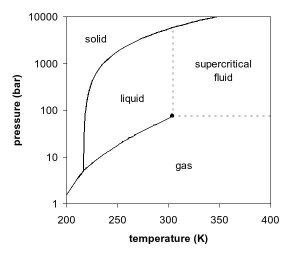
42 carbon monoxide phase diagram
Comparatively little is known about the phase diagram of carbon monoxide, especially at the higher pressures. Some of the Graph available attached here, CO Phase D
Carbon monoxide is formed from the combination of a carbon atom with an oxygen atom. Not only flammable, it is also very hazardous since it is very toxic and odorless. It is produced, among other ways, from incomplete combustion due to lack of oxygen. It can therefore cause domestic accidents due to poorly maintained heating systems.
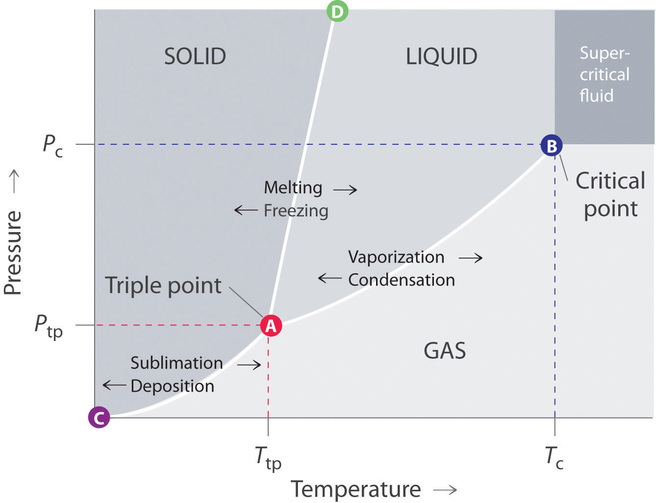
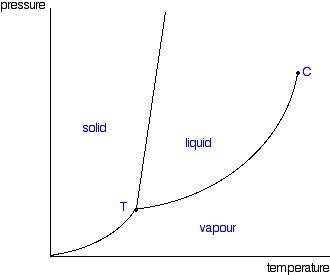
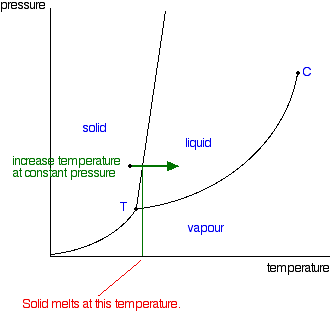
Here is the phase diagram from CO2 and water (Sorry, can't see to find a CO one) The vertical axis is pressure, the horizontal is pressure. You'll see if you start at the bottom left and follow the red and blue lines, both water and CO2 have a single interface line between solid and gas and then fork eventually to have a liquid state in between.
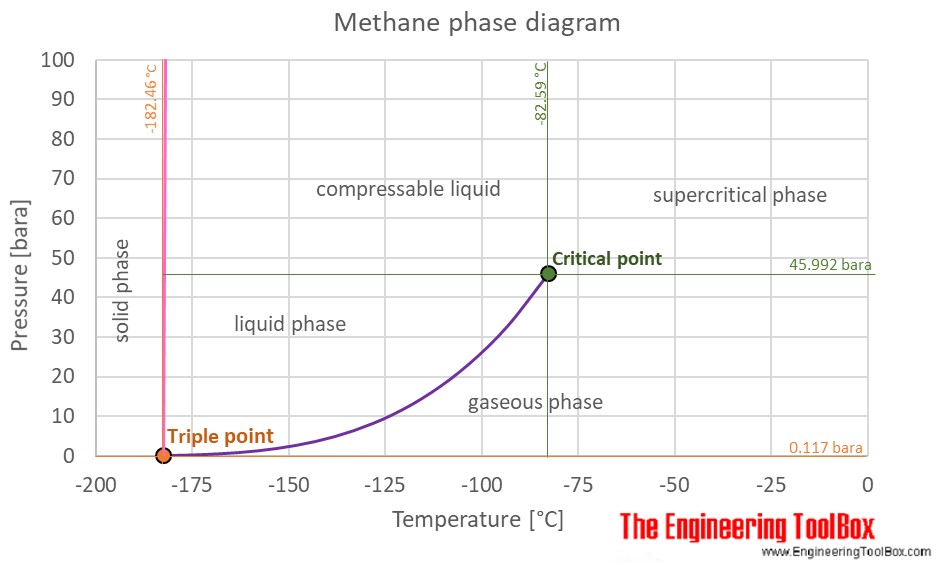
Carbon monoxide phase diagram
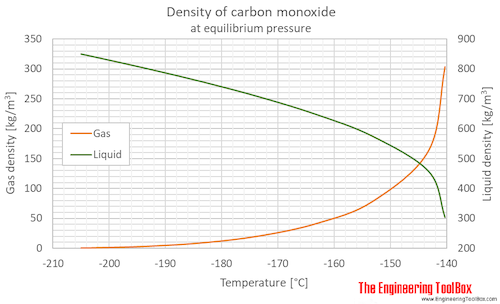
Carbon monoxide is a highly poisonous, odorless, colorless, and tasteless gas. It is very flammable in air over a wide range of concentrations (George 2001) and burns in air with a bright blue flame (O'Neil et al. 2006). It becomes a liquid at 81.62 K (-191.53 °C) and is insoluble in water above 70 °C (George 2001).
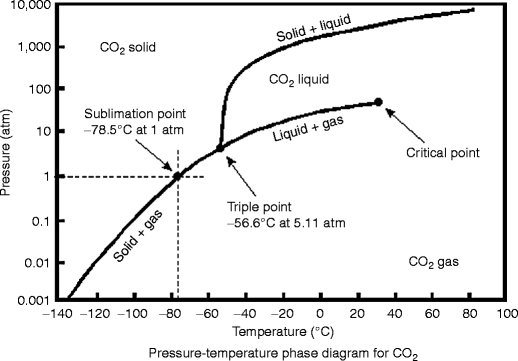
The Phase Diagram of Carbon Dioxide In contrast to the phase diagram of water, the phase diagram of CO 2 (Figure 12.4. 3) has a more typical melting curve, sloping up and to the right. The triple point is −56.6°C and 5.11 atm, which means that liquid CO 2 cannot exist at pressures lower than 5.11 atm.
phase diagrams. for carbon dioxide and water are shown in figure 1. A phase diagram shows the temperatures and pressures at which the various phases (i.e., solid, liquid and vapor) of a substance can exist. Both phase diagrams for water and carbon dioxide have the same general . Y-shape, just shifted relative to one another.
Carbon monoxide phase diagram.
Meanwhile, carbon monoxide and nitrogen are very similar in many characteristics of physics due to the crystal structural similarities, which makes structural information and phase diagram of N 2 a good reference for the investigation of CO crystal.
Water, hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon monoxide, for example, are all pure substance. A pure substance can also be a mixture of various chemical elements or ... The projection of the p-v-T surface onto the p-T plane is known as the phase diagram as shown in Figure 3.1 (b). The two-phase regions of the p-v-T surface reduce to lines in the
3. Determine the ratio of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide that will be able to reduce the oxide to metal at a given temperature. Ease of Reduction The position of the line for a given reaction on the Ellingham diagram shows the stability of the oxide as a function of temperature. Reactions closer to the top of the diagram are the most
This chemistry video tutorial explains the concepts behind the phase diagram of CO2 / Carbon Dioxide and the phase diagram of water / H2O. This video contai...
Phase diagram: carbon monoxide . Phase diagram: argon . Phase diagram: methane . Phase diagram: krypton . Phase diagram: xenon . 103 supercritical 10 solid liquid crltlcalpomt 10-1 saturation curve sublim ation curve 20 40 60 100 t em rat u re (K) eltill curve supercritical liquid critical point solid sa turation curve
The Fe-O (iron-oxygen) phase diagram in the range of the nonstoichiometric monoxide and magnetite at the Fe-rich limit: Reduction diagrams. P. Vallet 1 & C. Carel 2 Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams volume 10, pages 209-218 (1989)Cite this article
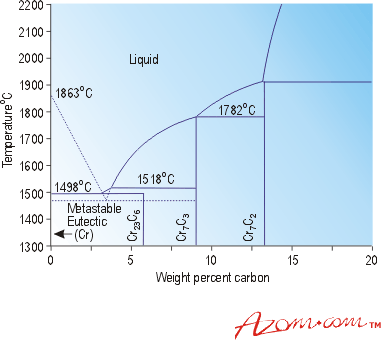
The iron-carbon equilibrium phase dia-gram is the foundation on which all steel heat treatment is based. The diagram defines the temperature-composition regions where the various phases in steel are stable, as well as the equilibrium boundaries between phase fields. Expanded iron-carbon phase diagram showing both the eutectoid and eutectic regions.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of carbon dioxide. Phase diagram included. Carbon dioxide, CO2, is a colourless and odorless gas. It is relatively nontoxic and noncombustible, but it is heavier than air and may asphyxiate by the displacement of air. When CO 2 is solved in water, the mild carbonic acid, is formed.
Carbon dioxide CO 2 44.01 0.04513 0.2438 547.5 1071 1.51 Carbon monoxide CO 28.011 0.07090 0.3831 240 507 1.49 Carbon tetrachloride CCl 4 153.82 0.01291 0.06976 1001.5 661 4.42 Chlorine Cl 2 70.906 0.02801 0.1517 751 1120 1.99 Chloroform CHCl 3 119.38 0.01664 0.08988 965.8 794 3.85 Dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12) CCl 2F 2 120.91 0.01643 0.08874 ...
, The Heat Capacity and Entropy of Carbon Monoxide. Heat of Vaporization Vapor Pressure of Solid and Liquid. Heat of Vaporization Vapor Pressure of Solid and Liquid. Free Energy to 5000 K from Spectroscopic Data , J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1932, 54, 2610.
Carbon monoxide is a one-carbon compound in which the carbon is joined only to a single oxygen.It is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, toxic gas. It has a role as a neurotoxin, a signalling molecule, a vasodilator agent, a neurotransmitter, a metabolite, a P450 inhibitor, a ligand, a biomarker, a probe, a human metabolite, a mouse metabolite, an EC 1.9.3.1 (cytochrome c oxidase) inhibitor ...
The phase diagram constructed in this study is the first P-T phase diagram for CO extending to 140 GPa and 5000 K. We found that carbon existed in 1-coordination in CO molecules as a molecular liquid at low temperatures and pressures. Between 8-13 GPa we observed a transition from a molecular liquid to a polymeric liquid. Additional work ...
The carbon cycle is associated with the availability of other compounds as well. Further Reading: Nitrogen Cycle - An Elemental Cycle. Explore more information about the carbon cycle, its definition, process, carbon cycle diagram, or any other related topics by registering at BYJU'S.
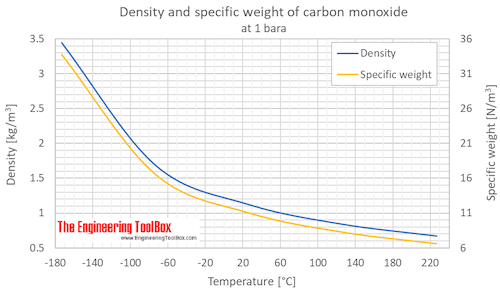
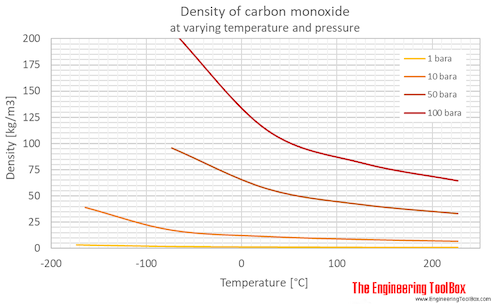
Phase diagram included. Carbon Monoxide - Specific Heat vs. Temperature - Carbon Monoxide Gas - CO - specific heat of at temperatures ranging 175 - 6000 K. Carbon Monoxide and Health Effects - Exposure to Carbon Monoxide - CO and health effects. Ethane - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Ethane - C 2 H 6.
The phase diagram Ar-CO has been determined by cooling curves and x-ray diffraction. Like the Ar-N 2 system, a solid solution of hcp structure extends over essentially the entire range of concentration at temperatures just under the solidus, but unlike the Ar-N 2 system, the hcp phase decomposes (eutectoidally) into a fcc Ar-rich phase and a primitive cubic CO-rich phase at 53°K; the ...
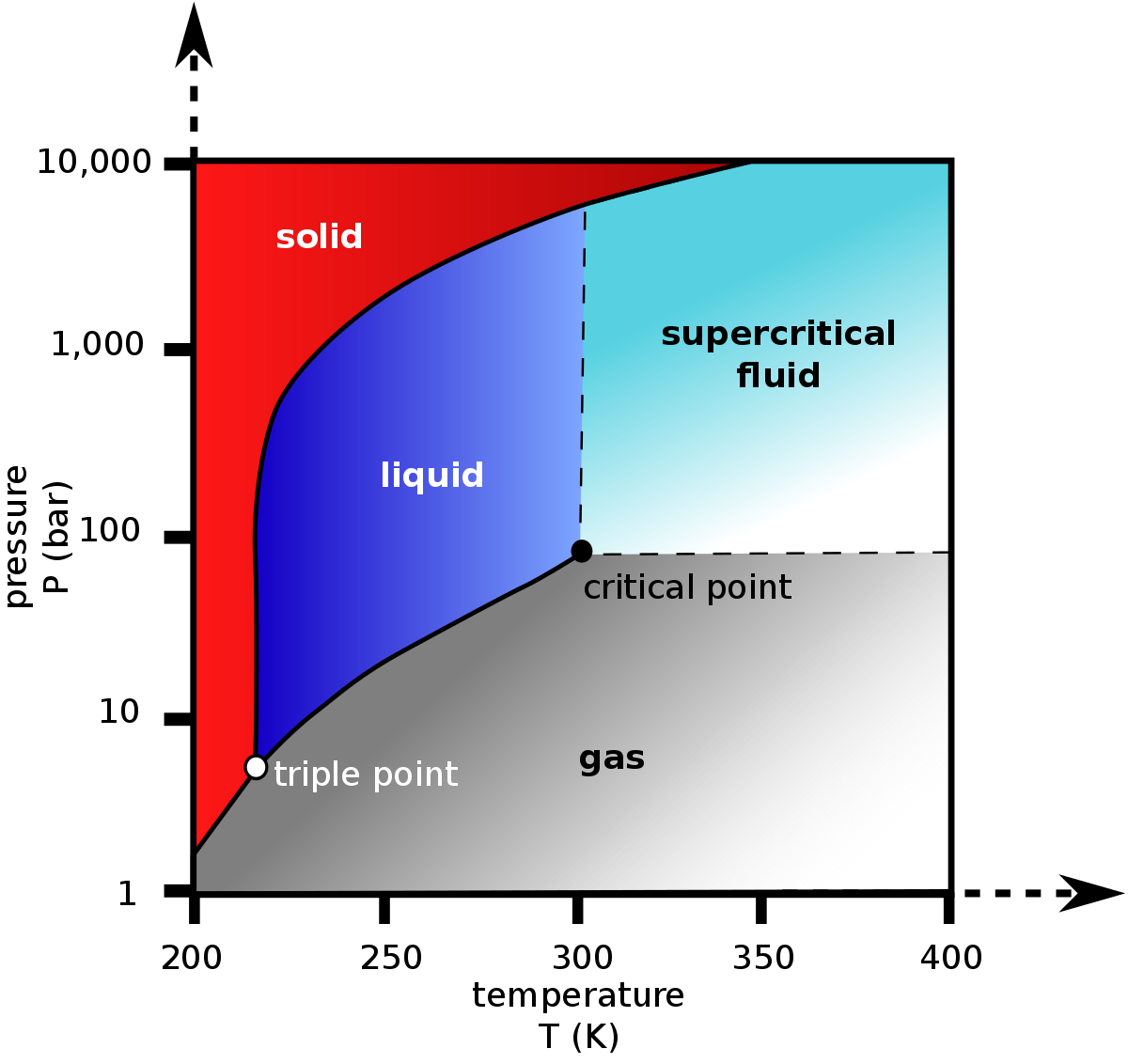
Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and two different solid phases, as shown in the phase diagram: (a) On the phase diagram, label the gas and liquid regions. (b) Graphite is the most stable phase of carbon at normal conditions. On the phase diagram, label the graphite phase.
image via www.gridgit.com The phase diagram of CO2 is similar to the phase diagram of water: sublimation curve, vaporization curve, triple point, critical temperature and pressure. Of course, the P and T values of are unique to carbon dioxide. Solid CO2 is more dense than liquid CO2. Solid CO2 sublimes when heated.
, The Heat Capacity and Entropy of Carbon Monoxide. Heat of Vaporization Vapor Pressure of Solid and Liquid. Free Energy to 5000 K from Spectroscopic Data, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1932, 54, 2610. Gill and Morrison, 1966
Answer (1 of 2): Actually a double bond does not satisfy the octet. in the triple bond picture, there is a negative charge on the carbon and a positive on the oxygen. also in the triple bond picture is an oxygen that has three bonds and a lone pair (meaning it owns 5 electrons, but has 8 in its o...
Carbon Dioxide: Temperature - Pressure Diagram S a t u r at i o n Li ne. Title: phase_diagram.xls Created Date: 11/10/1999 5:44:57 PM
Carbon monoxide MO diagram Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements. The valence molecular orbitals in both atoms are the 2 s and 2 p orbitals. The molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide (Figure 5.3.1.
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air.Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl.It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry.
EXAMPLE #2: Carbon Monoxide, CO Recall: The MO energy level diagram for O 2 is not the same as the MO energy level diagram for the C 2 gas phase fragment. This is also true for molecular orbitals. • All Molecular Orbital Nodes must be symmetrically disposed. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide CO.




























0 Response to "42 carbon monoxide phase diagram"
Post a Comment