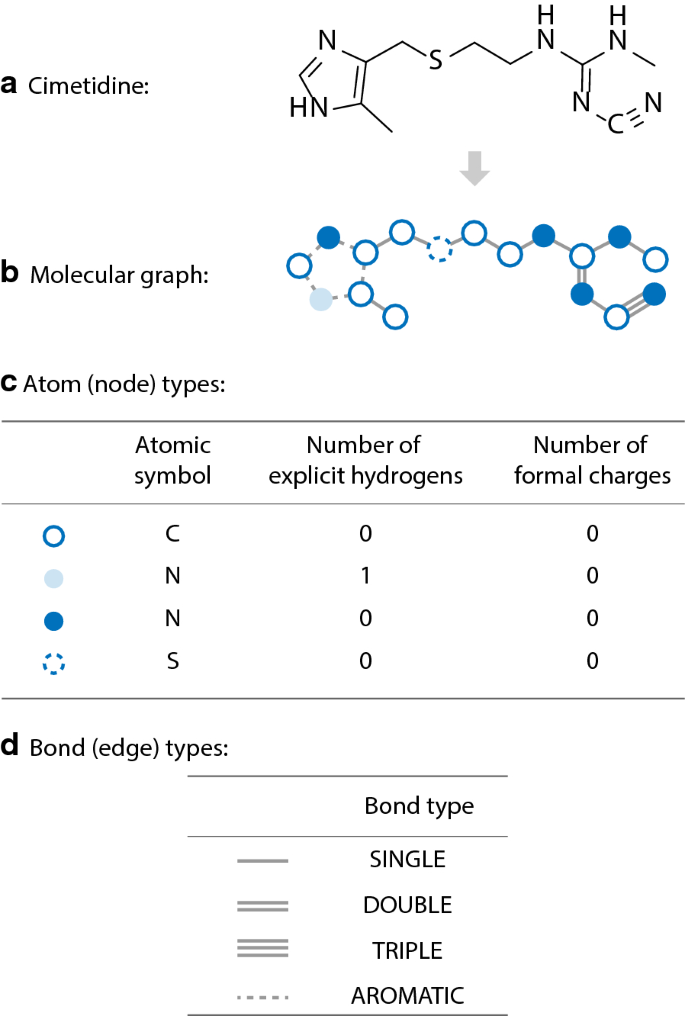
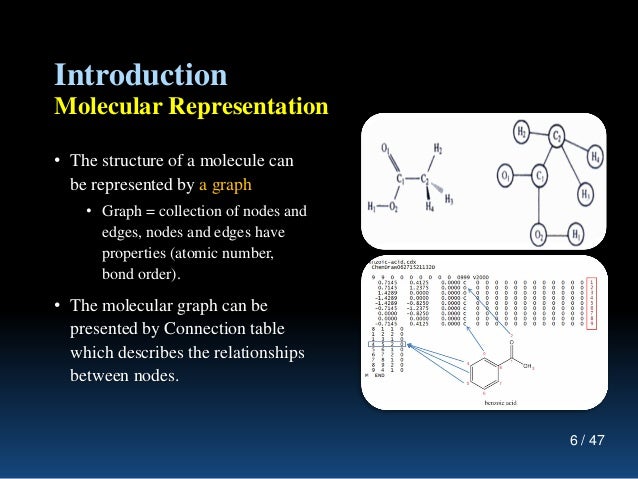
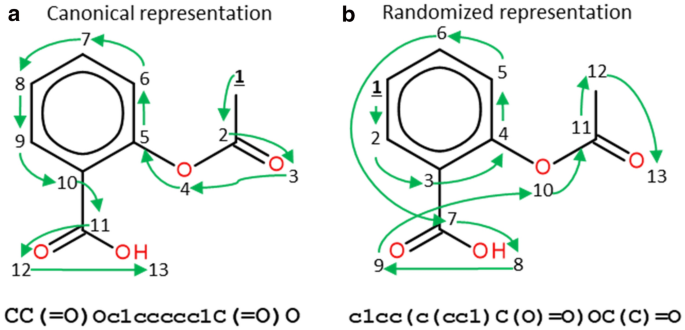
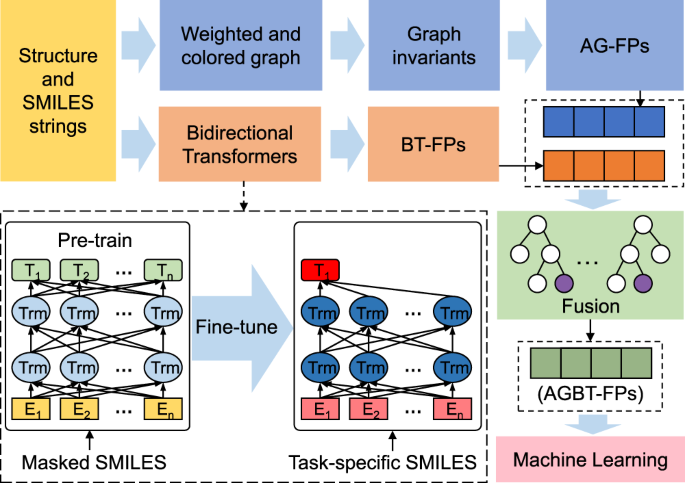
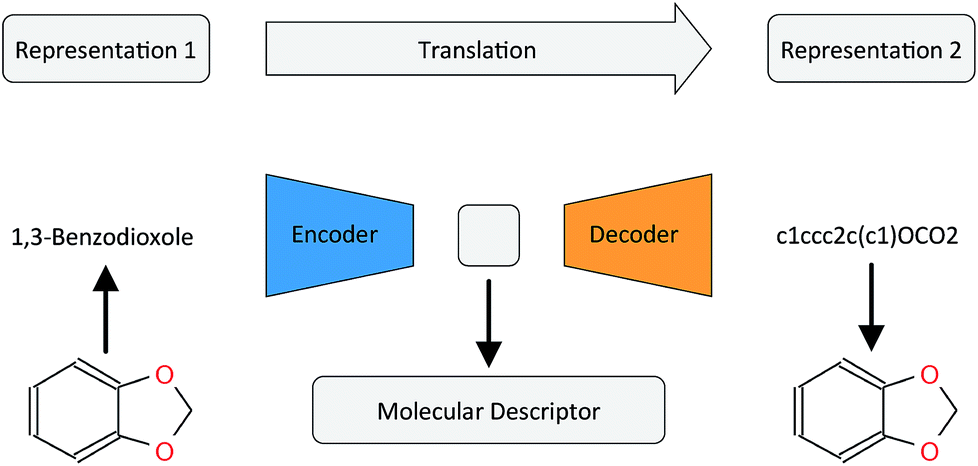
One central problem in this endeavour is the representation of molecules for computers. There are two main approaches, adjacency-matrix-based and string-based approaches to represent graphs. In the former, molecular graphs are represented by adjacency matrices where every element of the matrix indicates whether two vertices share a connection.
When two or more atoms come together, they form a molecule. The number of atoms in a molecule denotes the prefix, so a molecule containing two atoms is called diatomic. There are different types of diatomic molecules. Let's begin this discussion by better understanding the workings of a molecule.
Lewis structure is also known as electron dot structure or Lewis dot structure because the valence electrons are represented as dots in the Lewis structure of the molecule. It is the two-dimensional structure in which every atom in the molecule tends to complete its octet either by sharing or gaining or losing electrons.
By structure, the nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane. It is a porous membrane (like cell membrane) and forms a wall between cytoplasm and nucleus. Within the nucleus, there are tiny spherical bodies called nucleolus. It also carries another essential structure called chromosomes.
A nice example of the combination of two different representations (space filling and licorice) to represent different actors in a chemical reaction: the space filling representation is a Cu (100) surface, instead the licorice one is a hexylbenzene molecule absorbed on the copper surface.
Graph Representation in Data Structure. Below are the two most common ways of representation of graph in data structure: 1. Adjacency Matrix. An Adjacency Matrix is the simplest way to represent a graph. It is a 2D array of V x V vertices with each row and column representing a vertex.
Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell.
Regardless of the type of molecule, matter normally exists as either a solid, a liquid, or a gas. We call this property of matter the phase of the matter. The three normal phases of matter have unique characteristics which are listed on the slide. Solid. In the solid phase the molecules


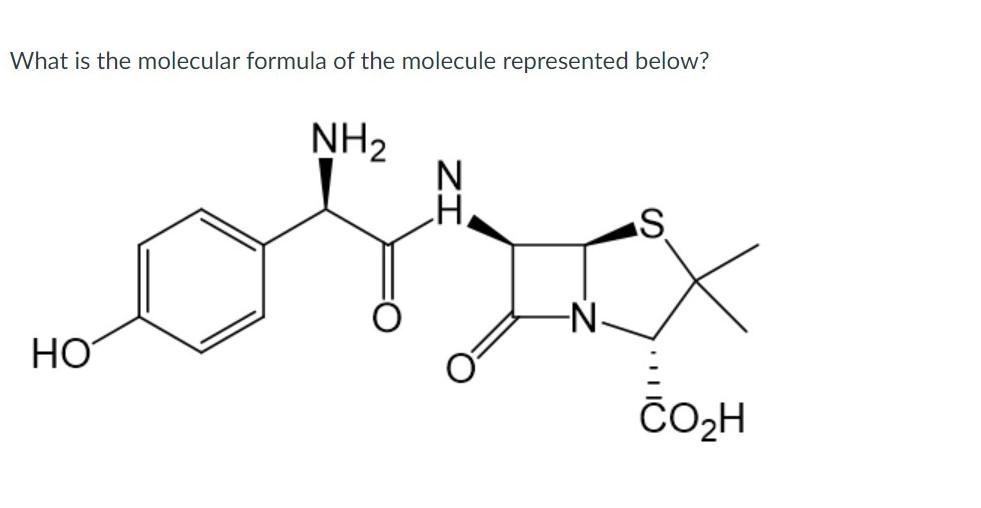


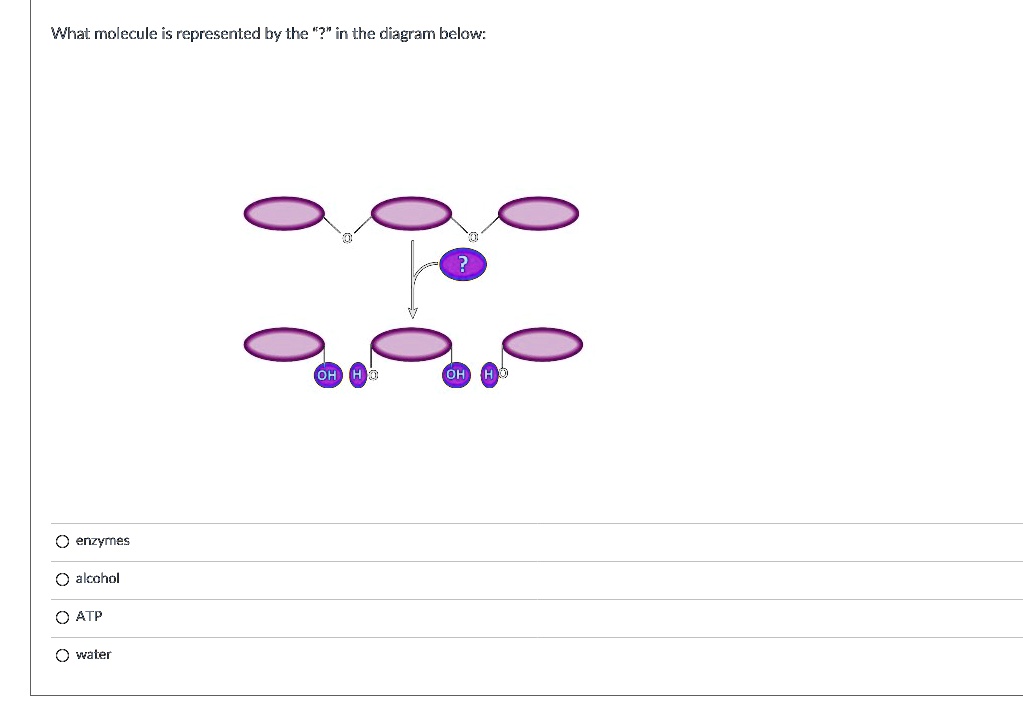
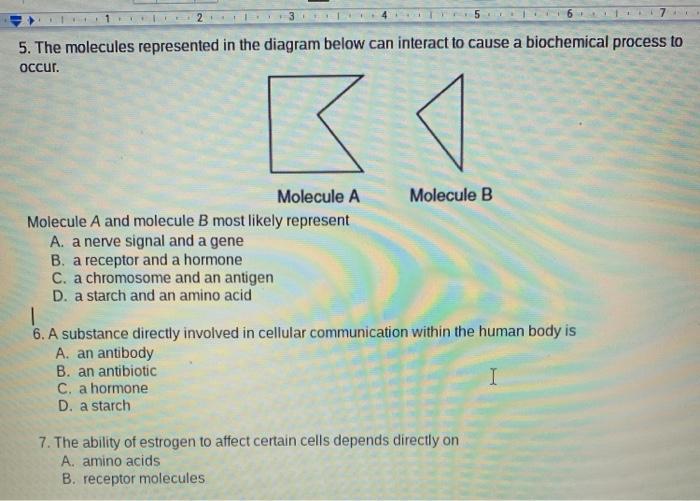
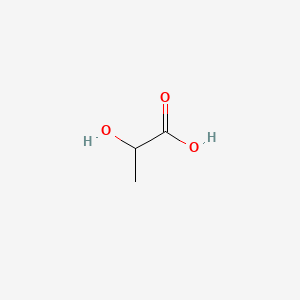














0 Response to "45 what kind of molecule is represented in the diagram"
Post a Comment