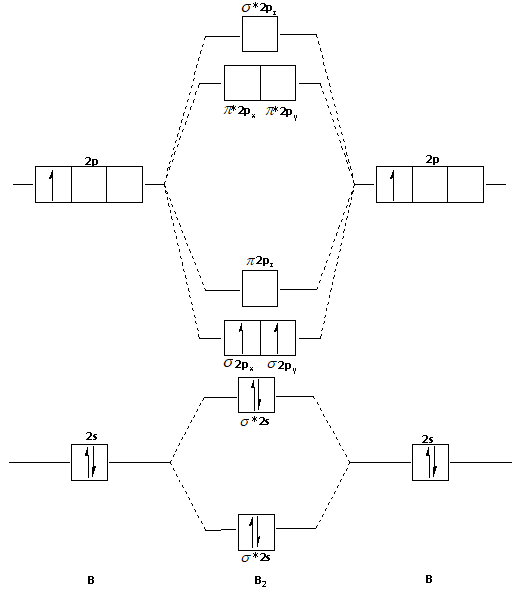
42 molecular orbital diagram of b2
B2 Molecular orbital Diagram. molecular orbital theory b2 this video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals paramagnetism and the mo diagrams for b2 molecular orbital diagram s of diatomic molecules chem in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons ...
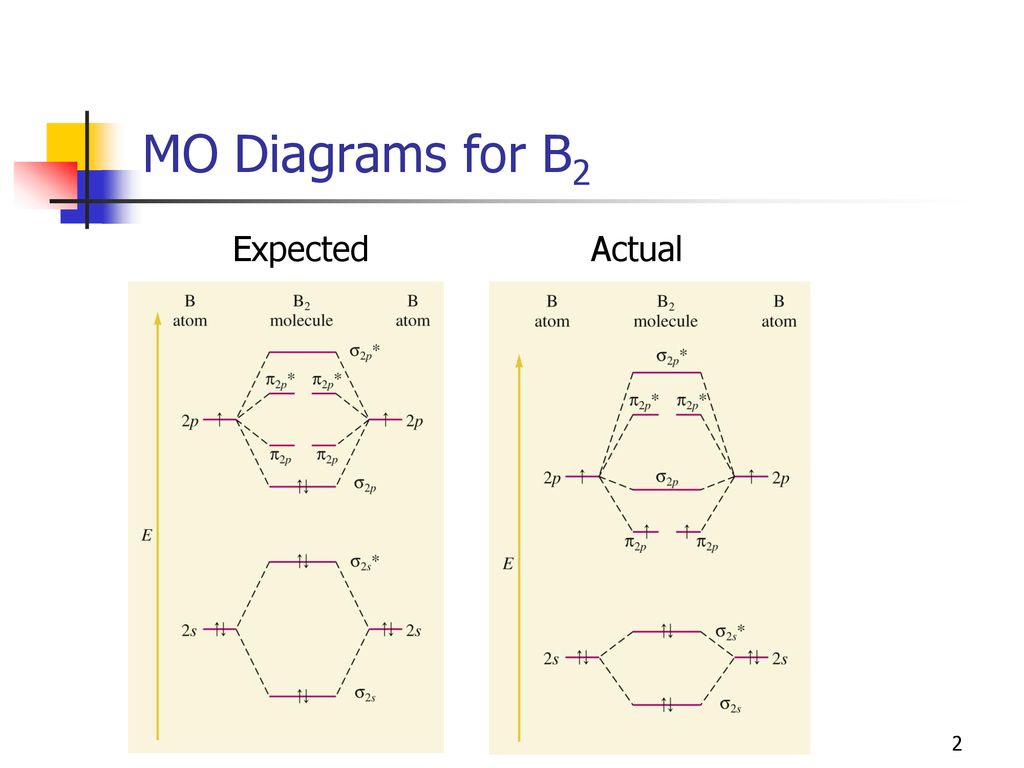
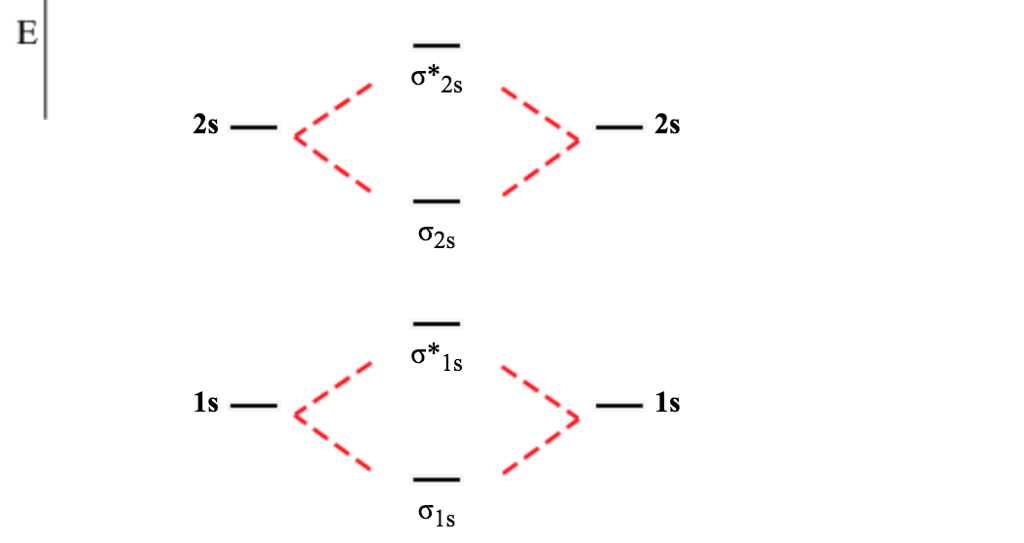
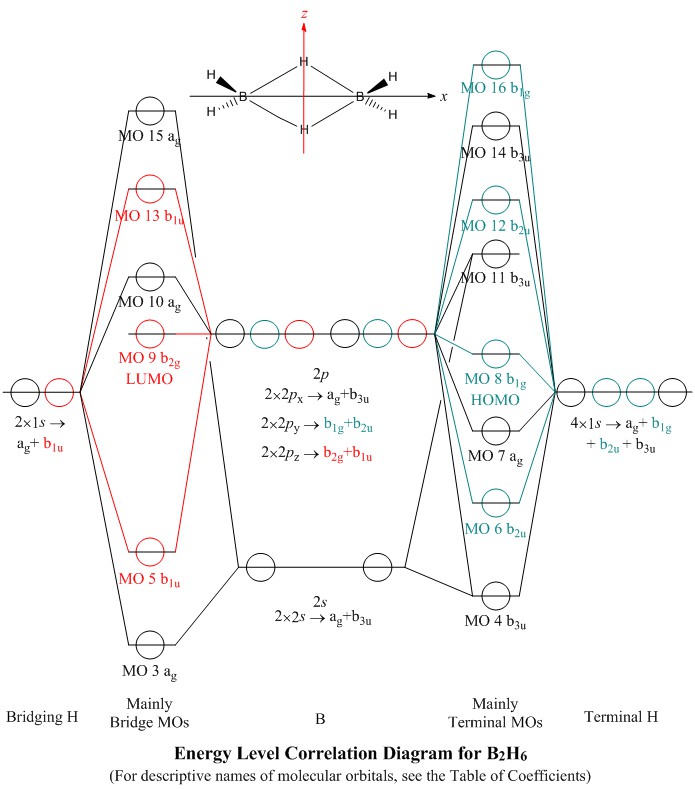
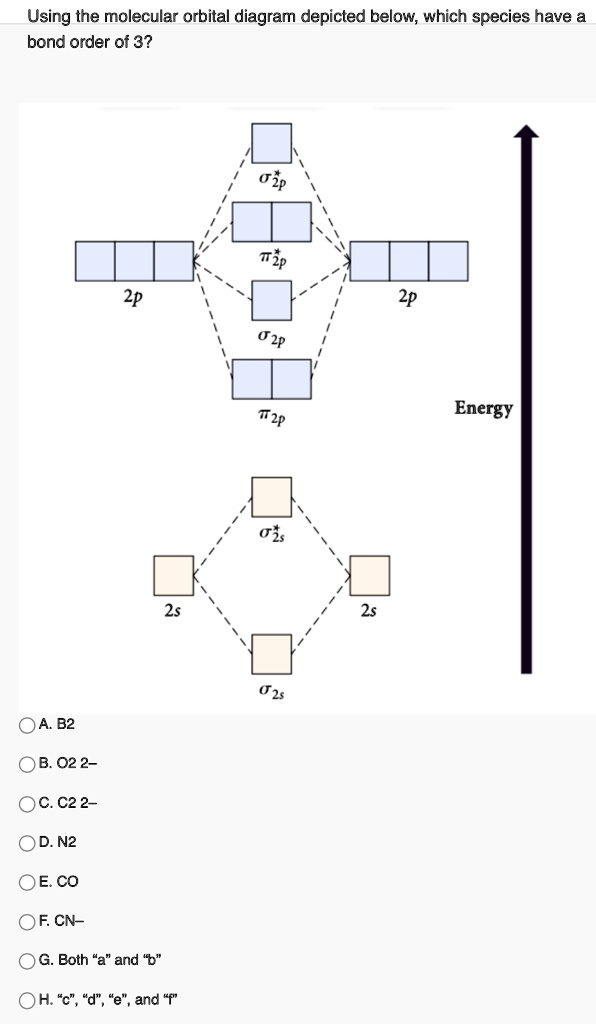
November 27, 2017 - Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons.
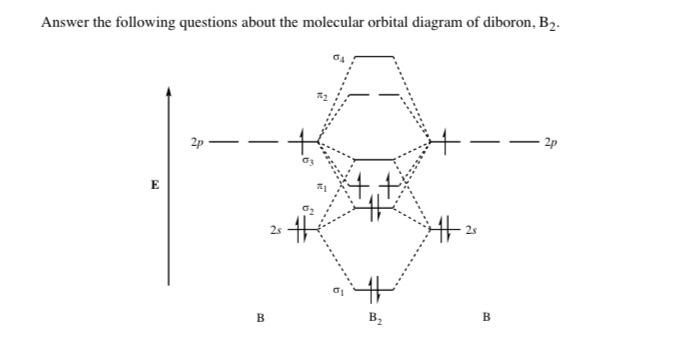
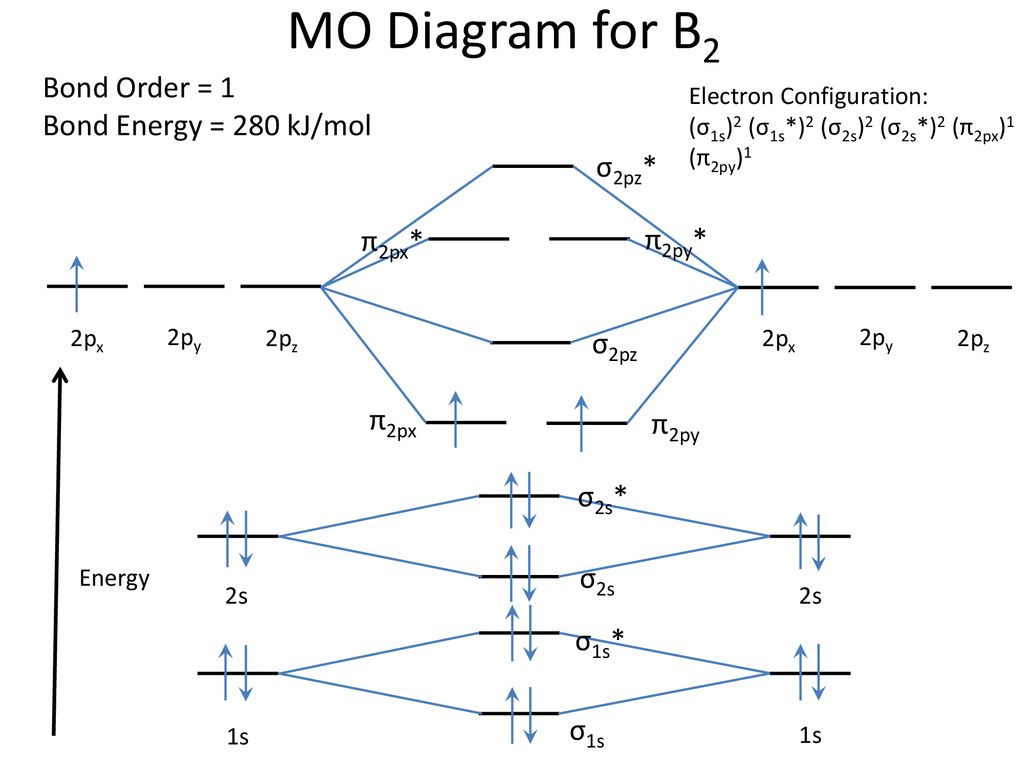
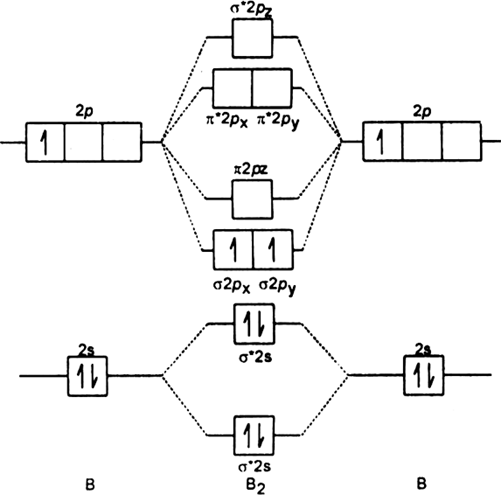
Thus, B22+ ion has 4 valence electrons. In the formation of B2 2 valence electrons will be added to the molecular orbitals. Thus, Bion has 8 valence electrons Fill these electrons in the molecular orbitals that are shown in the following MO diagram by following Hunds's rule.
Molecular orbital diagram of b2
the vocabulary associated with the various parts of a reed (vamp, stock, rail, heart, etc.), those words are illustrated in the "Parts of the Saxophone Reed" diagram.Using this diagram also may be helpful if the vocabulary you normally have used is di"erent from mine. In many sections of the guide, such as "Adjusting and Customizing Jiayouy 25 Pieces Leather Pads Alto Sax Pads Replacement Set ...
Download the PDF Question Papers Free for off line practice and view the Solutions online. Currently only available for. Class 10 Class 12 ... Draw the molecular orbital diagram for: (i) Be2 (ii) B2 and predict bond order and magnetic properties.
Q. Place the species B2+, B2, and B2- in order of increasing bond length and increasing bond energy. Solved • Nov 27, 2018. MO Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules. Q. The highest occupied molecular orbital of a molecule is abbreviated as the HOMO. The lowest unoccupied molecular orbital in a molecule is called th...
Molecular orbital diagram of b2.
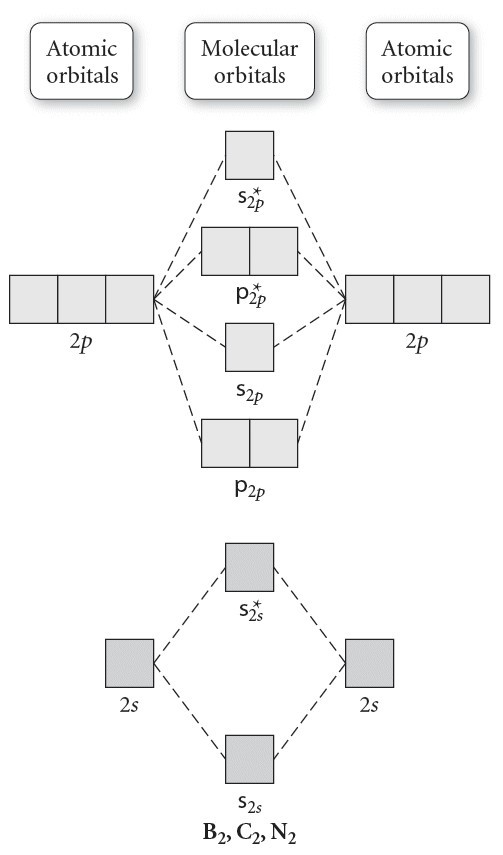
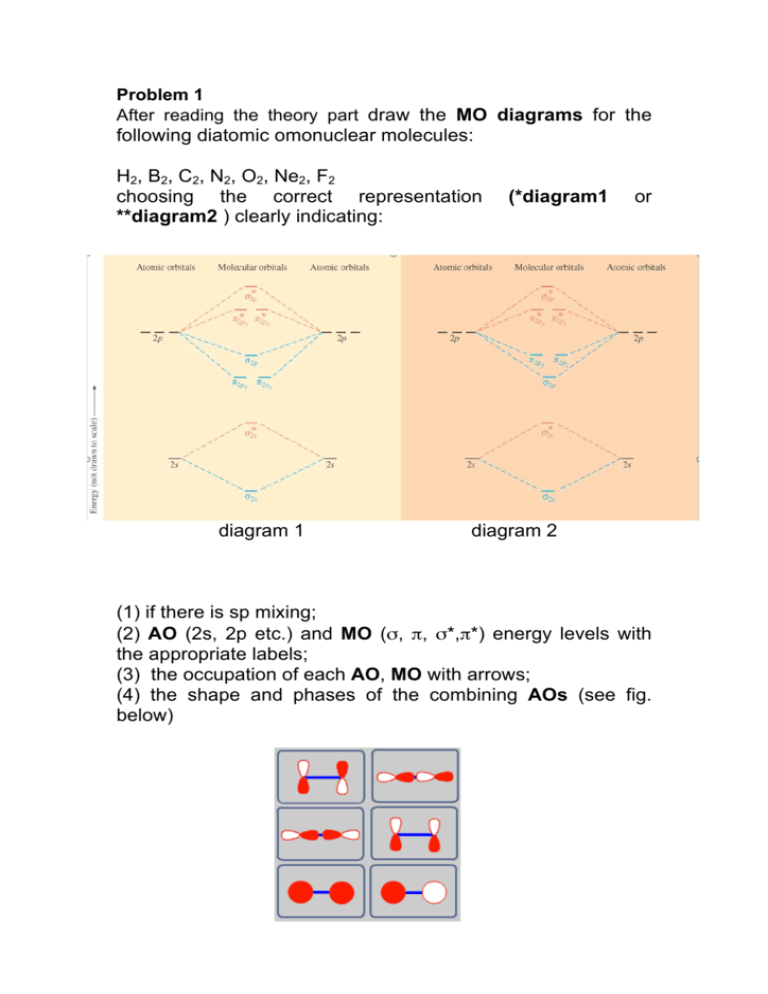
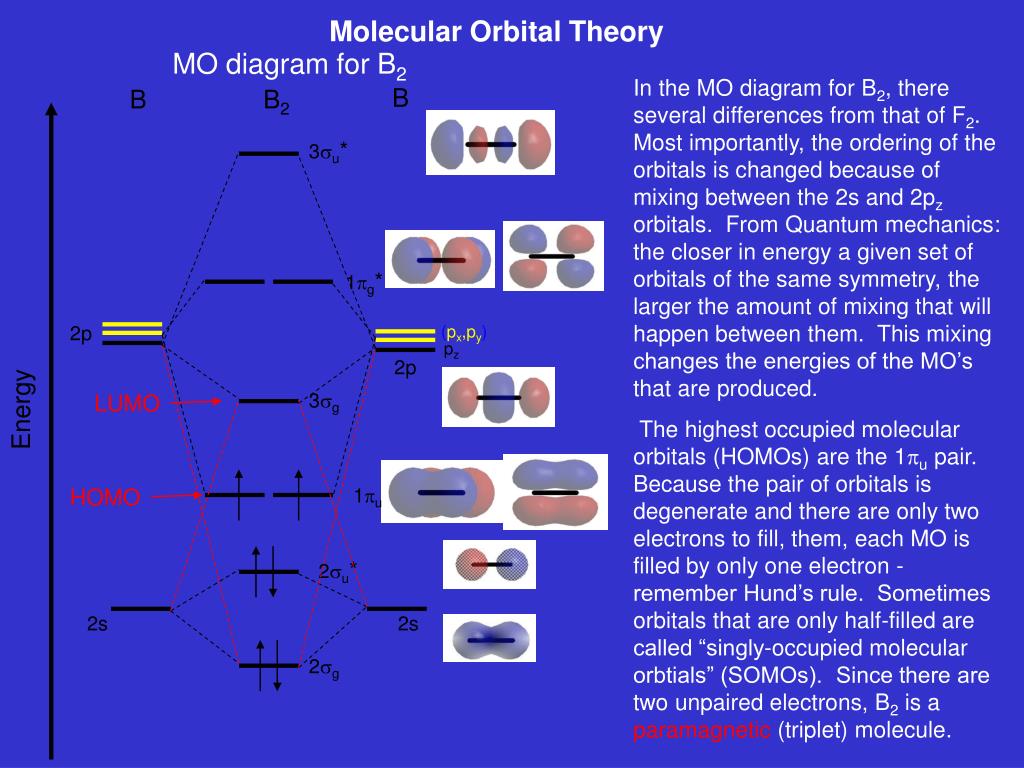
At the moment I'm learning about molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear molecules, namely: B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. I understand that the energy of the 2p sigma bond is at a higher level for B2, C2, and N2, leading to the 2p sigma bond and the 2p pi bond switching places in the MO diagram (with 2p pi bond appearing under 2p sigma bond) for B, C, and N but not for O, F, or Ne. My lectures state that this is due to s and p mixing and my textbook states that it is due to electron repulsion ...
- - Orbital Diagram for Oxygen. The bonds of oxygen molecules are broken by sunlight. Trova immagini stock HD a tema Oxygen Molecular Orbital Diagram Energy Level e milioni di altre foto, illustrazioni e contenuti vettoriali stock royalty free nella vasta raccolta di Shutterstock.
I have a homework problem asking me to construct the molecular orbital diagram for methylene chloride, and I am not too sure what to do next. I have determined that all of the orbitals transform as follow: C 2S=A1 C 2Pz=A1 C 2Py=B2 C 2Px=B1 2H 1S=A1+B2 2Cl 3S=A1+B1 2Cl 3Pz=A1+B1 2Cl 3Py=A2+B2 2Cl 3Px=A1+B1 My thoughts were to construct the MO for the CH2 side, then add the two chlorines from there. Let me know if you have any pointers. thank you
The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons. ... Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, ...
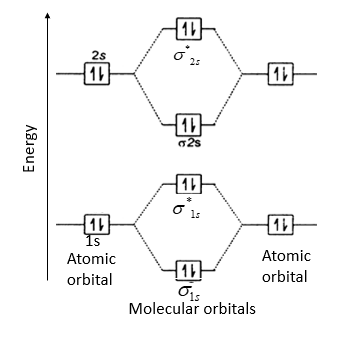
A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the H 2 molecule are in the σ 1s bonding orbital; the electron configuration is ( σ 1 s) 2. We represent this configuration by a molecular orbital energy diagram (Figure 8.4.
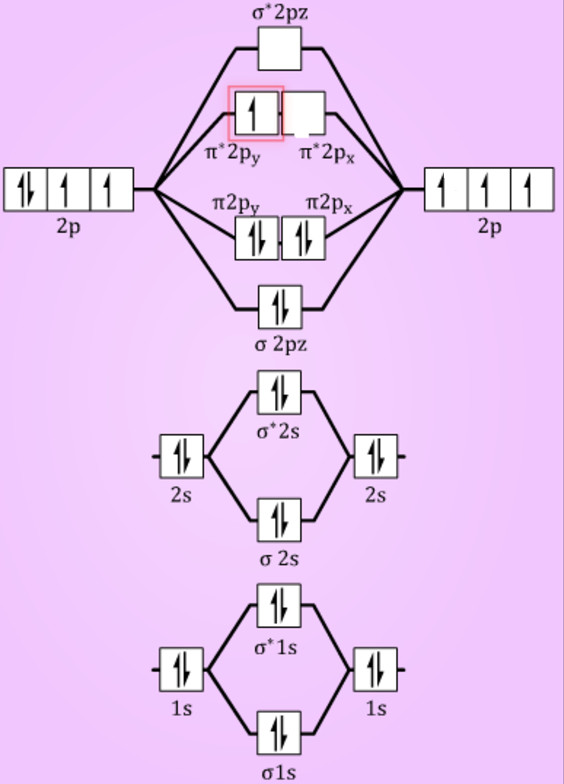
January 18, 2017 - "BO" = 1/2 Boron atom is atomic number 5 in the periodic table, so it has five electrons. Thus, B_2 carries ten total electrons. The atomic orbitals each boron contributes consists of the 1s, 2s, and 2p. The ns orbitals combine to give a portion of the molecular orbital (MO) diagram like this: ...
Answer to Molecular Orbital theory predicts that the B2 2- ion would have a bond order of ________. If one of the highest valence ...
August 15, 2020 - This gives you the total number of electrons you will have to distribute among the molecular orbitals you form. For example consider B2 (each atom has an electron configuration of [He]2s22p), which has a total of 6 valence electrons. Draw a cartoon energy level diagram with lines for the valence ...
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ✍️ Q11 Draw mot 4 calculate diagram for B2 molecule its bond order:
This section contains the course materials for Unit II, including lecture videos, readings, lecture notes, and practice problems.
Molecular orbitals of O 2. 1. Electronic configuration of O atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 . 2. Electronic configuration of O, molecule is. σ1s 2 σ*1s 2 σ2s 2 σ*2s 2 σ2p x 2 π2p y 2 π2p z 2 π*2p y 1 π*2p z 1. 3. Bond order = \(\frac{N_b-N_a}{2}\) = \(\frac{10-6}{2}\) = 2. 4. Molecule has two unpaired electrons, hence it is paramagnetic ...
Both hydrogen and helium only have 1s atomic orbitals so they produce very simple correlation diagrams. However, we have already developed the techniques necessary to draw a correlation diagram for a more complex homonuclear diatomic like diboron, B2. Before we can draw a correlation diagram for B2, we must first find the in-phase and out-of...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ...Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 - and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding ...
Use MO diagrams to place B2+,B2, and B2- in order of(a) decr... ... We have solutions for your book! ... JavaScript is required to view textbook solutions. ... Molecular orbitals: Molecular orbitals are formed by linear combination of atomic orbitals. Atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals ...
November 11, 2016 - As discussed in class the MO diagram for B2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond.
So the bond order of B2 is the same as 1, which you will get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). Nevertheless, once you draw the Lewis construction of B2, you get a triple bond.
The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n (2px) 2 n (2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons. C2 molecular orbital diagram.
C2 exists whereas Be2 does not exist. It can be explained with the help of molecular orbital diagram. Since, its bond order is 1 so, C2 exists. Since, the bond order of Be2 is zero, so it does not exist as a molecule. Does B2 exist?
Now, from MO theory, let us calculate the bond order in the F2 molecule using the following formula. Bond order (BO) = 0.5 * (no. of electrons in bonding orbitals - no. of electrons in antibonding orbitals) For fluorine molecule, BO = 0.5 (8 - 6) = 1. The case of F2 is a simple one because of the symmetry and diatomicity of the molecule.
15 F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. We assume that the electrons would fill the molecular orbitals of molecules like electrons fill atomic we will use this diagram to describe o2, f2, ne2, co, and no. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2p_ (sigma), so that is where the extra electron will be added.
So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond.
The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n (2px) 2 n (2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons. Molecular orbital diagram for c2 2-. The bond order of B2, C2, and N2 are 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
Molecular orbital diagram for b2. B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is for med as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs.
Hint: We know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to determine the bonding in a diatomic molecule. The molecular orbital diagrams are used to predict the magnetic properties of a molecule. Molecular orbital diagrams help in determining the bond order of the molecule.
On the other hand, the 2p orbitals, say 2p x , can also overlap frontally to originate a σ bond and two molecular orbitals σ 2px and σ 2px *. As in the cases of σ 1s and σ 1s *, the σ 2px orbital shows a higher electron density between the two nuclei; which is the opposite in σ 2px *, where the electrons are oriented to the outer sides.
Question: Use Molecular Orbital Theory To Determine Whether He2 Or He2+ Is More Stable. These properties can be explained by the molecular orbital diagram of BN". The bond order of two suggests that the oxygen molecule is stable. Correct option (a) O-2. Diamagnetic Metals + properties give you a broad overview of these metals from multiple angels.
Qualitative molecular orbital diagram showing the most important electronic transitions involved in the absorption spectra of fac-[Re(CO) 3 (deeb)B2] +. Finally, the unoccupied molecular orbitals immediately around the LUMO are centered in both deeb and B2 , suggesting that the ligands are directly involved in the observed emission.
Molecular Orbital Theory and MO diagram of Dibromine (Br2) The MO diagram or Molecular Orbital diagram is an extension of the 3-dimensional molecular design and gives a better understanding of the structure of an atom. Molecular Diagram also reflects upon bond length, bond shape, bond energy, and the bond angle between 2 atoms.
ChemistryQ&A LibraryBelow are the molecular orbital diagrams for B2, C2, and N2. Please use it to predict the bond order for B2, B2+ ,B2 -, C2, C2+, C2 -, N2, N2+, and N2-. Which of these molecules or ions would be paramagnetic? What are the shapes of the molecular orbitals?
1 So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond. Nov 11, 2016
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4.The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be. The Molecular Orbital Diagram For C2 ^ 2-Question: The Molecular Orbital Diagram ...
November 23, 2015 - 12/20: Andy's paper on supported nanocrystal catalysts is published in Chem. Mater.! 10/20: Our joint paper with the Klimov group using ALD to produce CMOS circuit elements from CIS quantum dot films is published in Nature Comms. 9/20: Our paper with Adam Moule's group on electron tomography ...
Find expert-verified textbook solutions to your hardest problems. Our library has millions of answers from thousands of the most-used textbooks. We’ll break it down so you can move forward with confidence.
The oxygen atomic orbitals are labeled according to their symmetry as a1 for the 2s orbital and b1 (2px), b2 (2py) and a1 (2pz) for the three 2p orbitals. The two hydrogen 1s orbitals are premixed to form a1 (σ) and b2 (σ*) MO. Mixing takes place between same-symmetry orbitals of comparable ...
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ Which molecules or ion out of the following does not contain unpaired electron? (a) Na+ (b) O2 (c) 2 O2 (d) …
1 Answer. 1. Electronic configuration of N atom is 1s2 2s2 2p3. 2. Electronic configuration of O atom is 1s2 2s2 2p4. 3. Electronic configuration of NO molecule is σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2px2 π2py2 π2pz2 π*2px1. 4. Bond order = N b−N a 2 N b − N a 2 = 10−5 2 10 − 5 2 = 2.5.
So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond . What is the electron configuration of sr2 +?
September 15, 2017 - Upon ionization one π electron ... and B2+ is formed, which has a one electron σ bond, instead of a π bond. It has been shown that a few carefully chosen VB configurations are enough to describe the bonding; with these structures, geometrical parameters as well as dissociation energies of these unusual molecular species are ...
Answer: Let's consider the valence electrons for each atom: C: 2s22p2 N: 2s2p3 Overlapping of s orbital will not contribute to the formation of bonds since they are full. Let's consider the remaining p electrons: 2 + 3 + 1 = 6. 1 electron is added for the negative charge -. Overlapping of p ...
September 15, 2016 - Board index Chem 14A Molecular Shape and Structure *Molecular Orbital Theory (Bond Order, Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism) ... Hello, If there are an odd amount of electrons, (ex. B2+), how would we draw the atomic orbitals for this? There are an uneven amount of electrons, so which electrons would ...
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron.
Figure 4.9.3 Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Part (a) in Figure 4.9.3 shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
What is the molecular orbital of B2? B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3.





















0 Response to "42 molecular orbital diagram of b2"
Post a Comment