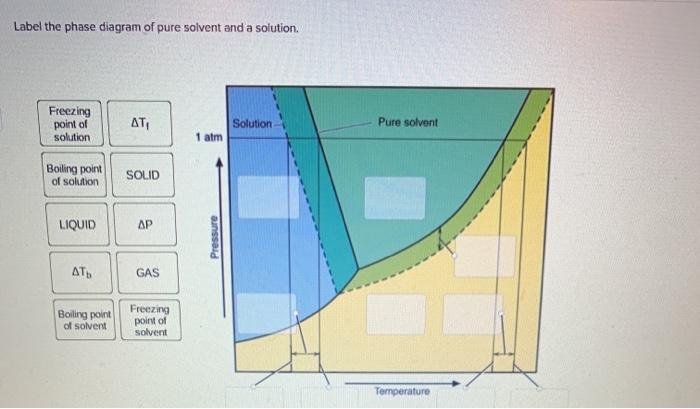
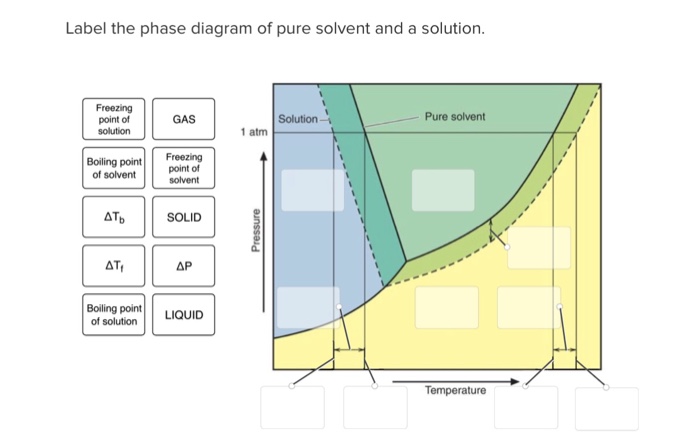
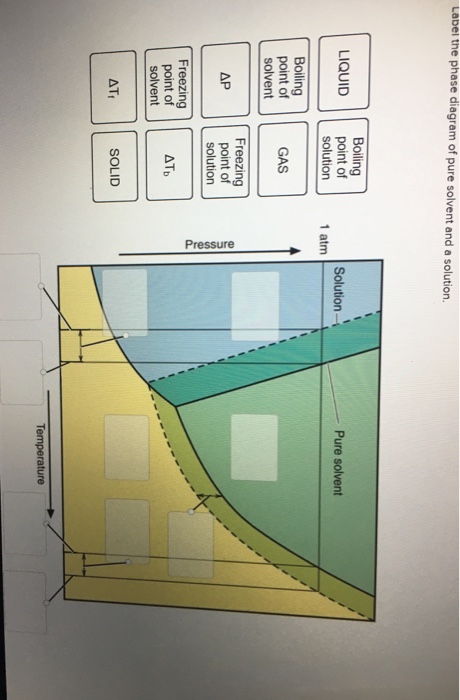
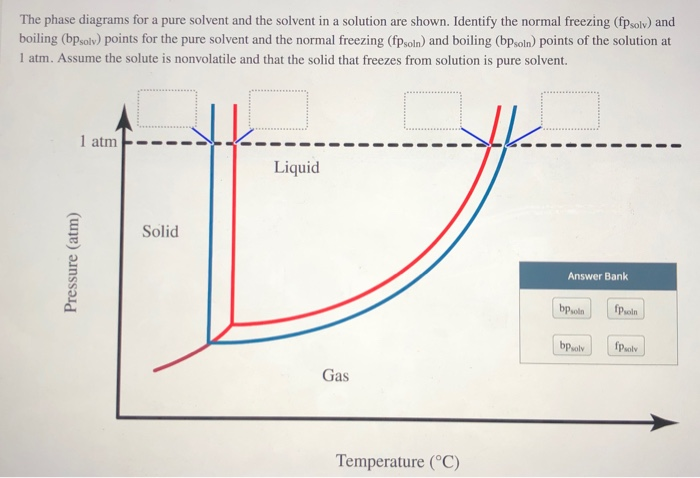
39 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
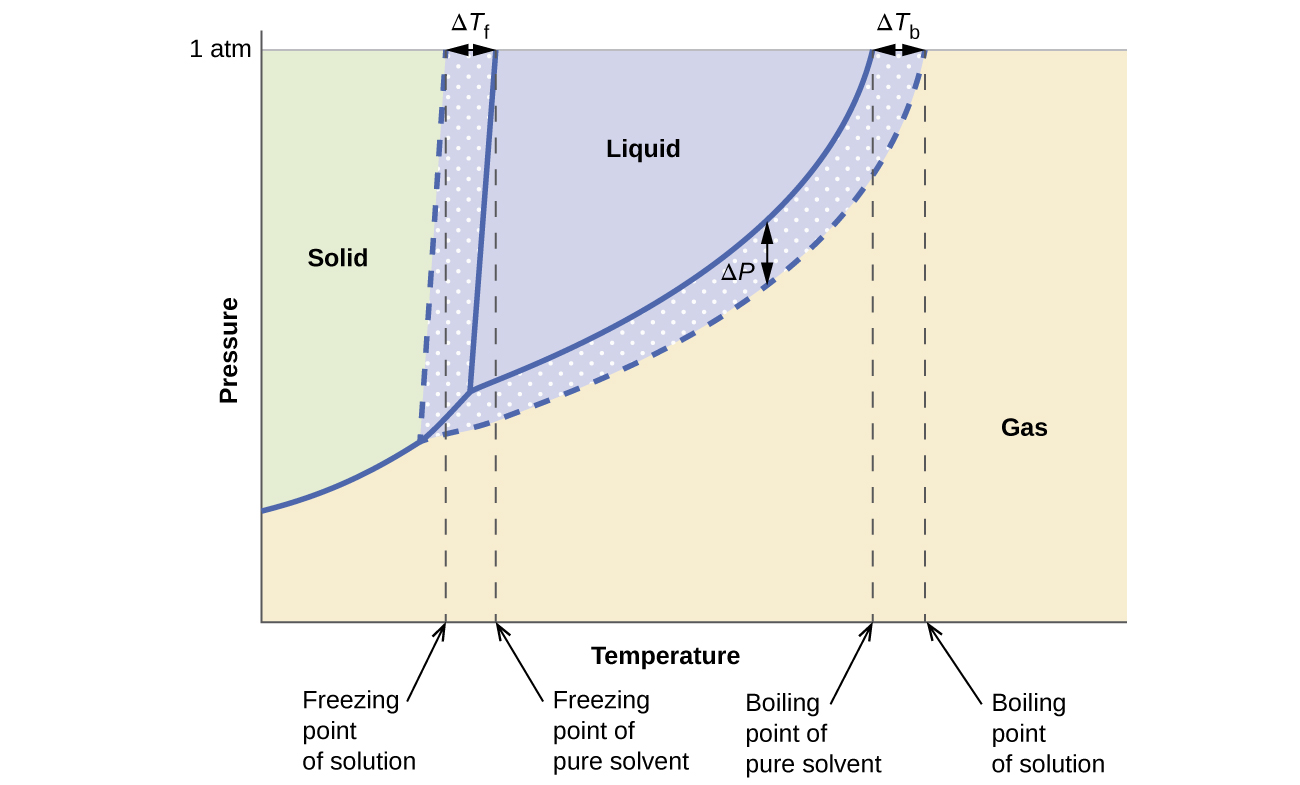
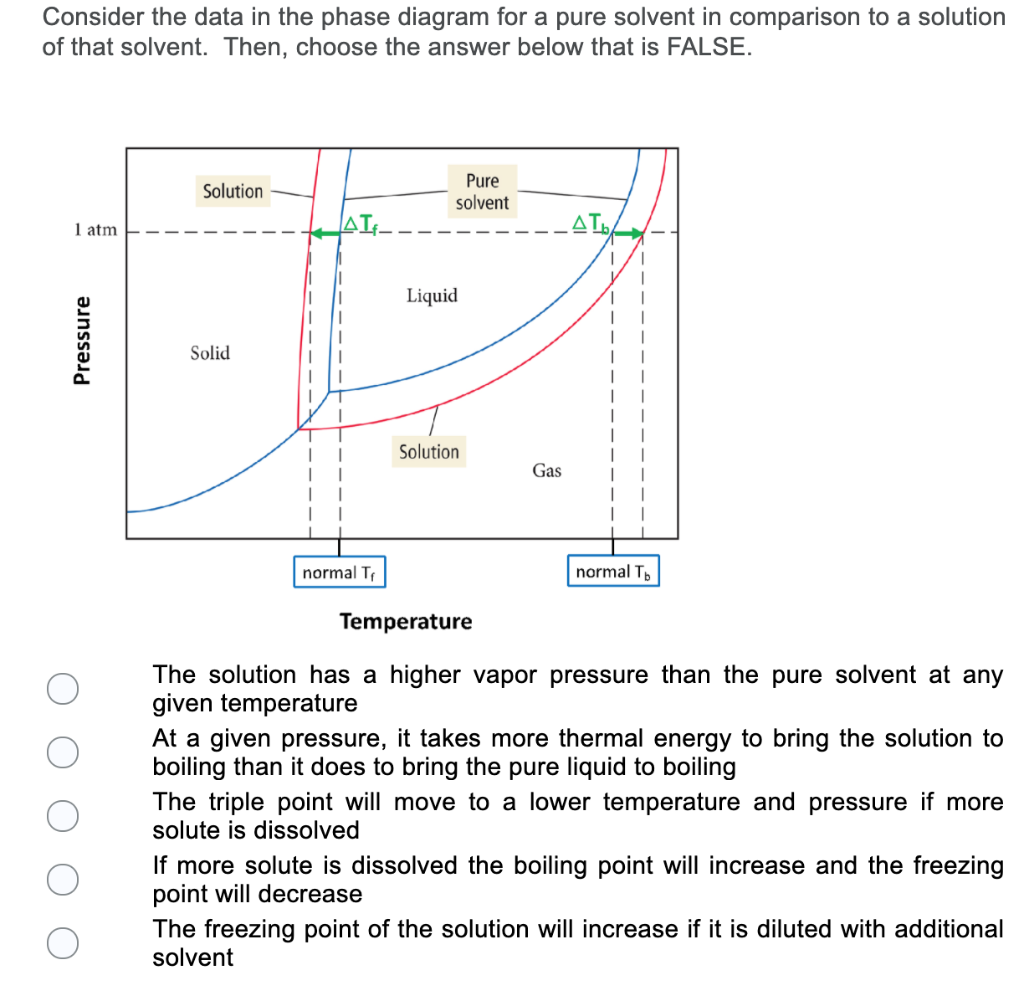
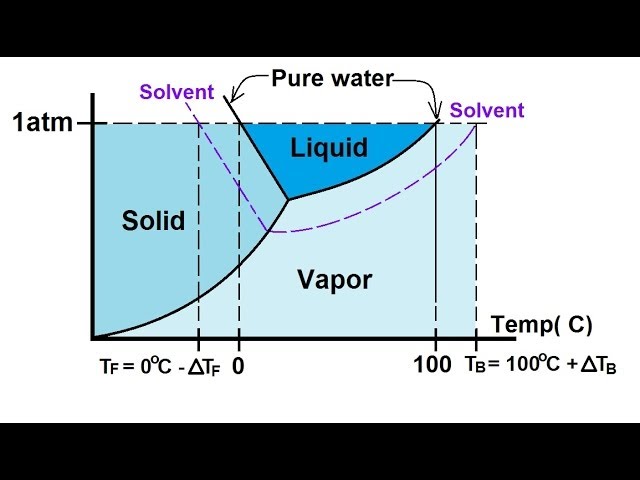
16.02.2021 · The diagram also includes the melting and boiling points of the pure water from the original phase diagram for pure water (black lines). Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\): Because of the changes to the phase diagram, you can see that: the boiling point of the solvent in a solution is higher than that of the pure solvent;
Solutions 1. Circle the following that are true statements about solutions a) a solution consists only of a single phase b) a solution must have more than one component c) solutions must be liquid. 2. The component in the solution with the largest mode fraction is referred to as the (solvent, solute). Solvent 3.
the pure solvent is present. Thus the vapor pressure above the solution containing solute will be lower than the vapor pressure of the pure solvent. The dissolved solute molecules physically block the surface of the solvent, preventing some of the solvent molecules from evaporating at a given temperature. Shown below are two phase diagrams for ...

Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
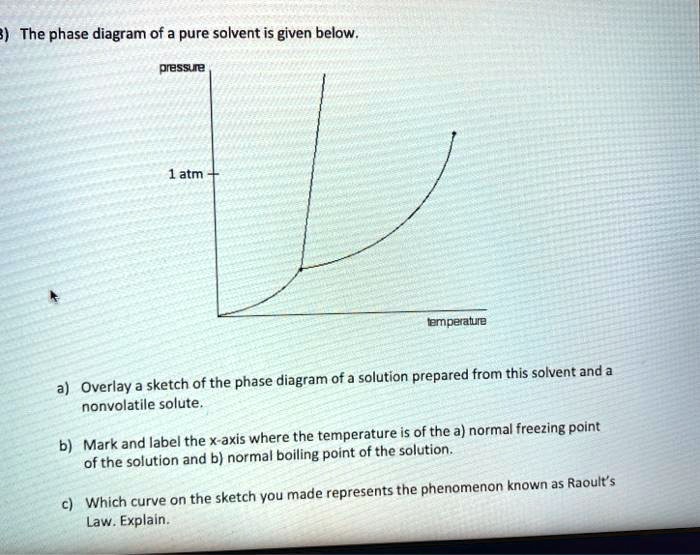
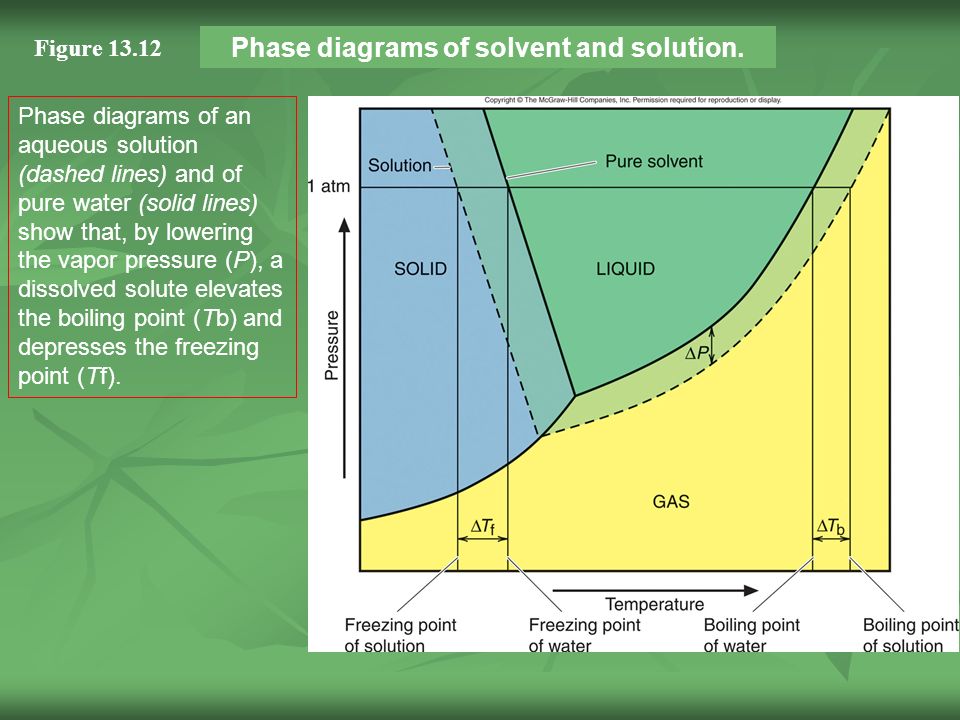
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. The vaporization curve for the solution lies below the curve for pure water at all temperatures which results in an increase in the boiling point and a decrease in the freezing point of the solution. This is the case for many solutions comprising liquid solvents and nonvolatile solutes.
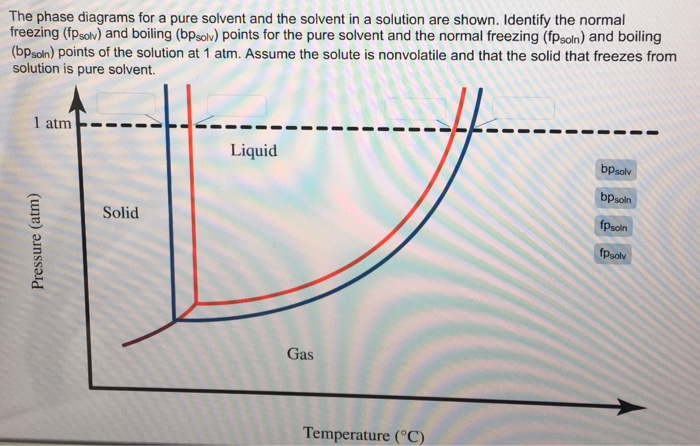
Transcribed image text: The phase diagrams for a pure solvent and the solvent in a solution are shown. Identify the normal freezing (fp_solv) and boiling (bp_solv) points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing (fp_soln) and boiling (bp_soln) points of the solution at 1 atm. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent.
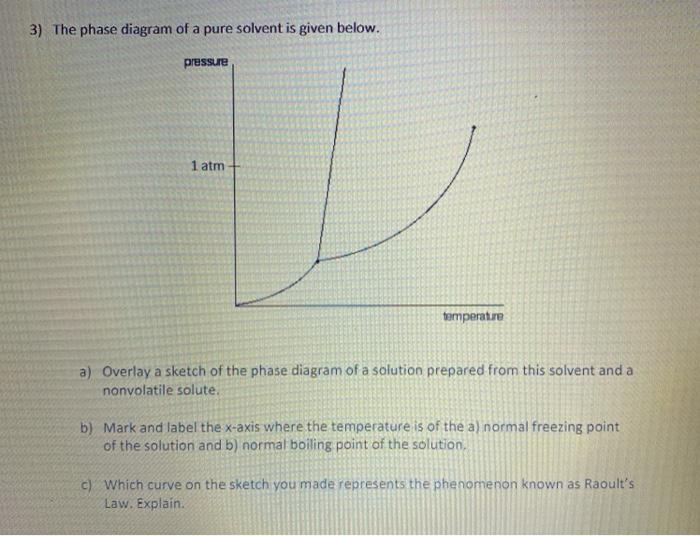
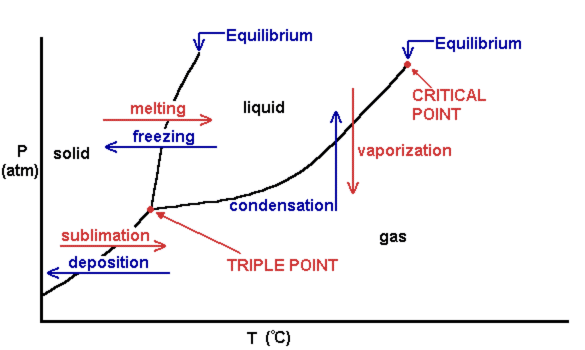
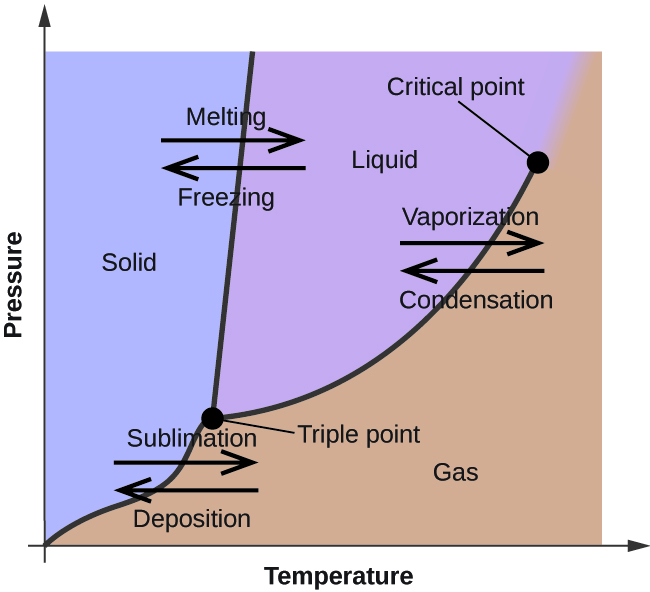
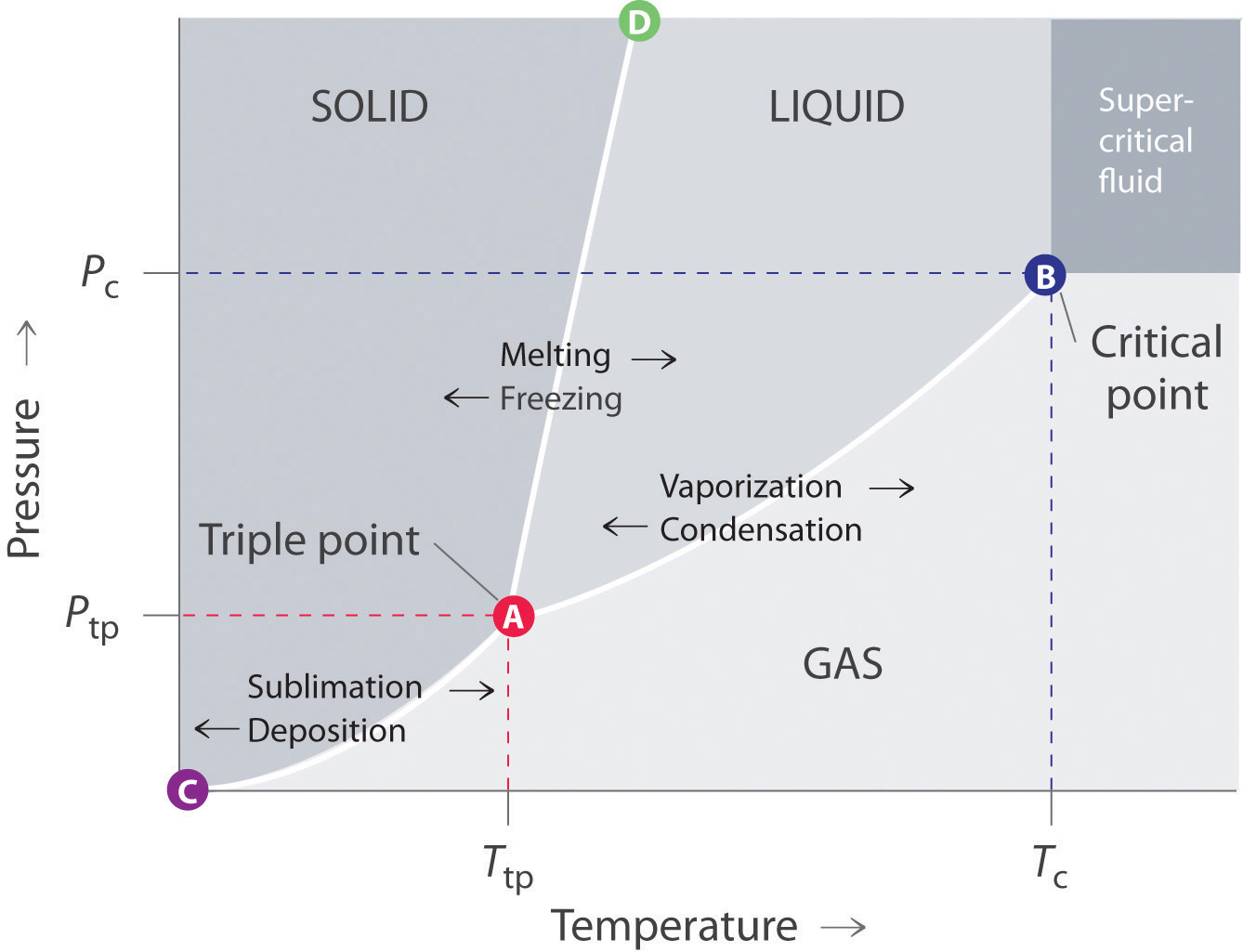
A phase diagram combines plots of pressure versus temperature for the liquid-gas, solid-liquid, and solid-gas phase-transition equilibria of a substance. These diagrams indicate the physical states that exist under specific conditions of pressure and temperature, and also provide the pressure dependence of the phase-transition temperatures (melting points, sublimation points, …
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution..
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. This is …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
Phase Diagram 1. Chapter-5 PHASE AND PHASE EQUILIBRIUM Prepared By: PALLAV RADIA Asst prof. AITS, RAJKOT. 2. Introduction: One of the most important objective of engineering metallurgy is to determine properties of material. The properties of material is a function of the microstructure which depend on the overall composition and variable such as pressure and temperature. Hence to determine ...
Isomorphous Phase Diagrams Phase diagram Indicate phases as a function of Temp., Comp. and Pressure (under equilibrium condition) Binary phase diagram A phase diagram for a system with two components. Isomorphous phase diagram A phase diagram in which the components display unlimited solid solubility. Chapter 10: Solid Solutions and Phase ...
05.11.2021 · In the diagram, solvent traveled 5 centimeters, while the sample traveled 2.5 centimeters from the origin line. Figure 2. For each compound, an R f value is calculated based on how far it traveled along the stationary phase. In paper chromatography, R f values are used to compare different components to each other. R f values are calculated by looking at the …
Problem: Label the diagram of pure solvent and a solution. FREE Expert Solution Recall that a phase diagram shows the transition of matter between solid, liquid, and gas phases as temperature and pressure changes.
When a second compound is introduced to the system forming a homogeneous solution however, the phase diagram drastically changes. For example, the addition of a solute to a pure solvent (making a solution) can disrupt important interactions between solvent molecules, changing the temperature at which the solvent would typically freeze or boil.
solution which is just the sum of the two Raoult's law vapor pressures (the sum of two straight lines is a straight line). Vapor Pressure Diagrams and Boiling Diagrams We are now ready to begin talking about phase diagrams involving two components. Our first few phase diagrams will involve only the liquid and gas (or vapor) phases.
In normal phase chromatography, where the stationary phase is polar, polar molecules will spend more time adsorbed on the stationary phase, while less polar ones will be carried more quickly by the non-polar mobile phase. In the diagram below, assuming that the setup is normal phase, B represents a less polar compound, while A represents a more ...
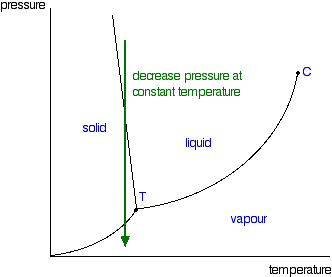
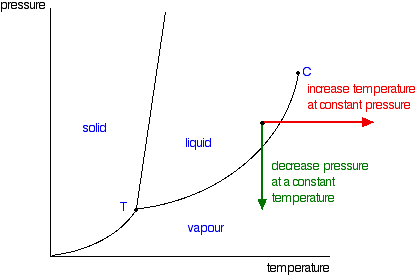
Phase diagrams. A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapour (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance.
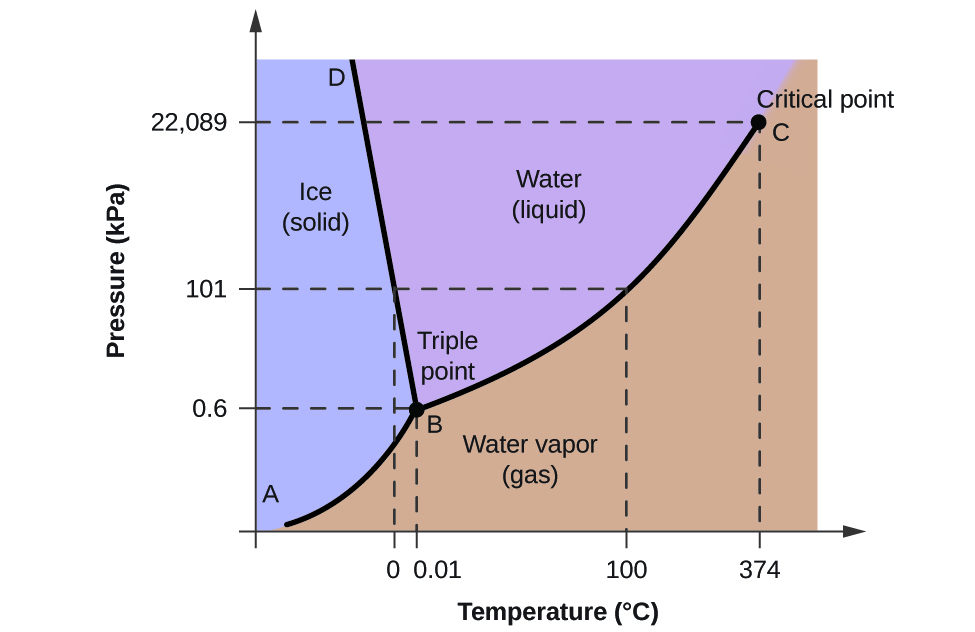
A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2.
25.08.2020 · At 100°C, the vapor pressure of pure water is 760 mmHg. Calculate the vapor pressure of an aqueous solution containing 30.2% ethylene glycol by mass, a concentration commonly used in climates that do not get extremely cold in winter. Given: identity of solute, percentage by mass, and vapor pressure of pure solvent
- Solutions - solid solutions, single phase - Mixtures - more than one phase • Solubility Limit : Max concentration for which only a single phase solution occurs. Question: What is the solubility limit at 20°C? Answer: 65 wt% sugar . If Co < 65 wt% sugar: syrup If Co > 65 wt% sugar: syrup + sugar. 65 Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram Pure ...
Identify the solvent and solute in each of the solutions A) salt (NaCl) in water ... Also, assume that the engine coolant is pure ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH), which is non-ionizing and non-volatile, and that the pressure remains constant at 1.00 atm. ... Label the phase diagram. A) Solid Phase B) Triple Point C) Sublimation Point/ Deposition Point
• 281 Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams Liquid (Water) Pressure (atm) Vapor (Steam) 1,000 100 10 1.0 0.1 0.01 0.001 20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Solid (Ice) Temperature (°C) T he graph below is the phase diagram for pure H
Expt. 5: Binary Phase Diagram CHEM 366 V-3 Combination1,2,3 of equations (2), (3), (6), (7) and (10) leads to the equation T≅TA+ RTA 2 ΔHA lnXA (11) or T≅TA+ RTA 2 ΔHA ln(1−XB) (12) or T≅TA- RTA 2 ΔHA lnXB (13a) T≅TB- RTB 2 ΔHB lnXA (13b) where T and TA are freezing points (K) of the mixture II and pure A, R is 8.314 J/K mole, ΔHA is the molar enthalpy of fusion of A and XB ...
A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. The pressure and temperature axes on this phase diagram of water are not drawn to constant scale in order to illustrate several important properties. We can use the phase diagram to identify the physical …
The phase diagram for a pure substance is shown above. Use this diagram and your knowledge about changes of ... Use the data above to draw a phase diagram for argon. Label the axes and label the regions in which the solid, ... phase, solid argon must be the denser phase. (K) 5. (a) pure solvent solution 0 Time 0 5 10 15 20
7 In Figure 9.3, the raffinate phase consisting of the solute A and the diluent D is fed into the system from the right hand side (RHS), with the total flow rate of o R (or R) and the concen- tration (in mole or mass fraction of the solute) of o x; note that the flow rate of just the diluent is D F The extract phase consisting of pure solvent S or the solvent S with some amount of solute
The figure shows the phase diagram of a system in which the liquids become fully miscible before they boil. Distillation of a mixture at a 1 leads to vapor with composition b 1, which condenses to completely miscible solution at b 2. Phase separation only occurs when the distillate is cooled to a point in the two-phase region such as point b 3.
If you live near a lake, a river, or an ocean, that body of water is not pure H 2 O but most probably a solution. Much of what we drink—for example, soda, coffee, tea, and milk are solutions. Solutions are a large part of everyday life. A lot of the chemistry occurring around us happens in solution. In fact, much of the chemistry that occurs in our own bodies takes place in solution, …
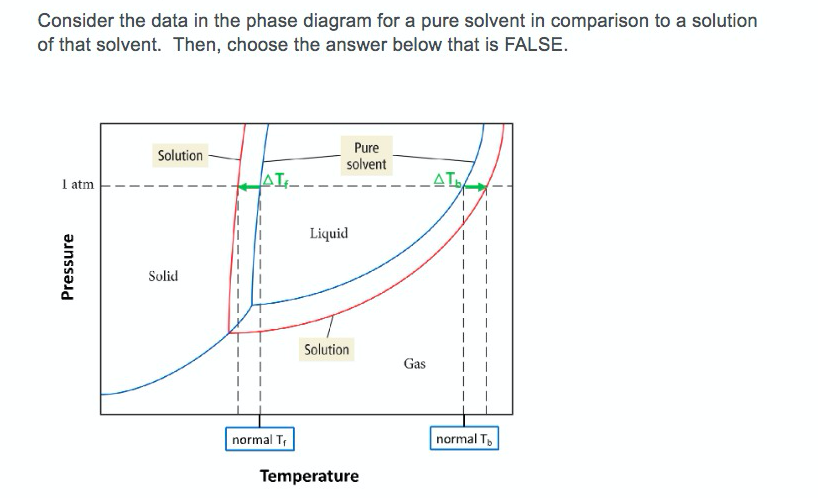
Consider the following general phase diagram: Now, consider the pure substance, whose phase diagram was represented by the black curves. The normal freezing point of the pure substance at constant pressure is indicated by B, and its reduced normal freezing point (due to addition of nonvolatile solute to the pure liquid substance) is A, since Tdarr leftwards.
III.1. Draw phase diagrams for the following type systems. Label the regions and in-tersections of the diagrams, stating what materials (possibly compounds or azeotropes) are present and whether they are solid, liquid or gas. (a) One component, pressure-temperature diagram, liquid density greater than that of solid. (b) Two component,
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. 12716 3 the phase diagram in figure 1 is for a pure compound. The liquid vapor pressure curve is shifted downward to lower pressures but the solid vapor pressure sublimation curve is unaffected.
Topics to be discussed are: terminology of phase diagrams and phase transformations, interpretation of phase, simple binary phase diagrams, and development of equilibrium microstructures upon cooling. DEFINITIONS AND BASIC CONCEPTS "Components": pure metals and/or compounds of which an alloy is composed (Ex.: solute and solvent in Cu-Zn brass).
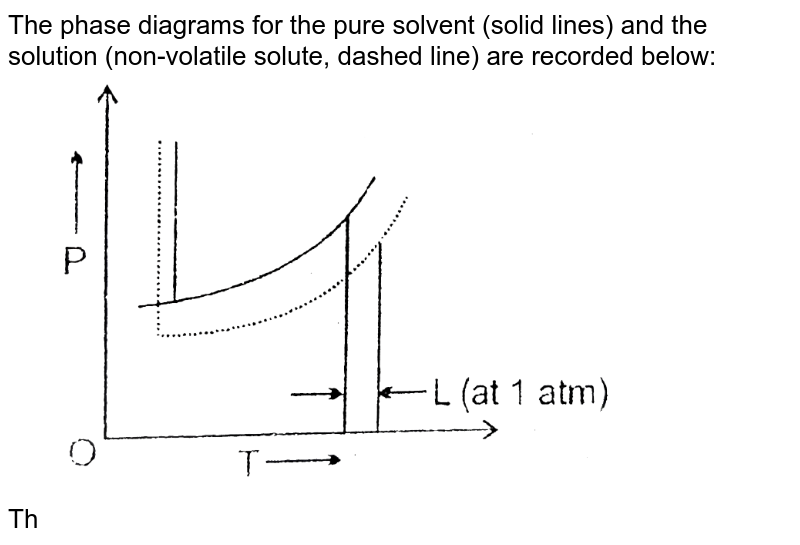
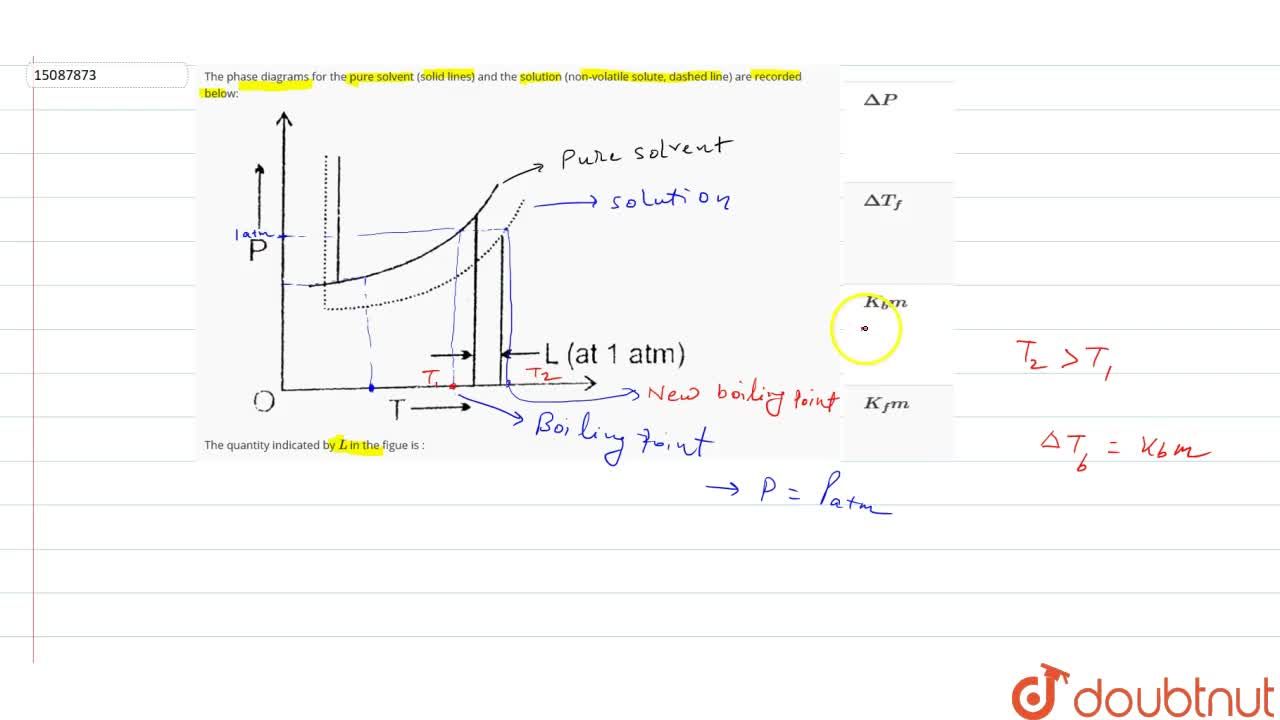
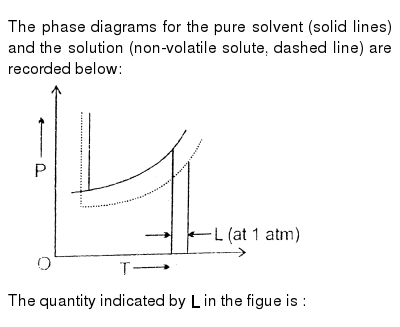
The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below: the quantity indicated by `l` in the figue is :
Ternary phase diagrams are used to represent all possible mixtures of three solvents [1]; they are described in Chapter 3.Here, we shall indicate how they should be used to minimize the solvent consumption. Figure 2.1 (top) shows the methanol–chloroform–water ternary phase diagram with the tie-lines in the biphasic domain. Five particular compositions are shown in the …
Q. Label the diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Q. Consider this phase diagram for carbon. Which phases are present at the lower triple point?a) diamondb) graphitec) gasd) liquidWhich phase is stable...
The phase diagram for sodium chloride solution. What the phase diagram looks like. ... because adding a non-volatile solute to a solvent increases its boiling point. ... in this case, that's the pure ice crystals. On the other end, it hits the sloping line - this tells you the composition of the remaining salt solution. ...
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Shown above is a phase diagram for water. Well look now at the phase diagram for sodium chloride solution in some detail. Phase diagrams of pure water and an aqueous solution of a nonvolatile solute. Pure a and pure b are also considered to be α and β phases respectively.
Phase diagrams of pure water and an aqueous solution of a nonvolatile solute. Pure a and pure b are also considered to be α and β phases respectively. It has b atom as the solute component. A terminal phase or terminal solution is one that exists in the extremes of concentration 0 and 100 of the phase diagram.
Three single-phase regions are found on the diagram: α, β, and liquid. The α-phase is a solid solution rich in A atom; it has B atom as the solute component. Otherwise in β-phase solid solution, A is the solute. Pure A and pure B are also considered to be α- and β-phases, respectively.














0 Response to "39 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution."
Post a Comment