41 rlc circuit phasor diagram
An RLC circuit (also known as a resonant circuit, tuned circuit, or LCR circuit) is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. This configuration forms a harmonic oscillator. 2. The phasor diagram for the RLC series circuit of . At any instant, the voltage across the RLC combination is the emf of the source. Since a component of a sum of vectors is the sum of the components of the individual vectors—for example, —the projection of the vector sum of phasors onto the vertical axis is the sum of the vertical ...
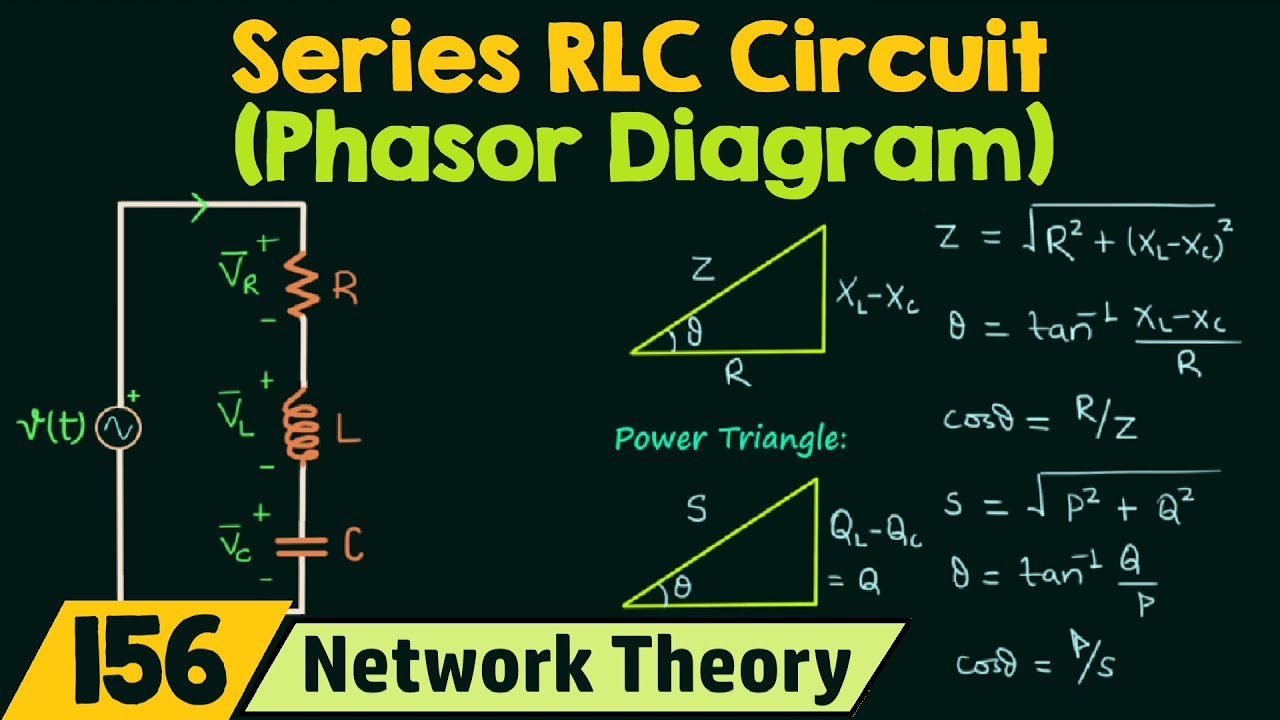
RLC Series circuit contains a resistor, capacitor, and inductor in series combination across an alternating current source. The behavior of components can be explained by phasor diagrams, impedance and voltage triangles.

Rlc circuit phasor diagram
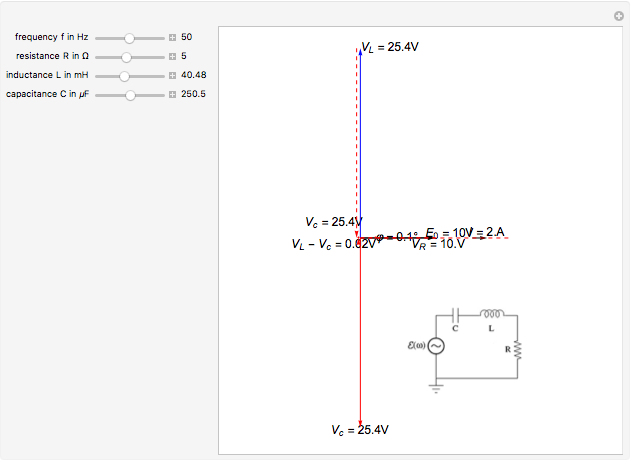
In this video, Phasor diagram representation of voltage and current for Series RC, RL and RLC circuit has been explained and the examples based on this phaso... Download Wolfram Player. This Demonstration shows a phasor diagram in an AC series RLC circuit. The circuit consists of a resistor with resistance , an inductor with inductance , and a capacitor with capacitance . The current in an RLC series circuit is determined by the differential equation. [more] , where and is the AC emf driving the circuit. Phasor diagram of parallel RLC circuit, I R is the current flowing in the resistor, R in amps. I C is the current flowing in the capacitor, C in amps. I L is the current flowing in the inductor, L in amps. I s is the supply current in amps. In the parallel RLC circuit, all the components are connected in parallel; so the voltage across each ...
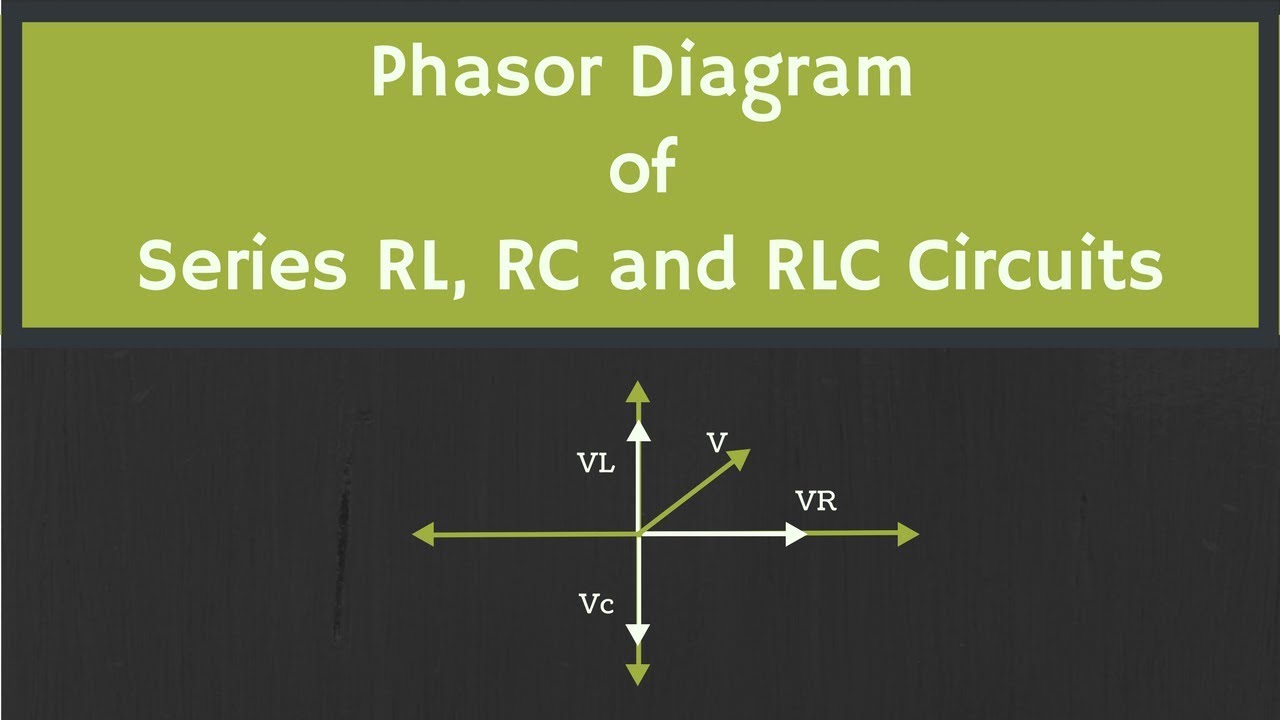
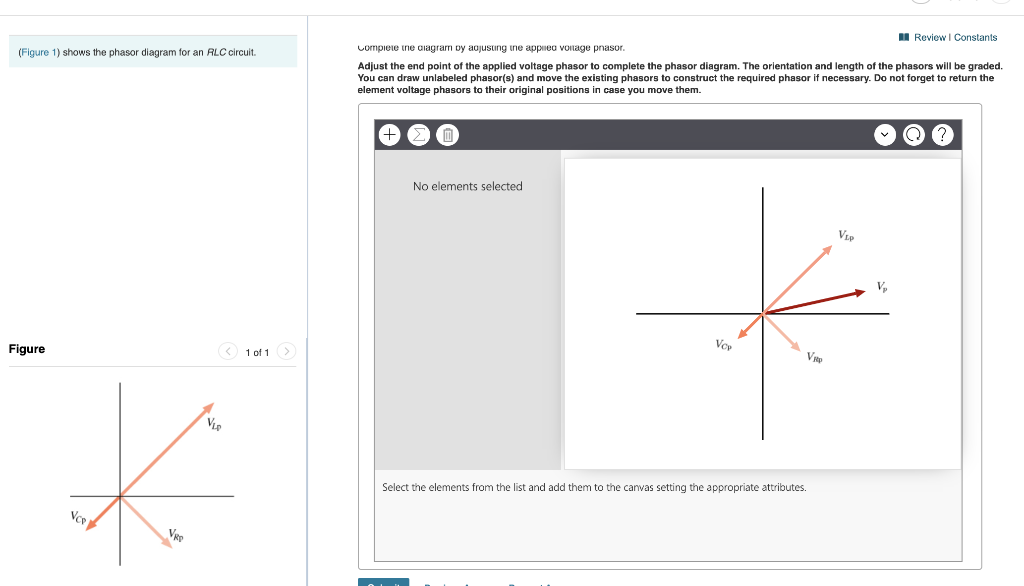
Rlc circuit phasor diagram. You can draw unlabeled phasor(s) and move the existing phasors to; Question: (Figure 1) shows the phasor diagram for an RLC circuit. Figure 1 of 1 VLE VCP VRP Complete the diagram by adjusting the applied voltage phasor. Adjust the end point of the applied voltage phasor to complete the phasor diagram. Parallel RL Circuit Phasor Diagram. The relationship between the voltage and currents in a parallel RL circuit is illustrated in the vector (phasor) diagram of Figure 2 and summarized as follows: The reference vector is labeled E and represents the voltage in the circuit, which is common to all elements. The phasor diagram for a series RLC circuit is produced by combining together the three individual phasors above and adding these voltages vectorially. A series RLC circuit contains elements of resistance, inductance, and capacitance connected in series with an AC source, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Series RLC circuit diagram. RLC Series Circuit Characteristics. The characteristics of the RLC series circuit can be summarized as follows: The current is the same through all components, but the voltage drops across the elements are out of ...
13+ Phasor Diagram Parallel Rlc Circuit. A rlc circuit as the name implies will consist of a resistor, capacitor and inductor connected in series or parallel. The rlc circuit is analogous to the wheel of a car driven over a corrugated road ( figure 15.15 ). These circuit has the ability to provide a resonant frequency signal as shown in the below. We recall from the previous tutorial about series RLC circuits that the voltage across a series combination is the phasor sum of V R, V L and V C. Then if at resonance the two reactances are equal and cancelling, the two voltages representing V L and V C must also be opposite and equal in value thereby cancelling each other out because with ... For drawing the phasor diagram of series RLC circuit, follow these steps: Step - I. In case of series RLC circuit; resistor, capacitor and inductor are connected in series; so, the current flowing in all the elements are same i.e I r = I l = I c = I. For drawing the phasor diagram, take current phasor as reference and draw it on horizontal ... it is a series RLC circuit. VR(voltage of resistor) is given by 10sin(ωt-53.13°) VL(voltage of inductor) is given by 20sin(ωt+36.87°) VC(voltage of capacitor) is given by 10sin(ωt-143.13°) How about the phasor diagram of E,VR,VL,VC?
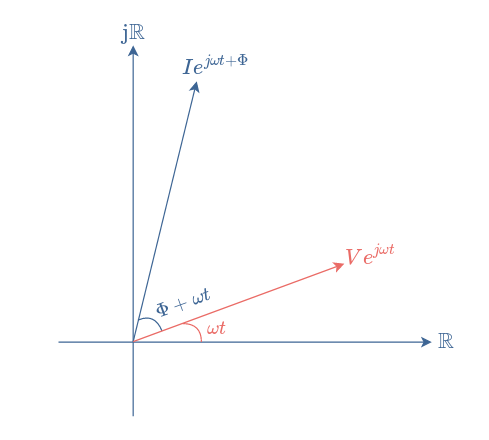
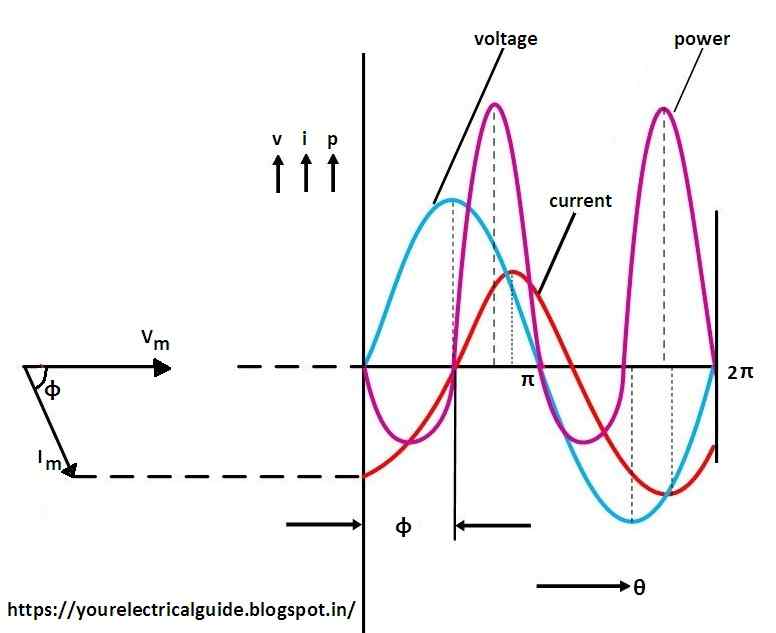
Phasor diagram, Circuit Diagram, Formula | Alternating Current (AC) - Resonance in series RLC Circuit | 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current Posted On : 24.03.2019 08:39 pm (b) Phasor diagram for the resistive circuit. The behavior of IR (t)and can also be represented with a phasor diagram, as shown in Figure 12.2.2(b). A phasor is a rotating vector having the following properties: VR (t) (i) length: the length corresponds to the amplitude. (ii) angular speed: the vector rotates counterclockwise with an angular ... Network Theory: Phasor Diagram of Series RLC Circuit Topics discussed:1) Phasor diagram of series RLC circuit.2) Voltage triangle of series RLC circuit.3) Im... Vectors, Phasors and Phasor Diagrams ONLY apply to sinusoidal AC alternating quantities. A Phasor Diagram can be used to represent two or more stationary sinusoidal quantities at any instant in time. Generally the reference phasor is drawn along the horizontal axis and at that instant in time the other phasors are drawn.
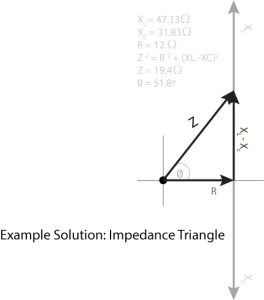
The LCR circuit analysis can be understood better in terms of phasors. For drawing the phasor diagram for rlc series circuit the current is taken as reference because in series circuit the current in each element remains the same and the. Calculate its impedance Z and its phase angle ɸ for this circuit at 125 kHz and show the results Z R X L X.
The phasor diagram is shown in Figure 12.4(c). Example 12.6. A series RLC circuit consists of a resistance R = 10Ω, inductance L = 0.2H, and capacitance C = 0.2μF. Calculate the frequency of resonance. A10 volts sinusoidal voltage at the frequency of resonance is applied across the circuit. Draw the phasor diagram showing the value of each ...
Network Theory: Phasor Diagram of Parallel RLC Circuit Topics discussed:1) Phasor diagram of Parallel RLC circuit.2) Current triangle of Parallel RLC circuit...
Chapter 12.3 - Phasor Diagram of Series RLC Circuit ... frequency f of the applied signal in relation to the frequency of resonance f0. Three different cases may ...
For drawing the phasor diagram of parallel RLC circuit, voltage is taken as reference because voltage across each element remains the same and all the other currents i.e I R, I C, I L are drawn relative to this voltage vector. We know that in case of resistor, voltage and current are in same phase; so draw current vector I R in same phase and direction to voltage.
An LCR circuit, also known as a resonant circuit, tuned circuit, or an RLC circuit, is an electrical circuit consisting of an inductor (L), capacitor (C) and resistor (R) connected in series or parallel. The LCR circuit analysis can be understood better in terms of phasors. A phasor is a rotating quantity. Current Vs Voltage Graph.
The phasor diagram for the RLC series circuit shows the main features. Note that the phase angle, the difference in phase between the voltage and the current in an AC circuit, is the phase angle associated with the impedance Z of the circuit.
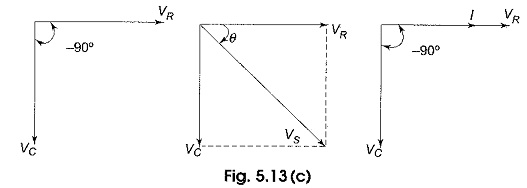
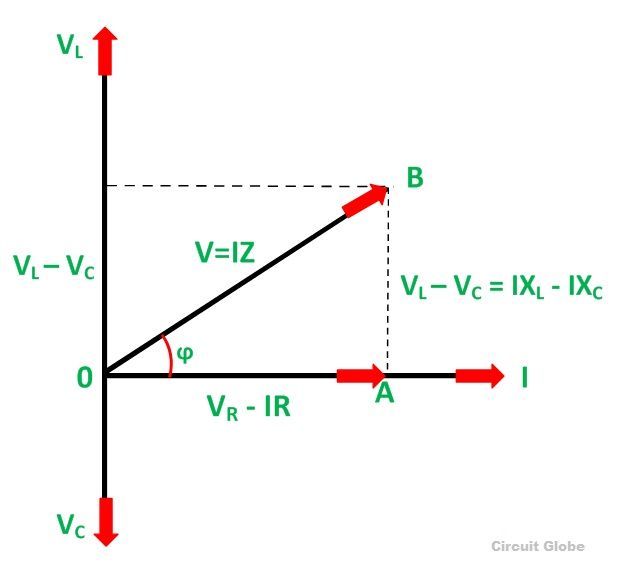
The phasor diagram for a series RLC circuit for capacitive (left), inductive (center) and pure resistive (right) impedance. The voltage vectors on the diagram produce a rectangular voltage triangle with a hypotenuse V T , vertical leg V L -V C and horizontal leg V R .
RLC Parallel circuit is the circuit in which all the components are connected in parallel across the alternating current source. In contrast to the RLC series circuit, the voltage drop across each component is common and that's why it is treated as a reference for phasor diagrams.
One way to visualize the behavior of the RLC series circuit is with the phasor diagram shown in the illustration above. The phasor diagram shown is at a ...
Phasor diagram for series RLC circuit Example: for the circuit shown in figure (a), draw the phasor circuit , impedance diagram and voltages phasor diagram. V=50∟0, so the phasor circuit is shown in figure (b). Z T =Z R +Z L +Z C o. Impedance diagram is shown in figure (c). V R =IZ R
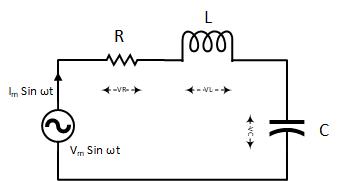
PHY2054: Chapter 21 2 Voltage and Current in RLC Circuits ÎAC emf source: "driving frequency" f ÎIf circuit contains only R + emf source, current is simple ÎIf L and/or C present, current is notin phase with emf ÎZ, φshown later sin()m iI t I mm Z ε =−=ωφ ε=εω m sin t ω=2πf sin current amplitude() m iI tI mm R R ε ε == =ω
Series RLC Circuit Impedance with Phasor Diagram. October 15, 2019. October 6, 2019. A series RLC circuit consists of resistance, inductance, and capacitance in series. Whenever we apply a sinusoidal voltage across the series RLC circuit every voltage and current in the circuit will be also sinusoidal in its steady-state condition.
Steps to draw the Phasor Diagram of the RLC Series Circuit. Take current I as the reference as shown in the figure above; The voltage across the inductor L that is V L is drawn leads the current I by a 90-degree angle.; The voltage across the capacitor c that is V c is drawn lagging the current I by a 90-degree angle because in capacitive load the current leads the voltage by an angle of 90 ...
Phasor diagram of parallel RLC circuit, I R is the current flowing in the resistor, R in amps. I C is the current flowing in the capacitor, C in amps. I L is the current flowing in the inductor, L in amps. I s is the supply current in amps. In the parallel RLC circuit, all the components are connected in parallel; so the voltage across each ...
Download Wolfram Player. This Demonstration shows a phasor diagram in an AC series RLC circuit. The circuit consists of a resistor with resistance , an inductor with inductance , and a capacitor with capacitance . The current in an RLC series circuit is determined by the differential equation. [more] , where and is the AC emf driving the circuit.
In this video, Phasor diagram representation of voltage and current for Series RC, RL and RLC circuit has been explained and the examples based on this phaso...





















0 Response to "41 rlc circuit phasor diagram"
Post a Comment