43 invariant point phase diagram
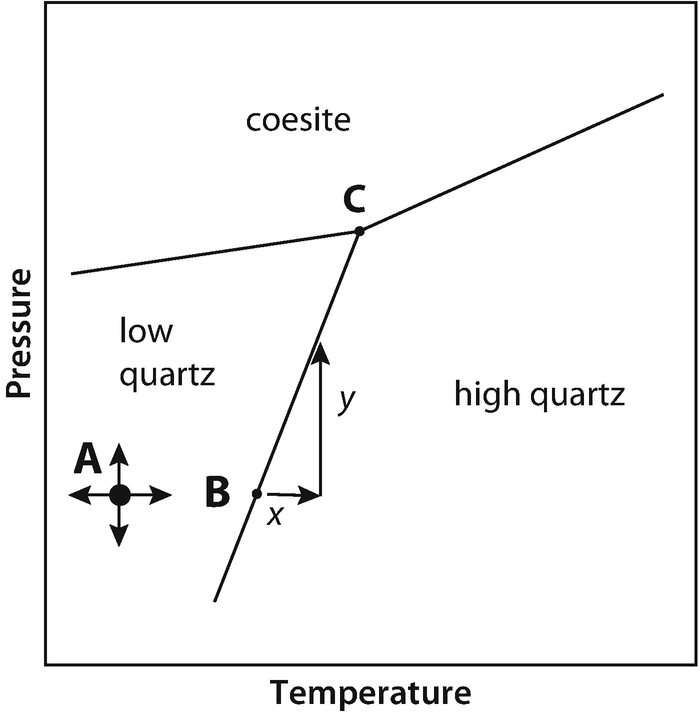
phase diagrams In phase: Unary systems Point C is therefore an invariant point; a change in either pressure or temperature results in the loss of one or more phases. The phase rule also reveals that no more than three phases can stably coexist in a one-component system because additional phases would lead to negative variance. Read More
phase, the diagram now shows two separate solid terminal phases, which are in three-phase equilibrium with the liquid at point P, an invariant point that occurred by coincidence (Three-phase equilibrium is discussed in the next section.) Fig. 5 Schematic binary phase diagrams with invariant points.
Phase diagram topologies for chemical systems with m n+2 are fairly well-understood, even as m grows large. For m n+1 they are essentially trivial, and for m = n+2, they look roughly like Figure 1, having an invariant point surrounded by several univariant reaction curves. The schematic picture of such an invariant point surrounded

Invariant point phase diagram
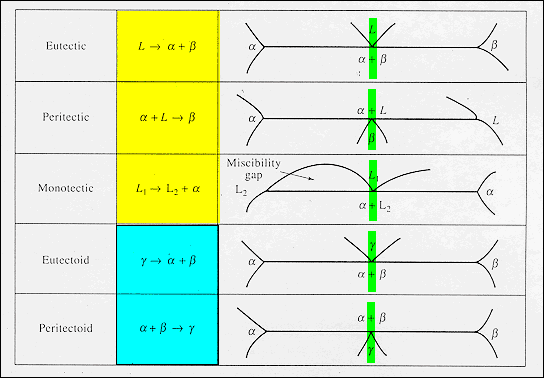
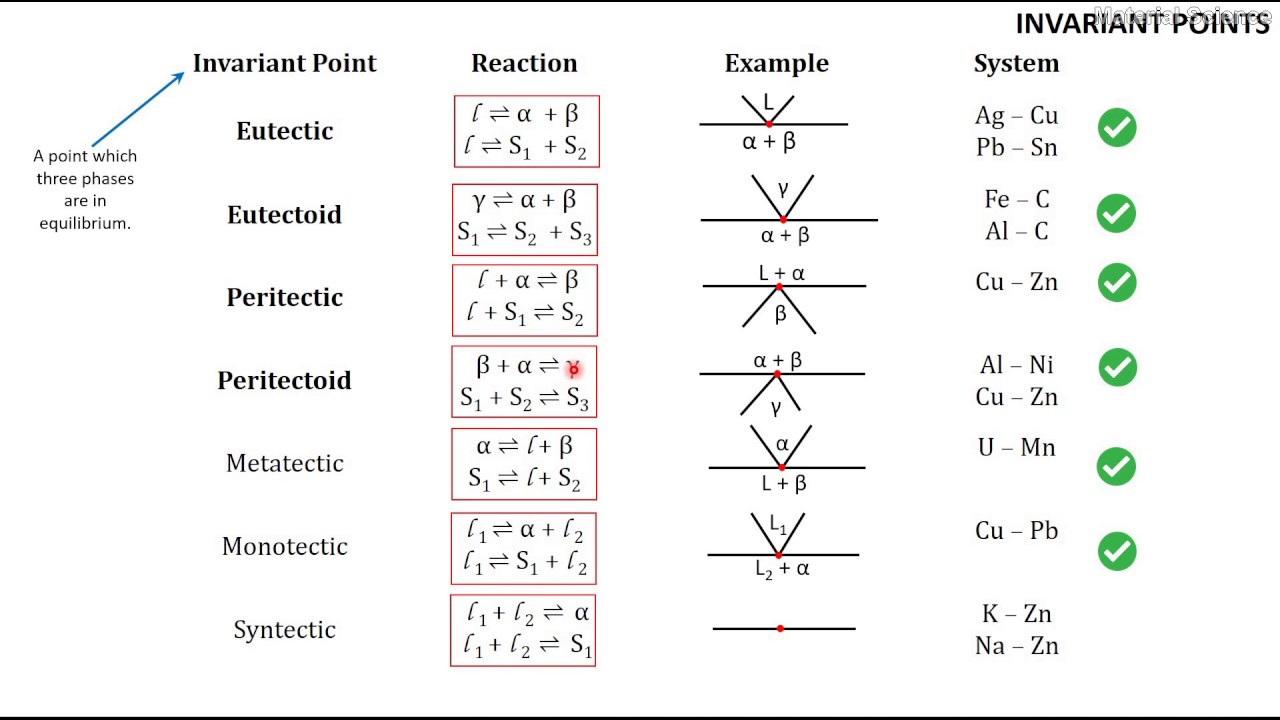
Phase Diagrams: Invariant Reactions · The possible types of invariant reaction are shown below.The vertical green bar identifies the composition required for the invariant reaction, the horizontal line is the temperature of the reaction, and the phase points on the isotherm represent their compositions during the reaction.
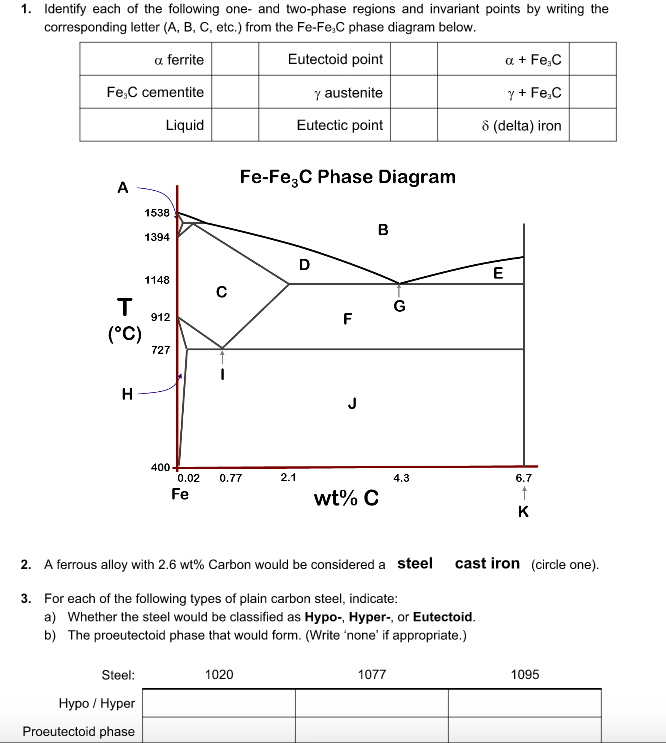
Clarification: A unary phase diagram has a single component thus, at triple point, the number of degrees of freedom, according to Gibbs phase rule F = 1 - 3 + 2 = 0. 3. The invariant reaction involving, a liquid phase decomposing into two different solids on cooling is known as _________
Gib's phase rule, invariant points and reactions in phase diagrams.
Invariant point phase diagram.
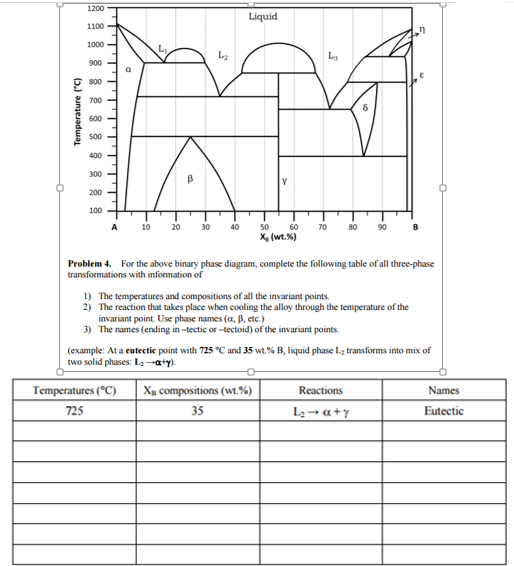
Phase Diagram Summary • Be familiar with all of the phase diagram assignments • Know the "modified" phase rule for igneous phase diagrams • Be able to explain why an invariant point on a phase diagram is a peritectic or eutectic. • Be able to explain the difference between a regular cotectic and reaction cotectic
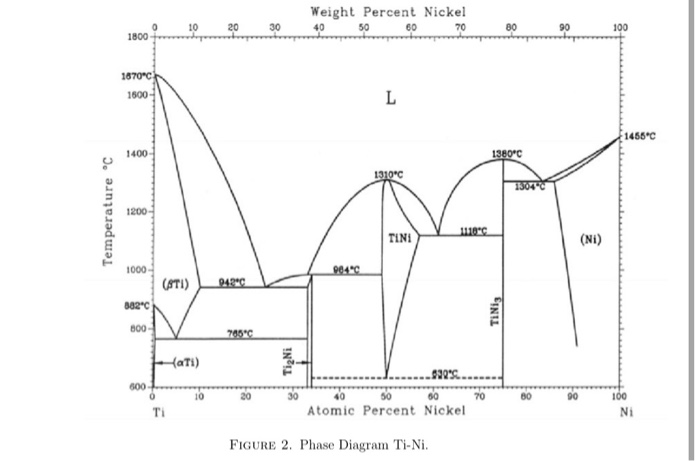
Invariant Phase Equilibria There are three degrees of freedom for a binary system. If three phases meet the conditions are invariant. This means that the phase composition acts like a pure component. An azeotrope or congruent melting point splits the phase diagram into two phase diagrams. There are several types of "invariant reactions".
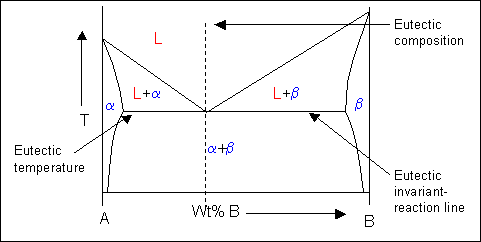
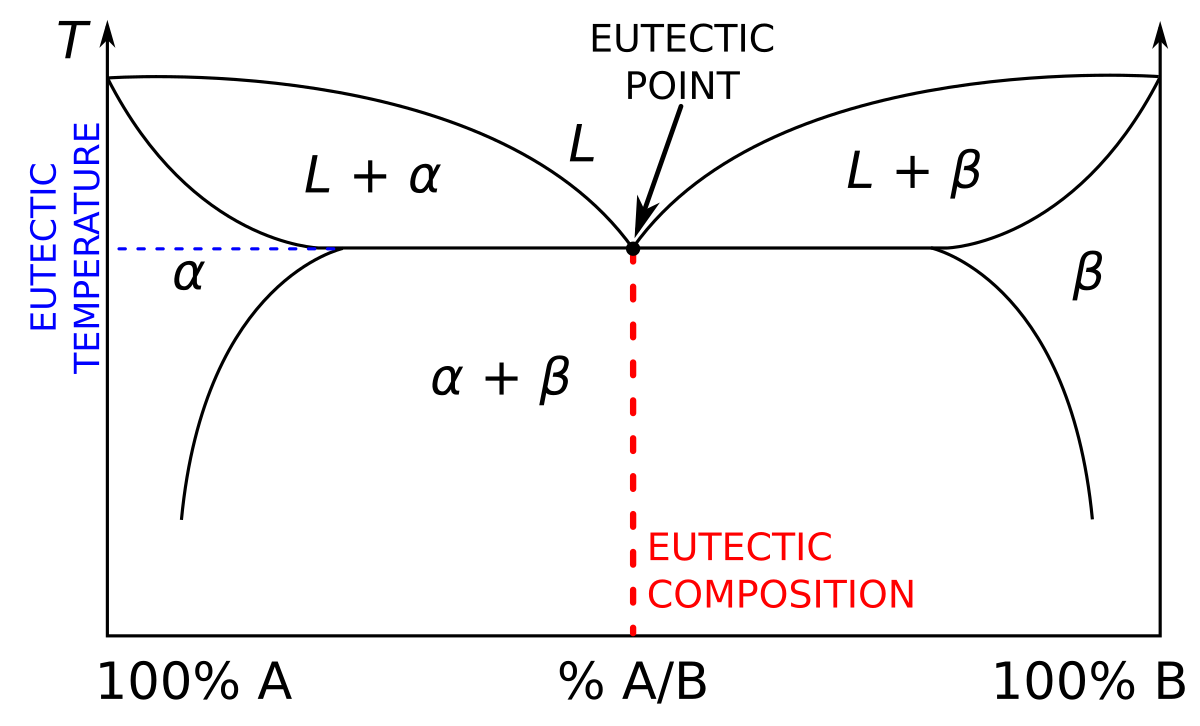
Point E on the phase diagram it is called invariant point at this point an important reaction takes place at constant temperature Called Eutectic reaction where liquid (L) is directly converted to (α) and β phase. iii. Line CEG is called eutectic isotherm.
Unary Diagrams Invariant Equilibrium. According to the phase rule, three phases can exist in stable equilibrium only at a single point on a unary diagram (f= 1 - 3 + 2 = 0). This limitation is illustrated as point O in the hypothetical unary pressure-temperature (PT) diagram shown in Fig. 2. In this diagram, the
Phase diagrams tell us about equilibrium phases as a function of T, P and composition (here, we'll always keep P constant for simplicity). Chapter 9 - 6 Unary Systems Triple point. Chapter 9 - 7 Phase Equilibria Cu FCC 1.8 0.1278 Ni FCC 1.9 0.1246 Crystal electroneg r (nm) Structure
invariant point. Peritectic point- The point on a phase diagram where a reaction takes place between a previously precipitated phase and the liquid to produce a new solid phase. When this point is reached, the temperature must remain constant until A peritectic is also an invariant point.
of reaction curves that intersect at an invariant point in multicomponent systems. This method produces topologically correct bundles or sequences of reactions around an invariant point, and can be applied to a wide variety of phase diagrams such as P-T, T-X, activity-activity, etc. The method is fully described in Zen (1966,
Ternary phase diagram books by D.R.F. West - there are several . Ternary grid . Space diagram . C A B . ... Grey plane is the invariant plane, where the invariant reaction occurs Ternary eutectic reaction . Space diagram and isothermal sections (a)
Nd-Sb Phase Diagram Anlaysis
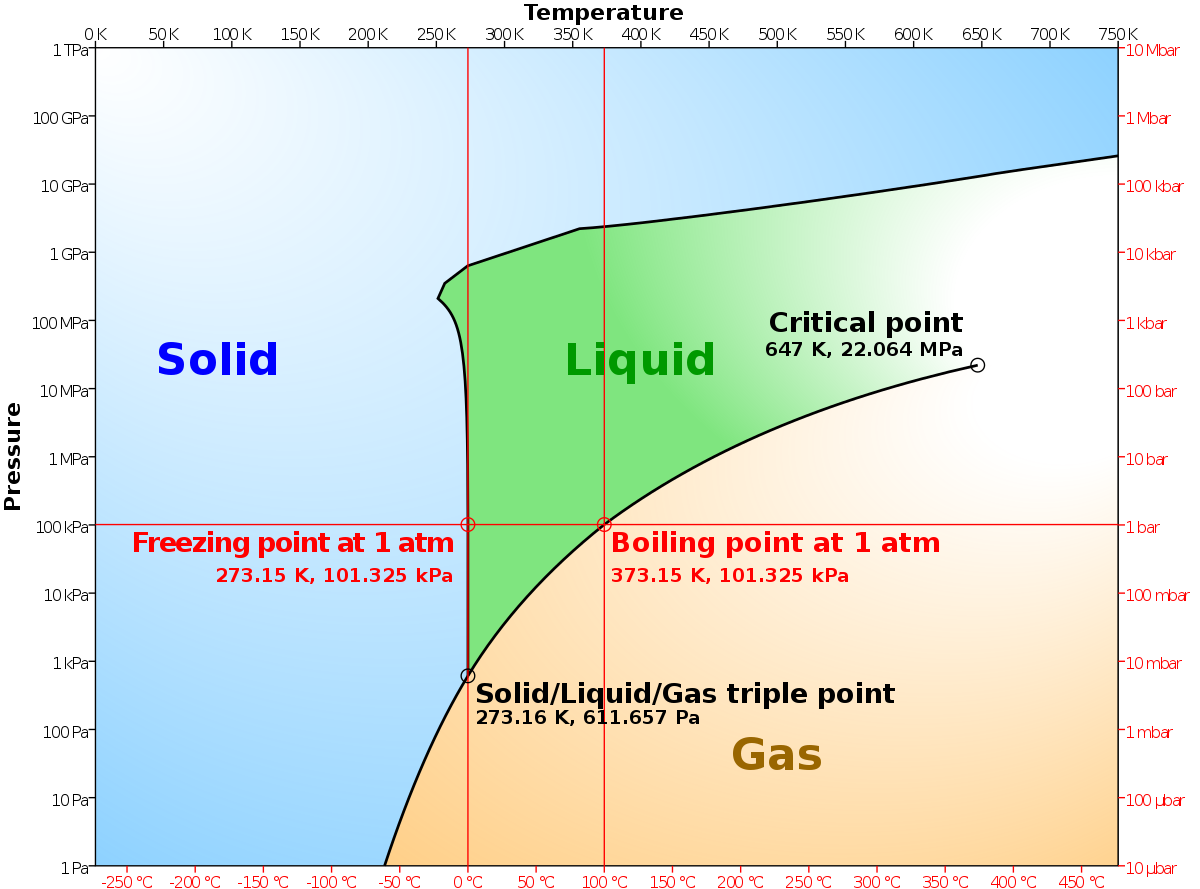
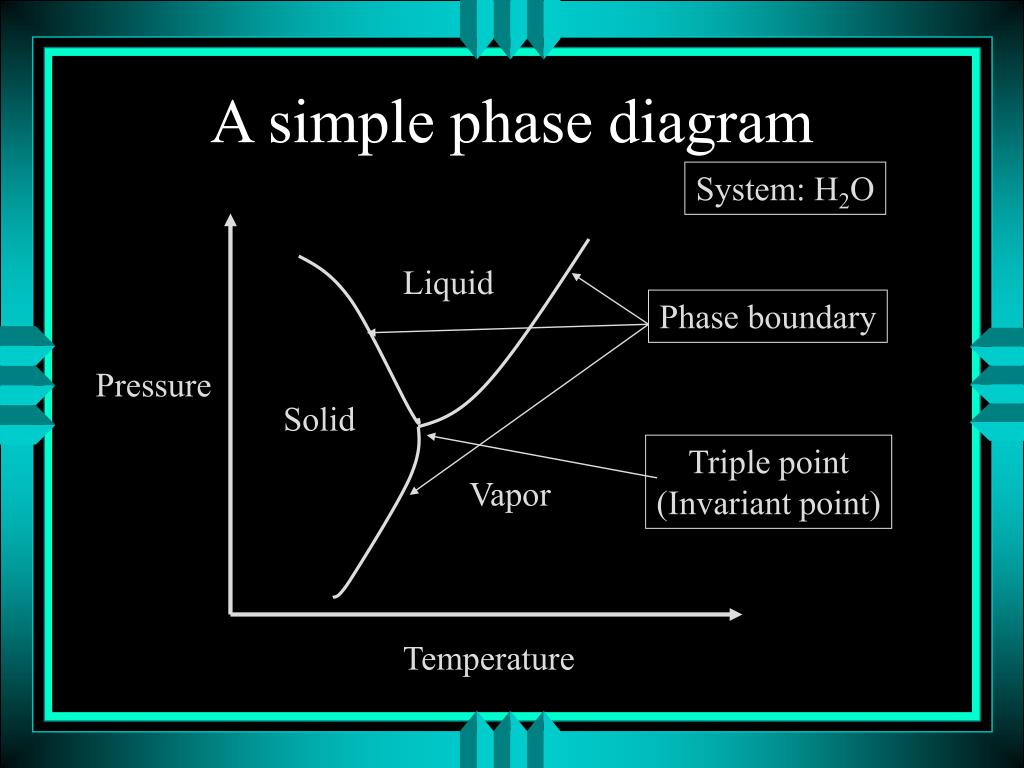
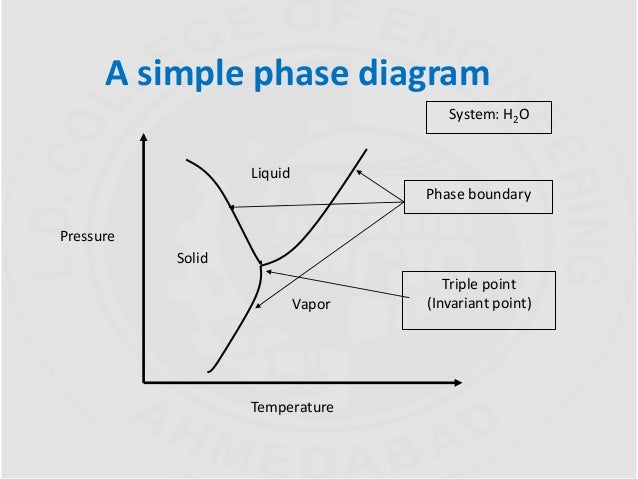
The simplest phase diagrams are pressure-temperature diagrams of a single simple substance, such as water.The axes correspond to the pressure and temperature.The phase diagram shows, in pressure-temperature space, the lines of equilibrium or phase boundaries between the three phases of solid, liquid, and gas.. The curves on the phase diagram show the points where the free energy (and other ...
Chapter 8 2 Phase diagram and "degrees of freedom" A phase diagrams is a type of graph used to show the equilibrium conditions between the thermodynamically-distinct phases; or to show what phases are present in the material system at various T, p, and compositions
An invariant point (where reactions intersect) has 0 degrees of freedom (F=0), a reaction line has 1 degree of freedom (F=1), and a divariant field between reactions has 2 degrees of freedom (F=2). For a PT diagram, what the phase rule tells us is that: Invariant points occur at a fixed P and T.
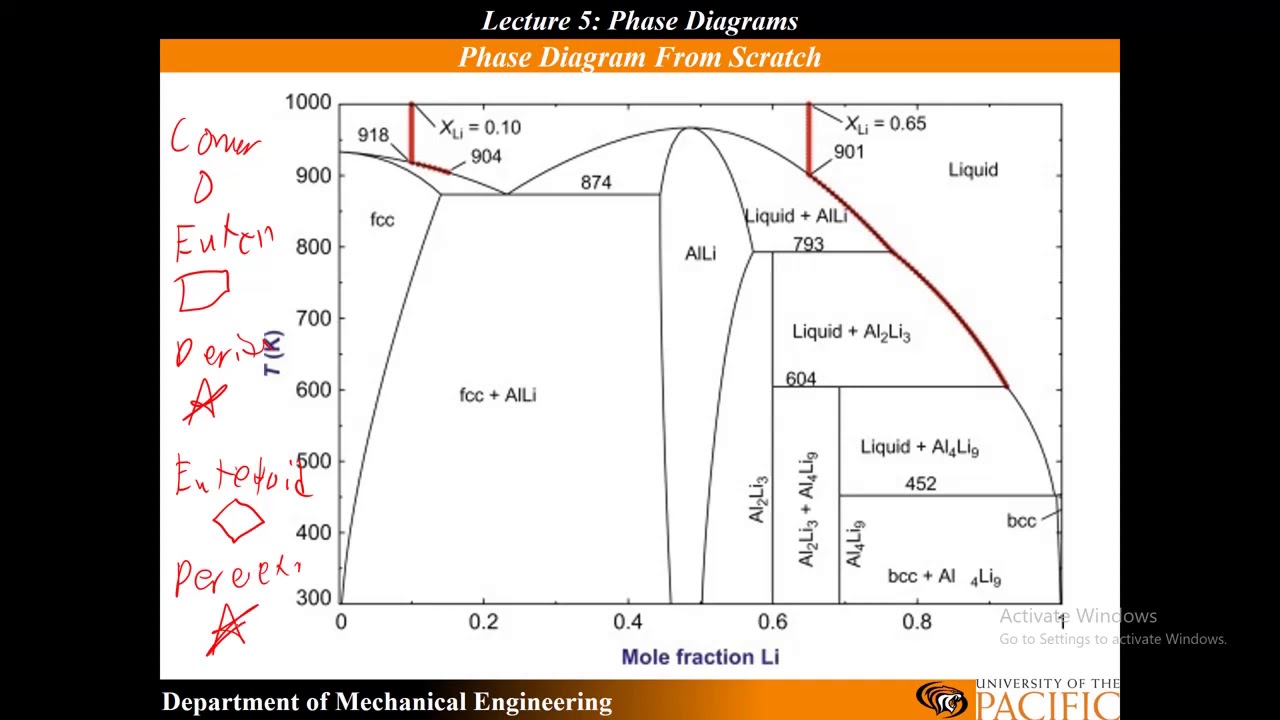
Knowing what phases must be present in the subsolidus assemblage for any composition in the system is important, because it tells us where the crystallization path will lead, i.e. to which of the invariant points in the system where 3 solid phases and a liquid will coexist prior to the disappearance of the liquid phase.
According to the phase rule, a one component system has no degrees of freedom when three phases are in equilibrium (F=0).The system is invariant. The triple point of water is at 273.16 K and 612 Pa. Phase diagram for water showing the triple point of water. This is an invariant point. This phase diagram is from Wikipedia. Binary systems
MIT3.00Fall2002°c W.CCarter 204 Classifying the Invariant Points: Drawing Phase Diagrams There are two fundamental ways that invariant points can arise:29 1. When two two-phase regions join at a temperature and become one two-phase region: Eutectic (fi +liquid)+(liquid+ fl) *) (fi +fl)Eutectoid (fi +°)+(° +fl) *) (fi +fl)Figure 30-14: Eutectic-type (EV-TYPE at MASSACHVSETTS INSTITVTE OF
crossing an invariant point. The validity of this feature, and similar features related to invariant temperatures, is easily demonstrated by constructing hypothetical free energy diagrams ... phase diagrams which, although they seemingly do not violate any of the above rules, are nevertheless very unlikely to be true phase representations. ...
There are three solid phases shown in this diagram: the polymorphs of Al 2 SiO 5 andalusite, kyanite and sillimanite. There is only one unique place on this diagram where all three phases can coexist in equilibrium--the invariant point at 3.8 Kb and 500 o C; at this point there are zero degrees of freedom.
A region of the copper-zinc phase diagram that has been enlarged to show eutectoid and peritectic invariant points , C, 74 wt% Zn) and P (598 C, 78.6 wt% Zn), respectively. Figure by MIT OCW.
The invariant points determine the topology of the phase diagram: Figure 30-16: Construct the rest of the Eutectic-type phase diagram by connecting the lines to the appropriate melting points. Figure 30-17: Construct the rest of Peritectic-type phase diagram, on the left a rule for all phase diagrams is illustrated--the ``lines'' must ...
hyperplanar coincidence of phase compositions in diagrams. The present study considers only phases of fixed compositions; this procedure is justified because, even for phases of variable composi tions, these compositions are constant at an invariant point. As conditions depart from those of the invariant point, of course, effects
MSE 2090: Introduction to Materials Science Chapter 9, Phase Diagrams 24 Binary Eutectic Systems (III) Lead - Tin phase diagram Invariant or eutectic point Eutectic isotherm Temperature, ° C Composition, wt% Sn Eutectic or invariant point- Liquid and two solid phases co-exist in equilibrium at the eutectic composition CE and the eutectic ...
Invariant Point Phase Diagram. invariant points and gibbs phase rule phase diagram a system with three independent ponents has f=5 p degrees of freedom an invariant point in a ternary system therefore contains 5 different phases in equilibrium with each other an invariant point can for example consist of a vapor phase a liquid phase and three solid phases in equilibrium with each other ...
Invariant reactions Observed triple point in unary phase diagram for water? How about eutectic point in binary phase diagram? These points are specific in the sense that they occur only at that particular conditions of concentration, temperature, pressure etc. Try changing any of the variable, it does not exist i.e. phases




















0 Response to "43 invariant point phase diagram"
Post a Comment