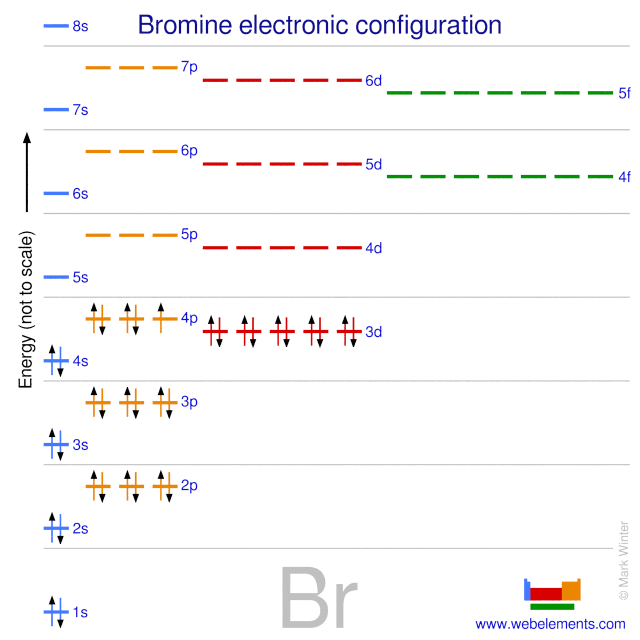
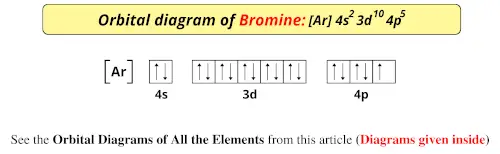
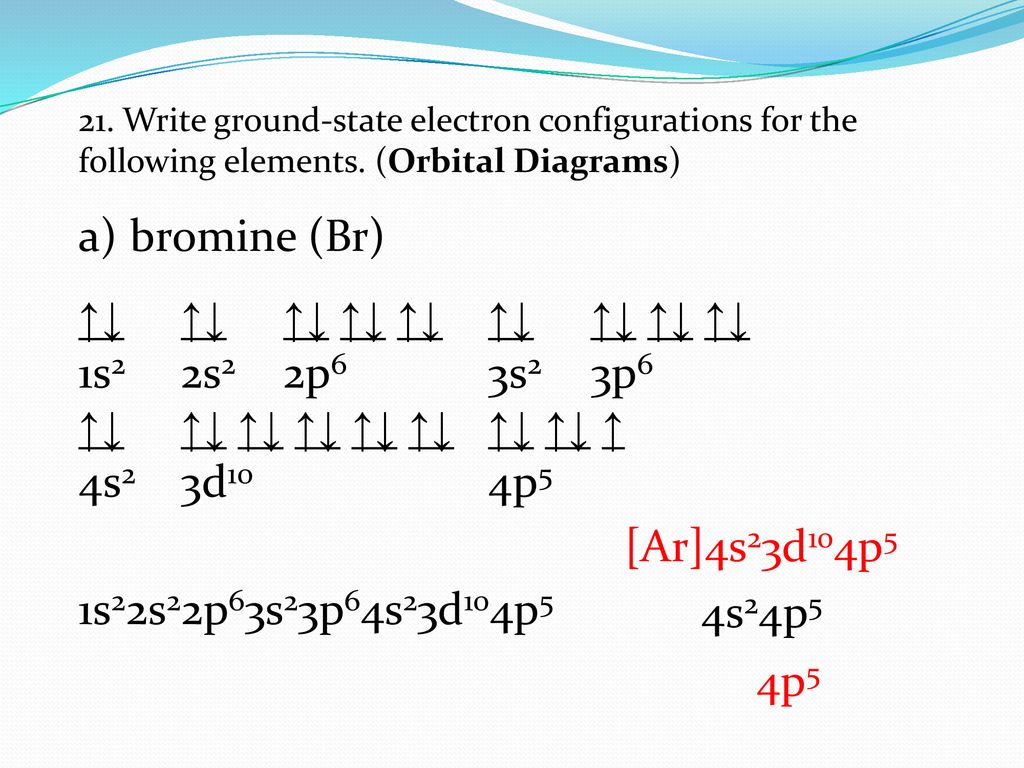
40 orbital filling diagram for bromine
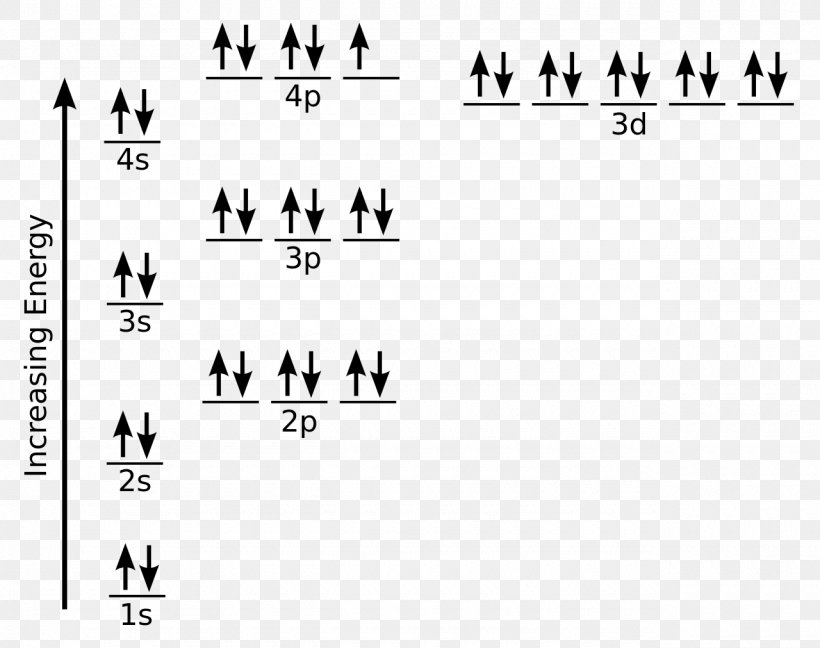
The diagram below represents the orbital representation diagram used in earlier chapters. The orbital representation diagram has a few different variations but all are used to draw electron configurations. Most show the orbitals in groups, as lines, boxes, or circles with each orbital having its own line (or circle) within each sublevel.
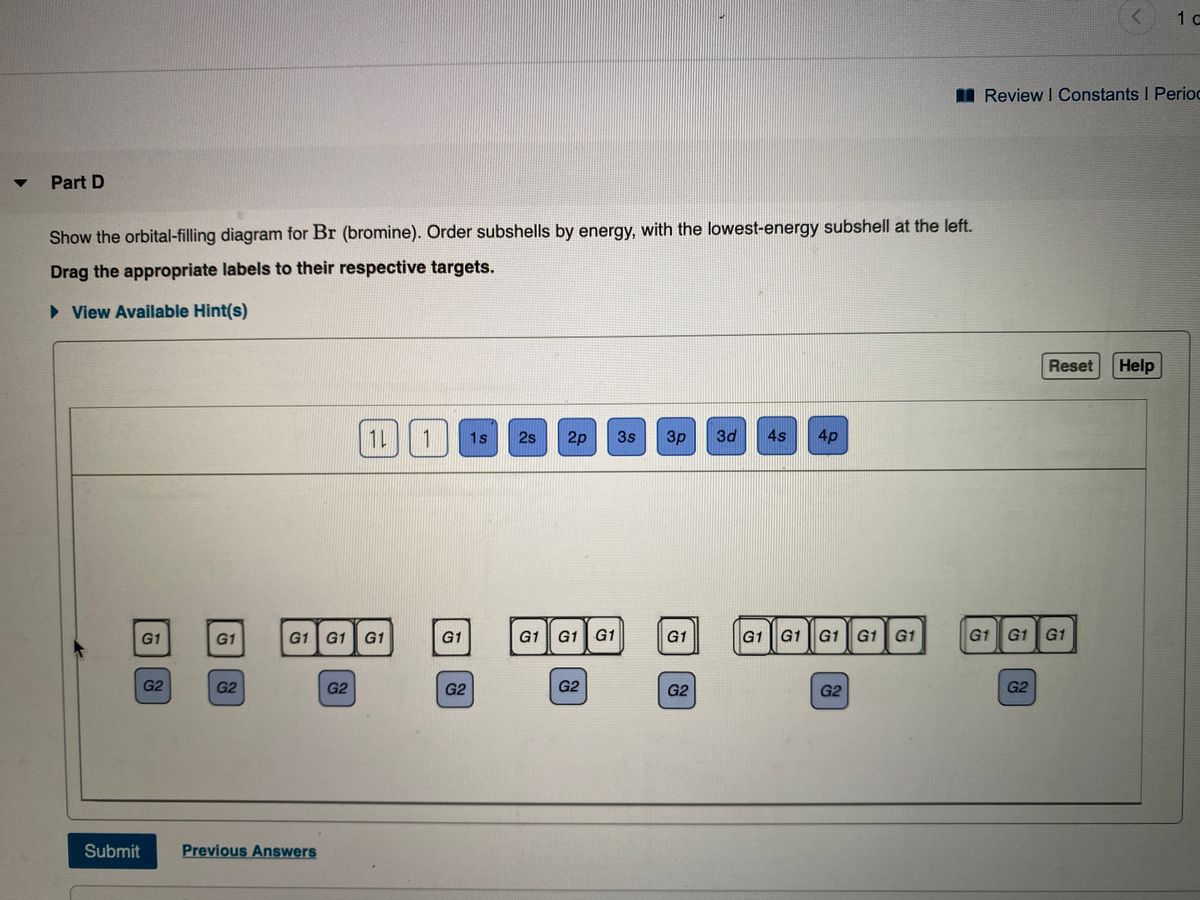
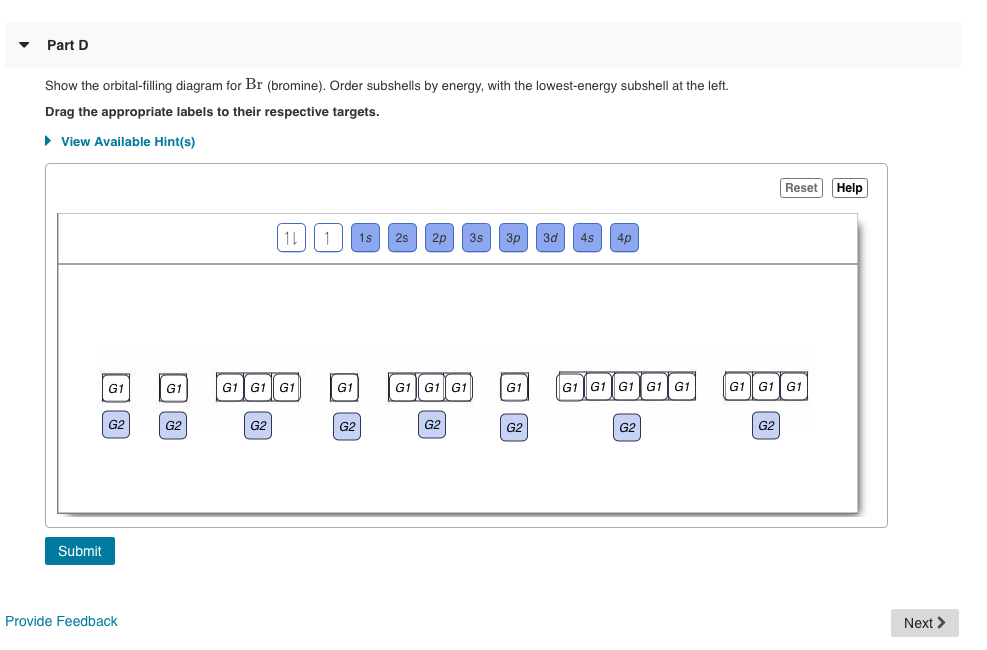
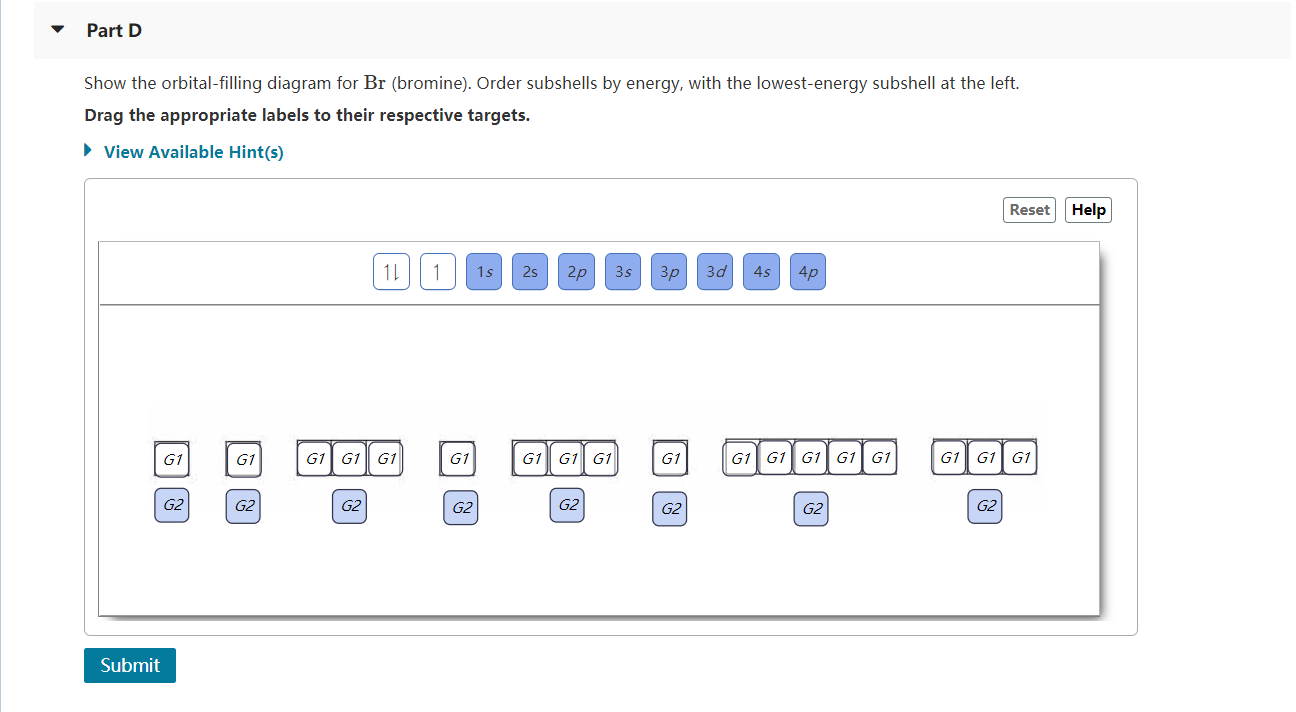
The order of the filling is from bottom to top, that adds the electrons to many sublevels that are 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, and 4p. You will see that the 3d sublevel is filled be for e the 4p after the 4s. Question: Part D Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left.
Bromine is a chemical element with atomic number 35 which means there are 35 protons and 35 electrons in the atomic structure. ... AUse the orbital boxes to fill in the electrons for a chlorine atom in the ground state. ... There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of carbon and 6A molecular orbital diagram or MO diagram is a qualitative ...

Orbital filling diagram for bromine
MO Diagram of SF2. MO diagram s are a good way to represent the different properties of a compound. These properties include shape, bond energy, bond angle, and more such things. With the help of this diagram, we can showcase the energy that different energy orbital acquires and have. Electronic configuration of Oxygen atom is.
Doc Brown's Advanced A Level Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry Periodic Table Revisi...
As such, each bromine atom only needs one more to fill that outer shell and achieve a stable configuration (as the bromide ion Br-). Electron configuration of radon is: Xe4f 14 5d 10 6s 2 6p 6. Answer to Write the electron configuration and give the orbital diagram of a bromine (Br) atom (Z = 35).
Orbital filling diagram for bromine.
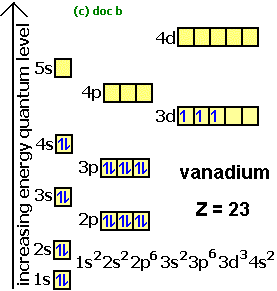
41 orbital diagram for titanium. The electron configuration for titanium is 1s22s22p63s23p63d24s2, according to the Jefferson Lab website. The element's 22 electrons are arranged in four energy levels surrounding the nucleus of the atom. Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels, which are also called shells.
Chapter 9 Electrons in Atoms and the Periodic Table. 9.1 True/False Questions. 1) When the elements are arranged in order of increasing number of protons, certain sets of properties recur periodically. 2) The early scientists who developed the quantum-mechanical model were bewildered by the model and it altered our fundamental view of matter.
Electron Configuration (quicker to draw than orbital filling diagrams) Ex. O 2 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 3. Electron Dot shows only the valence (outer energy level) electrons. . Ex. Oxygen atom. O :. Where are the Electrons? Write the full electron configuration, short-hand electron configuration, and fill in the orbital diagrams, for the following elements.
In this video we will write the electron configuration for I- the Iodide ion. 1 sodium iron bromine barium neptunium 1-134 qp In the space below write the abbreviated electron. The radioactive element neptunium atomic number 93 has theelectron configuration. 6s2 and the term symbol is 1S0. Xe 6s2 for barium.
Answer to Draw an orbital diagram for each element: (a) magnesium; (b) aluminum; (c) bromine.. How can we draw the orbital diagram of a magnesium atom and a magnesium ion. What is the orbital diagram for magnesium. 100 10 ratings or. Electron configurat ion s and
Molecular Orbital Theory and MO diagram of Dibromine (Br2) The MO diagram or Molecular Orbital diagram is an extension of the 3-dimensional molecular design and gives a better understanding of the structure of an atom. Molecular Diagram also reflects upon bond length, bond shape, bond energy, and the bond angle between 2 atoms.
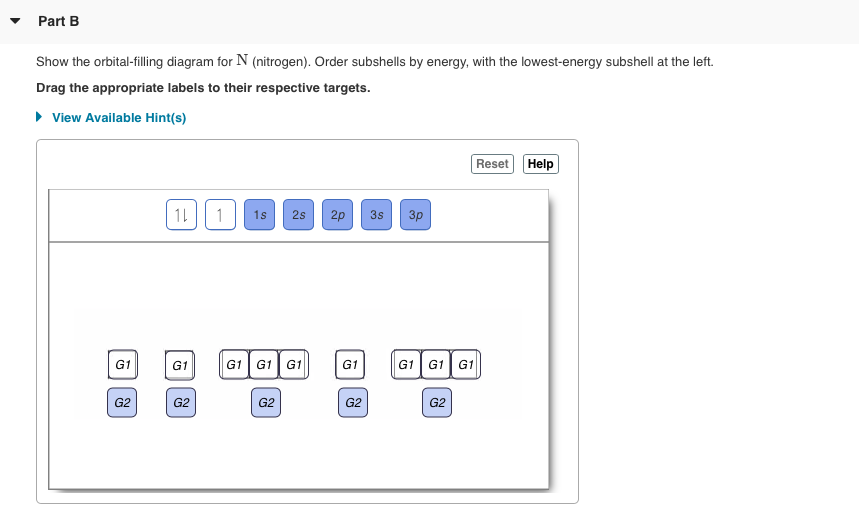
Diagram of Hund's rule in boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Figure 1. The 2p.Show transcribed image text Show the orbital-filling diagram for N. Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital.
Orbital filling diagram for bromine. nitrogen b. Atom Y has 9 protons, 9 neutrons, and 9 electron s. The orbital can be found in every energy level except the first two. The correct electron configuration for calcium is 1) 1s22s22p63s23p63d2 2) 1s 22s 2p63s23p64s2 3) 1s 22s 2p63s23p8 Learning Check Nitrogen appears as a colorless odorless gas. For example, the Lewis electron dot diagram for ...
So based on what we know about the quantum numbers and using the chart above, you need 2 electrons to fill an s orbital, 6 electrons to fill a p orbital, 10 electrons to fill a d orbital and 14 electrons to fill the f orbital. BUT what we haven't discussed is how these orbitals get filled...the order of fill. Order of Fill
42 show the orbital filling diagram for br bromine; 42 venn diagram dna and rna; 39 stihl bg 85 parts diagram; 40 in the provided diagram, at the profit-maximizi... 39 jacks parts lookup model diagram; 41 honda fit fuse box diagram; 41 2001 jeep grand cherokee parts diagram; 41 cat 70 pin ecm wiring diagram; 37 the _____ is a diagram that ...
Under the orbital approximation, we let each electron occupy an orbital, which can be solved by a single wavefunction. In doing so, we obtain three quantum numbers (n,l,m l), which are the same as the ones obtained from solving the Schrodinger's equation for Bohr's hydrogen atom. Hence, many of the rules that we use to describe the electron's ...
37) The orbital diagram for fluorine shows 1 unpaired electron in a p orbital. 38) The correct electron configuration for magnesium is: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 3. 39) The element manganese (symbol = Mn) has five valence electrons. 40) Bromine has 17 valence electrons. 41) Bromine has 28 core electrons.
In general when filling up the electron diagram, it is customary to fill the lowest energies first and work your way up to the higher energies. Principles and rules such as the Pauli exclusion principle, Hund's rule, and the Aufbau process are used to determine how to properly configure electrons.
Molecular Orbital Theory, which is used to sketch the MO diagram of any given molecule, is a complex yet important concept of chemical bonding. In quantum mechanics, MO theory deals with spatial and energetic properties of electrons and talks about the LCAO (Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals) to form MO( Molecular Orbitals).
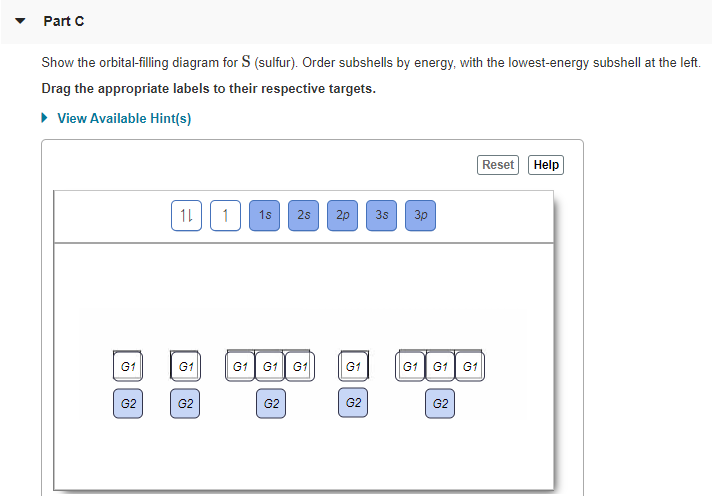
Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. Click within the orbital to add electrons. Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine).
41 refer to the diagram. if actual production and ... 42 show the orbital filling diagram for br bromine; 42 venn diagram dna and rna; 39 stihl bg 85 parts diagram; 40 in the provided diagram, at the profit-maximizi... 39 jacks parts lookup model diagram; 41 honda fit fuse box diagram; 41 2001 jeep grand cherokee parts diagram; 41 cat 70 pin ...
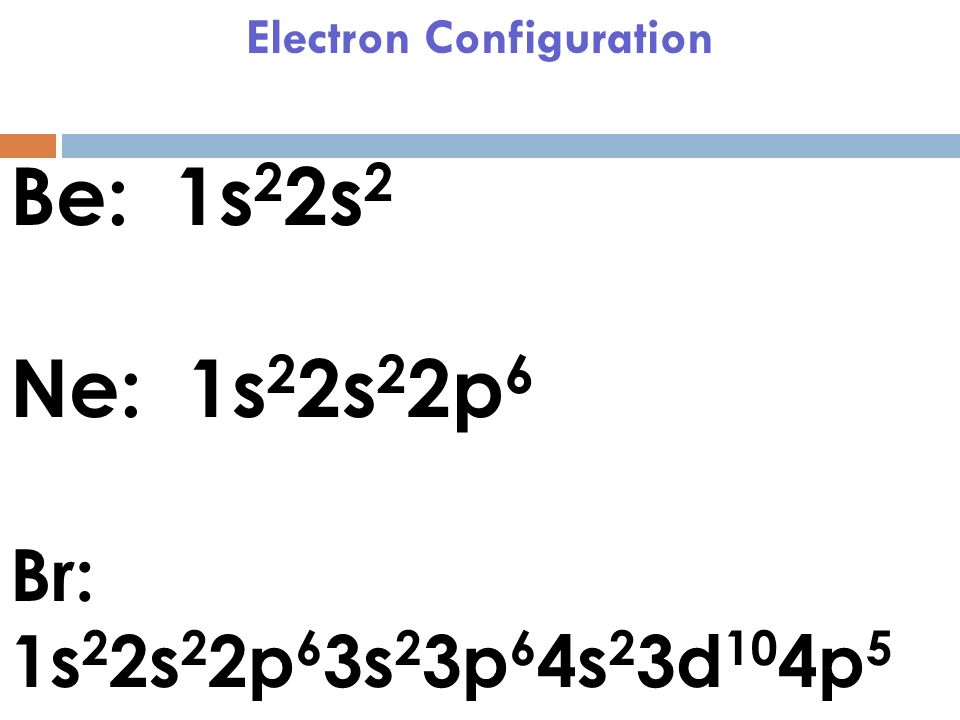
The electron configuration of bromine is 1s2 2s2p6 3s2p6d10 4s2p5 which can be shortened to Ar 4s2 3d10 4p5. It would retain the same number of protons but just have an extra electron. Therefore its electron configuration will be. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Lithium Li He 2s 2.
27) An orbital is a probability map showing exactly where an electron can be found in an atom. 28) The higher the principal quantum number, the lower the orbital energy. 29) The possible values for the principal quantum numbers are: . 30) The subshells of the orbital are represented by the possible letters: s, p, d, or f.
The sequence given above can be represented by a diagram as shown Fig. 3.25 Order of filling of atomic orbitals. Pauli's Exclusion Principle This principle limits the number of electrons that can occupy any orbital of an atom.


/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)




















0 Response to "40 orbital filling diagram for bromine"
Post a Comment