40 which ray diagram best represents the phenomenon of refraction
The incident ray is the ray that initially strikes a surface. The reflected ray, obviously, is the one that reflects off a surface. The law of reflection tells us that the angle of reflection is ... 25. In the fig. 41, PO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block. (a) Complete the path of the ray through the block. (b) In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles I and r? (c) Mark angle of emergence by the ...
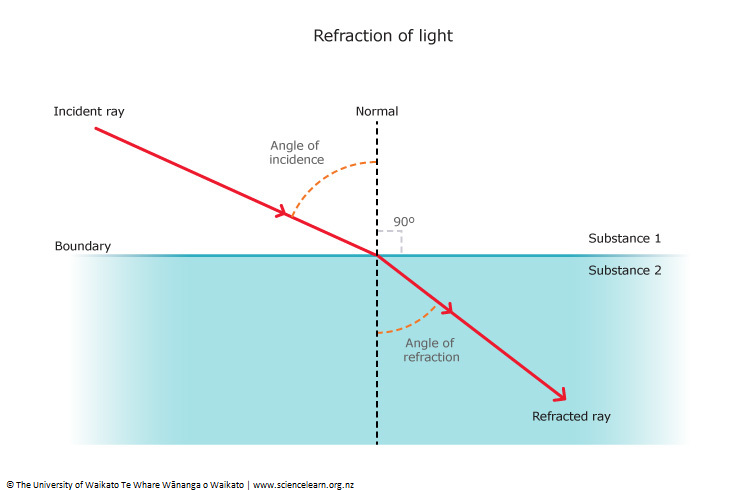
Refraction and Angles. Refraction is the change in the direction of a wave when it passes from one medium to another. A light wave traveling through air travels at a certain speed. A light wave ...

Which ray diagram best represents the phenomenon of refraction
The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason. Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P' when seen vertically from above. [Latest] Light Reflection And Refraction MCQ Assertion Cl.10 (a) Draw ray diagram of refraction of light through a prism and explain the phenomenon of dispersion of light. (b) Write the formula for lens power and define its unit. Or (a) Explain the following-(i) Atmospheric refraction and advance sunrise. (ii) Tyndall effect. (iii) Draw the ray diagram of an eye suffering from short sightedness. Old English hwilc (West Saxon, Anglian), hwælc (Northumbrian) "which," short for hwi-lic "of what form," from Proto-Germanic *hwa-lik- (source also of Old Saxon hwilik, Old Norse hvelikr, Swedish vilken, Old Frisian hwelik, Middle Dutch wilk, Dutch welk, Old High German hwelich, German welch, Gothic hvileiks "which"), from *hwi- "who" (from PIE root *kwo-, stem of relative and interrogative pronouns) + *likan "body, form" (source also of Old English lic "body;" see like (adj.)). In Middle English used as a relative pronoun where Modern English would use who, as still in the Lord's Prayer. Old English also had parallel forms hwelc and hwylc, which disappeared 15c.
Which ray diagram best represents the phenomenon of refraction. 6.3: Line Spectra and the Bohr Model. To know the relationship between atomic spectra and the electronic structure of atoms. The concept of the photon emerged from experimentation with thermal radiation, electromagnetic radiation emitted as the result of a source's temperature, which produces a continuous spectrum of energies.The ... A ray of light represents a beam. The direction of propagation of an obliquely incident (0° FIGURE 9.8 Refraction and reflection of light. Snell experimentally obtained the following laws of refraction: (i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. "act of refracting; state of being refracted," 1570s, from Late Latin refractionem (nominative refractio) "a breaking up," noun of action from past-participle stem of Latin refringere "to break up," from re- "back" (see re-) + combining form of frangere "to break" (from PIE root *bhreg- "to break"). According to Century Dictionary, "Almost exclusively restricted to physics" [1895]. Explain the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light with an example. Draw necessary ray of diagram. 12: 57: Rays parallel to the principle axis are refracted by the lens through the point: A . B. 2F ( c cdot F ) D. None: 12: 58: A biconvex lens is made of material of refractive index 1.5 each of radius of curvature of lens surface is ...
Geometrical optics approximation is a classic method for calculating the optical trapping force on particles whose sizes are larger than the wavelength of the trapping light. In this study, the effect of the lens misalignment on optical force was analyzed in the geometrical optics regime. We used geometrical optics to analyze the influence of off-axis placement and the tilt of the lens on the ... c. 1200, "that which is best," from best (adj.). From c. 1300 as "all that one can do;" 1570s as "highest possible state." From 1790 as "best clothes." At best "in the utmost degree" is from early 14c. For the best "tending to the best results" is from late 14c. To make the best of "use to best advantage" is from 1620s; to get or have the best of "the advantage over" (in a contest, etc.) is from 1640s. To be able to do something with the best of them is recorded by 1748. (c) The angle of refraction (r) of a ray of white light from air through a triangular glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is 29.0 0. Calculate the angle through which the ray is least deviated. (d) Study the ray diagram below and use it to answer the question that follow. A. 60 0 D "a skate, type of fish related to sharks and noted for its broad, flat body," early 14c., raie, from Old French raie (13c.) and directly from Latin raia. De Vaan describes this as a word of unknown origin but with apparent cognates in Germanic (Middle Dutch rogghe, Old English reohhe), perhaps a loan-word from a substrate language. The old etymology (Century Dictionary, etc.) was that the fish was so called from its resemblance to the rays of a fan and from the source of ray (n.1).
Ignore the reflected ray (the ray that remains in air). Using the protractor, measure the angle of refraction, θ 2, of the laser and record in Table 1. Repeat steps 4 and 5 of this lab for 4 more angles of incidence of your own choosing. Record the results in Table 1. Data: Note* For best results center the protractor where the beam splits on ... Draw a ray diagram to support your answer. OR (i) On entering in a medium from air, the speed of light becomes half of its value in air. Find the refractive index of that medium with respect to air? (ii) A glass slab made of a material of refractive index n1 is kept in a medium of refractive index n2. A light ray is incident on the slab. 1570s, "a fact directly observed, a thing that appears or is perceived, an occurrence," especially a regular kind of fact observed on certain kinds of occasions, from Late Latin phænomenon, from Greek phainomenon "that which appears or is seen," noun use of neuter present participle of phainesthai "to appear," passive of phainein "bring to light, cause to appear, show" (from PIE root *bha- (1) "to shine"). Meaning "extraordinary occurrence" is recorded by 1771. In philosophy, "an appearance or immediate object of experience" (1788). The plural is phenomena. 1610s, "an illustrative figure giving only the outlines or general scheme of the object;" 1640s in geometry, "a drawing for the purpose of demonstrating the properties of a figure;" from French diagramme, from Latin diagramma "a scale, a musical scale," from Greek diagramma "geometric figure, that which is marked out by lines," from diagraphein "mark out by lines, delineate," from dia "across, through" (see dia-) + graphein "write, mark, draw" (see -graphy). Related: Diagrammatic; diagrammatically. The verb, "to draw or put in the form of a diagram," is by 1822, from the noun. Related: Diagrammed; diagramming.
Answer : Laws of Refraction : 1 ) The incident ray, point of incidence, normal and refracted ray of light are coplanar. 2 ) The ratio of sine of angle of incidence and angle of refraction is constant. ( This constant term is nothing but the refractive index of the medium ) i.e, sin i / sin r = constant. Where i = angle of incidence.
Which phenomenon is depicted in the diagram given below ? (a) Diffraction of light (b) Scattering of light (c) Refraction of light (d) Reflection of light. Identify the optical element which forms a real magnified image and virtual magnified image of an object on front of it.
Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P Get the answers you need, now! aidencollazo10 aidencollazo10 05/17/2021 ... Which ray diagram demonstrates the phenomenon of refraction? X Two sound waves (speed 343 m/s) have different wavelengths. The first has a wavelength of 5.72 m, and the second a wavelength of 11 ...
7.4 The diagram below shows a ray of light in a triangular glass prism. 7.4.1 Name the phenomenon that light undergoes, as shown in the diagram. (1) For the phenomenon named in QUESTION 7.4.1 above, write down: 7.4.2 The TWO conditions necessary for the phenomenon to happen (2) 7.4.3 A medical instrument used to examine internal parts of the ...
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed: (i) between the optical center and principal focus of a convex lens. (ii)anywhere in front of a concave lens. (iii)At 2F of a convex lens. State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii). Ans.
Question.16. (a) Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by the ray of light while passing through the slab. (b) If the refractive index of glass for light going from air to glass is 3/2, find the refractive index of air for light going from glass to air.
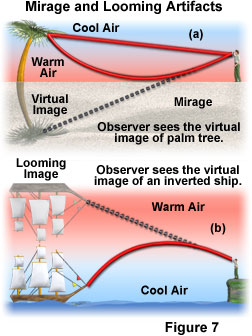
The two laws of reflection are the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal (at the point of incidence), all lie in the same plane and the angle of reflection (r) is always equal to the angle of incidence (i). Refraction of light is the phenomenon of change in the path of light in going from one medium to another. (i) Mirage is caused due to
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of real image of an object when refraction of light takes place through a convex lens. Mark as per the new Cartesian sign convention the object-distance (u), image distance (v) and the focal length (f) and also write the relation between u, v and f.
For locating the image formed by a concave mirror, minimum two rays are required. Following is the ray diagram for the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror: Q14. With the help of a ray diagram, determine the position, nature, and the size of the image formed of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. Answer:
Useless. Answer from: jessicapbailey52. SHOW ANSWER. D.) Diagram X shows refraction from a denser to a less dense medium, and diagram Y shows reflection. Explanation: As per ray diagram we can see that light ray moves from one medium to another medium. So this must be the phenomenon of refraction of light.
The best way to explain how the venn diagram works and what its formulas show is to give 2 or 3 circles venn diagram examples and problems with solutions. Source: images.twinkl.co.uk A class in uml diagram is a blueprint used to create an object or set of objects.
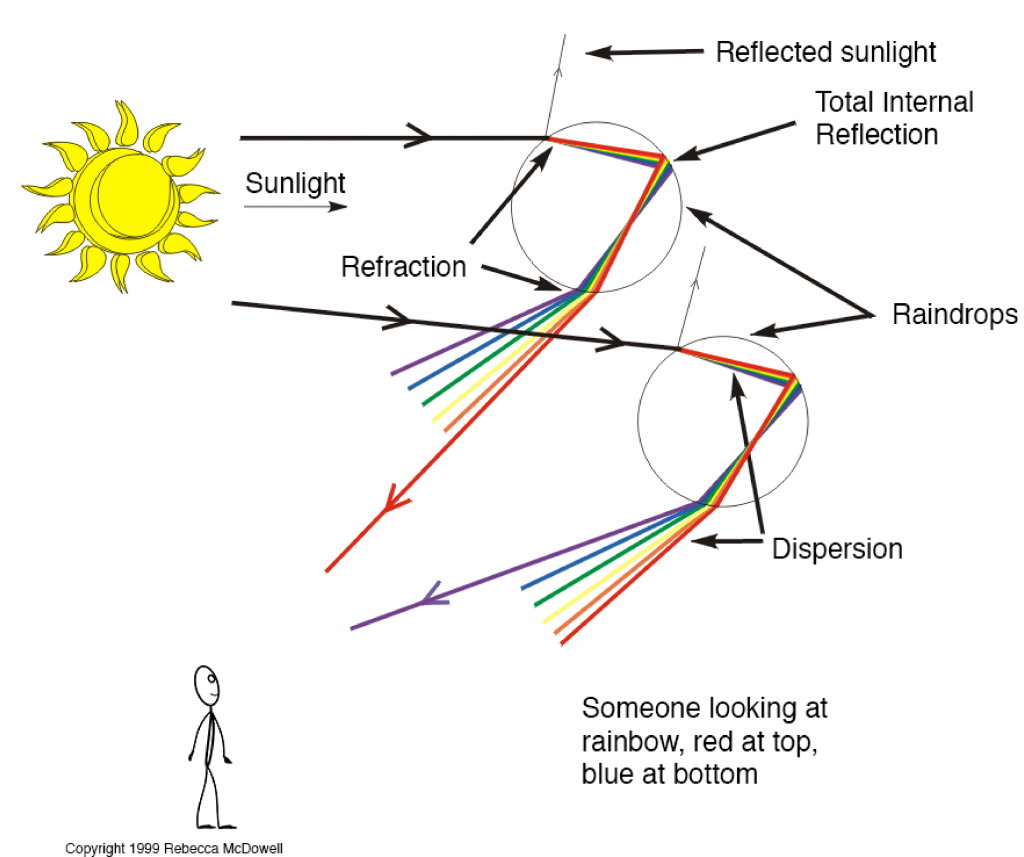
Select the correct statements w.r.t. the diagram above. (a) Dispersion occurs at point A (b) Internal refraction occurs at point B (c)Internal reflection occurs at point A (e) Dispersion occurs at point B. Answer: (a) Dispersion occurs at point A Explanation: At point A, dispersion occurs while at point B internal reflection occurs. Useful for you
A block is attached to the top of a spring that is oscillating vertically. A small coin with negligible mass is riding on top of the block (it is not …. attached to either the block or the spring). You measure that the largest possible time for the block to complete one full oscillation, without causing the coin to fall off, is 2.5 s.
"to get the better of, outdo, surpass," 1863, from best (adj.). Related: Bested; besting.
Here, Object AB is beyond 2F 1. First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it passes through focus after refraction. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2.
"beam of light, light emitted in a given direction from a luminous body," early 14c., rai, from Old French rai (nominative rais) "ray (of the sun), spoke (of a wheel); gush, spurt," from Latin radius "ray, spoke, staff, rod" (see radius). Not common before 17c. [OED]; of the sun, usually in reference to heat (beam being preferred for light). Ray is usually distinguished from beam, as indicating a smaller amount of light; in scientific use a beam is a collection of parallel rays. In ordinary language ray is the word usually employed when the reference is to the heat rather than the light of the sun .... [OED] Science fiction's ray-gun is recorded by 1931 (in Amazing Stories; electric ray gun as an imaginary weapon is from 1924; death-ray gun from 1926 as a prop in a vaudeville act), but the Martians had a Heat-Ray weapon in "War of the Worlds" (1898).
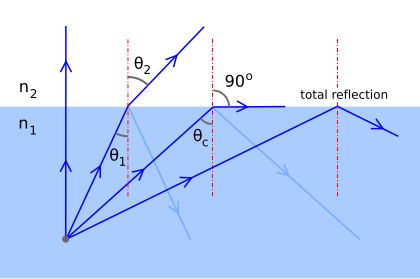
J is the reflected ray, r 4 is the angle of reflection (2) 1.8 Which of the following diagrams represents the phenomenon of total internal reflection? (2) 1.9 A light ray travels from air into water. Which ONE of the following combinations, relating to the angle of refraction and angle of incidence, is correct? (2)
The index of refraction, or refractive index, is a measure of how fast light rays travel through a given medium. Alternatively, it could be said that the refractive index is the measure of the bending of a light ray when passing from one medium to another. Mathematically, it can be represented as a ratio between two different velocities - the ...
Old English beste, reduced by assimilation of -t- from earlier Old English betst "of the highest quality or standing, first, in the best manner." This originally was the superlative of bōt "remedy, reparation" (Middle English bote "advantage, help, profit"), a word now surviving in its simple form only in the expression to boot (see boot (n.2)). Its comparative, better, and superlative, best, have been transferred to good (and in some cases well). Old English bōt is from Proto-Germanic root *bat-, with comparative *batizon and superlative *batistaz. The superlative form is the source also of Old Frisian, Old Saxon, Middle Dutch best, Old High German bezzist, German best, Old Norse beztr, Gothic batists. Also in Old English as an adverb, "in the most excellent manner." The best-laid schemes o' mice an' men Gang aft agley, An' lea'e us nought but grief an' pain, For promis'd joy! [Burns, from "To a Mouse, on Turning Her Up in Her Nest With the Plough, November, 1785"] From late Old English as "of greatest advan
1896, X-rays, translation of German X-strahlen, from X, algebraic symbol for an unknown quantity, + Strahl (plural Strahlen) "beam, ray." Coined 1895 by German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (1845-1923), who discovered them, to suggest that the exact nature of the rays was unknown. As a verb by 1899. Meaning "image made using X-rays" is from 1934, earlier in this sense was X-radiograph (1899).
It will represent the path of ray inside the glass slab, i.e. refracted ray. Measure the angle of emergence, i.e. ∠e = ∠N 1 O 1 S 1 and angle of refraction, i.e. ∠r = ∠NO 1 O 2 Repeat the experiment by taking the different angles of incidence such as 45° and 60° on the other part of paper and measure the angle of refraction and ...
Old English hwilc (West Saxon, Anglian), hwælc (Northumbrian) "which," short for hwi-lic "of what form," from Proto-Germanic *hwa-lik- (source also of Old Saxon hwilik, Old Norse hvelikr, Swedish vilken, Old Frisian hwelik, Middle Dutch wilk, Dutch welk, Old High German hwelich, German welch, Gothic hvileiks "which"), from *hwi- "who" (from PIE root *kwo-, stem of relative and interrogative pronouns) + *likan "body, form" (source also of Old English lic "body;" see like (adj.)). In Middle English used as a relative pronoun where Modern English would use who, as still in the Lord's Prayer. Old English also had parallel forms hwelc and hwylc, which disappeared 15c.
(a) Draw ray diagram of refraction of light through a prism and explain the phenomenon of dispersion of light. (b) Write the formula for lens power and define its unit. Or (a) Explain the following-(i) Atmospheric refraction and advance sunrise. (ii) Tyndall effect. (iii) Draw the ray diagram of an eye suffering from short sightedness.
The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason. Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P' when seen vertically from above. [Latest] Light Reflection And Refraction MCQ Assertion Cl.10






















0 Response to "40 which ray diagram best represents the phenomenon of refraction"
Post a Comment