45 buoyant force free body diagram
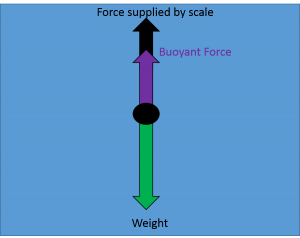
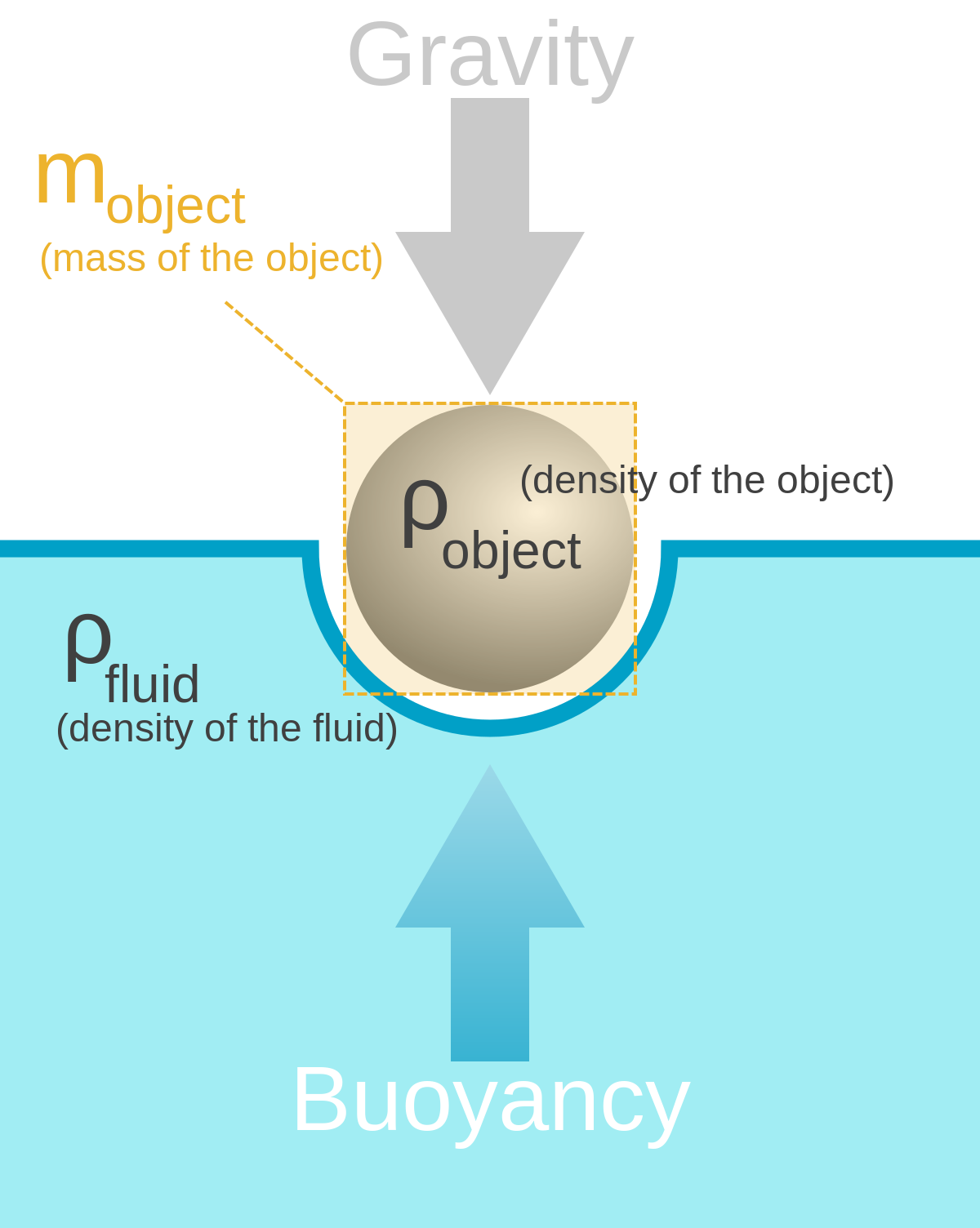
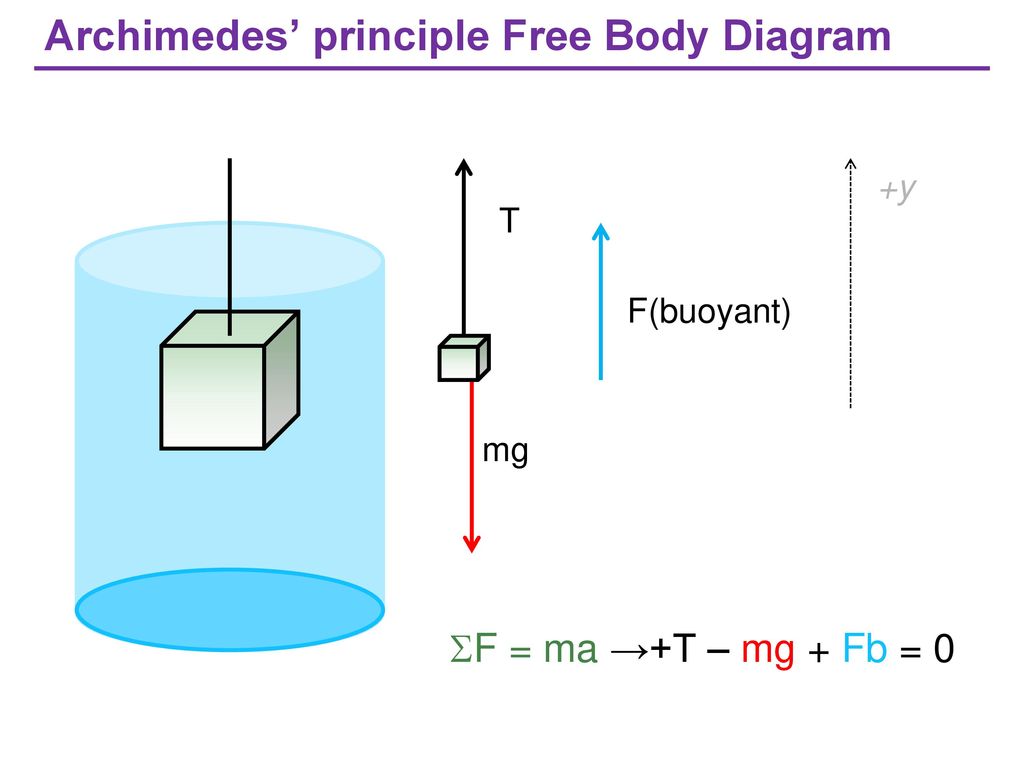
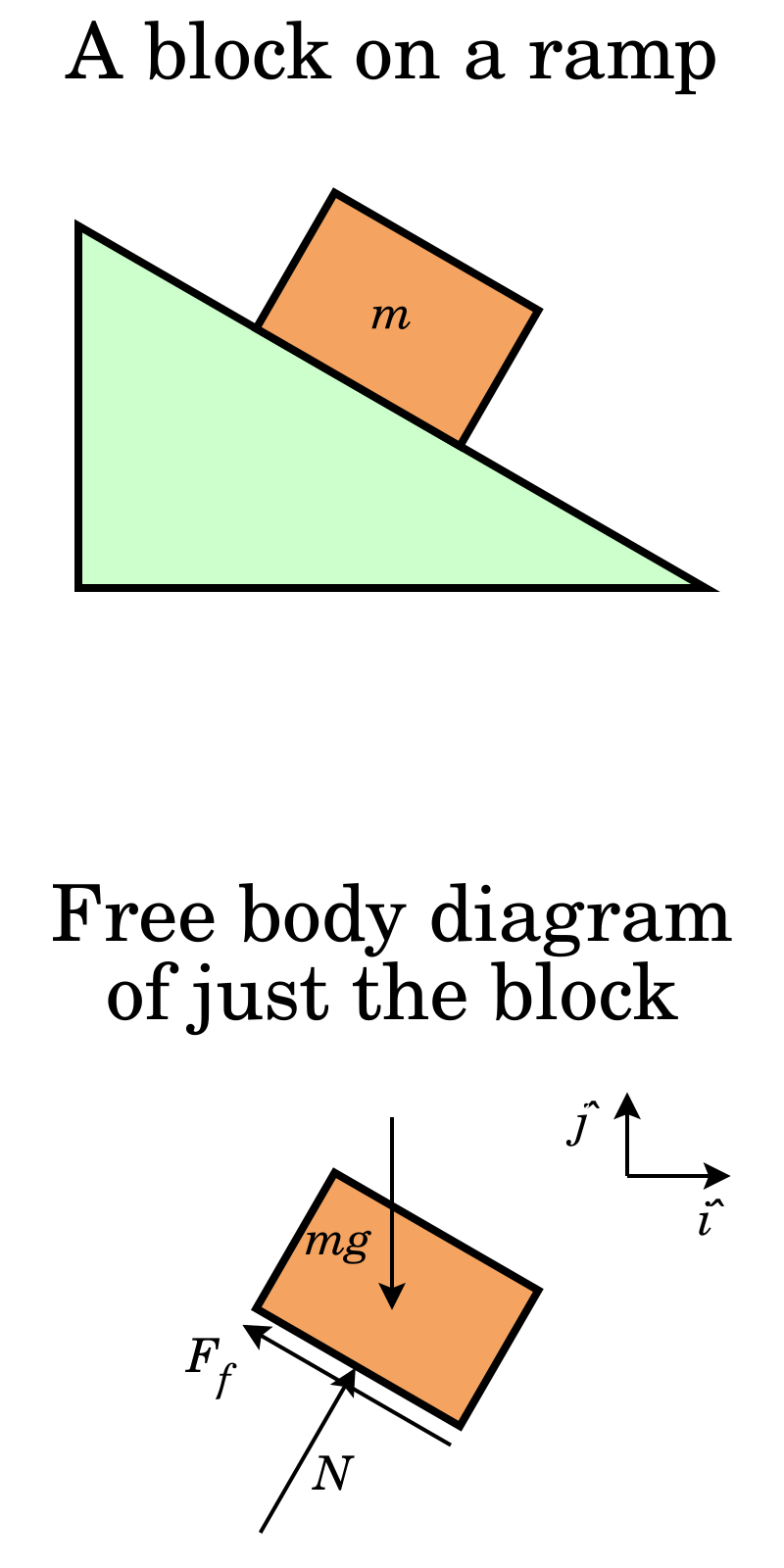
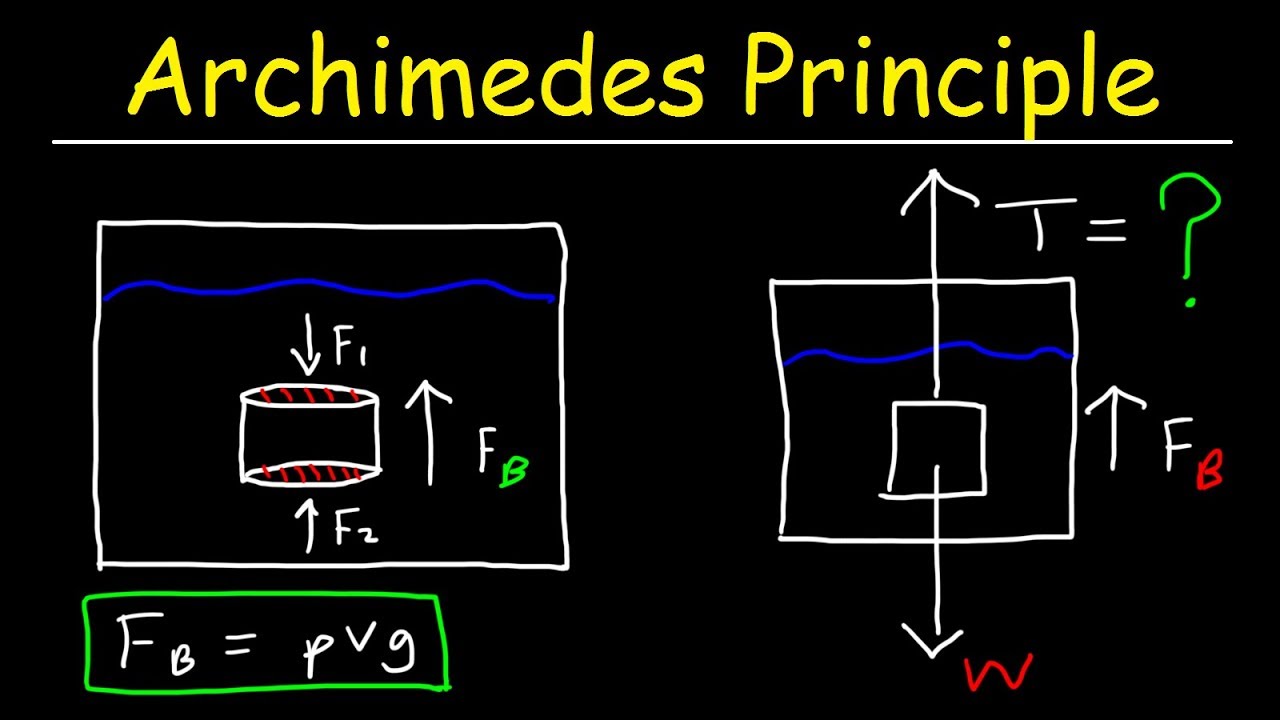
B) In the diagram you made, draw the forces that are acting on the block (i.e. a Free-Body Diagram). Next to your diagram, apply Newton's 2nd Law and then solve algebraically for the buoyant force. You should conclude that F B = W. If this is not your conclusion then go back and check your work. If you still do not get this result Buoyant Force • The magnitude of the buoyant force always equals the weight of the displaced fluid • The buoyant force equation is the same for a totally submerged object of any size, shape, or density BVgw=ρ fluid fluid fluid= BV==ρ fluid fluid fluid g w Totally Submerged Object mg = ρ objectV objectg For completely submerged object: V ...
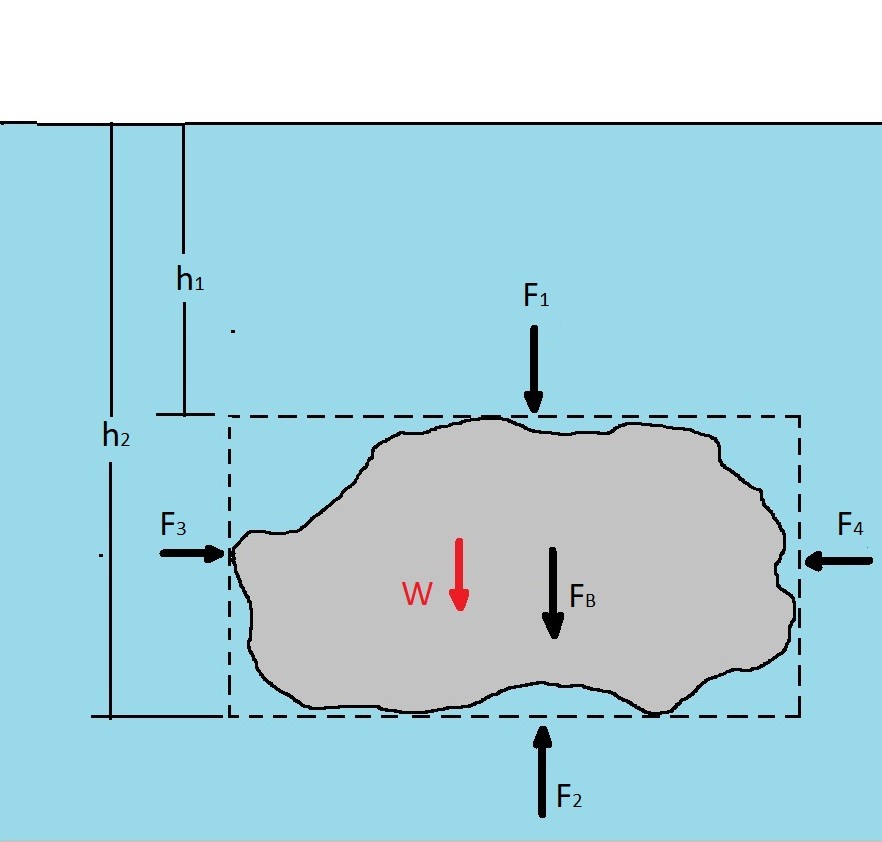
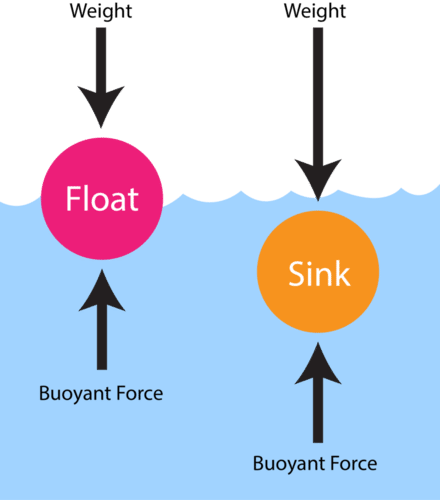
If you look at a free-body diagram of a floating boat it will be clear that the weight force will have to be cancelled out by an upward force by the water. This is because of Newton's Second Law. The upward force has to be bigger the bigger the floating object is. ... The buoyant force therefore depends on how much water gets displaced.

Buoyant force free body diagram
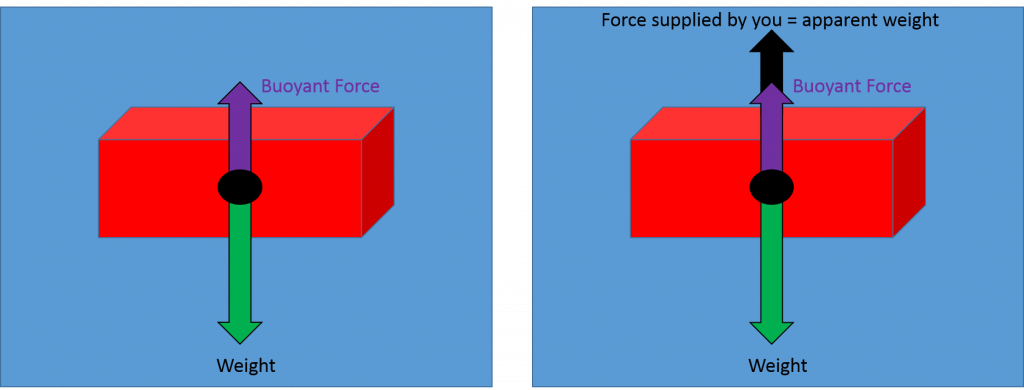
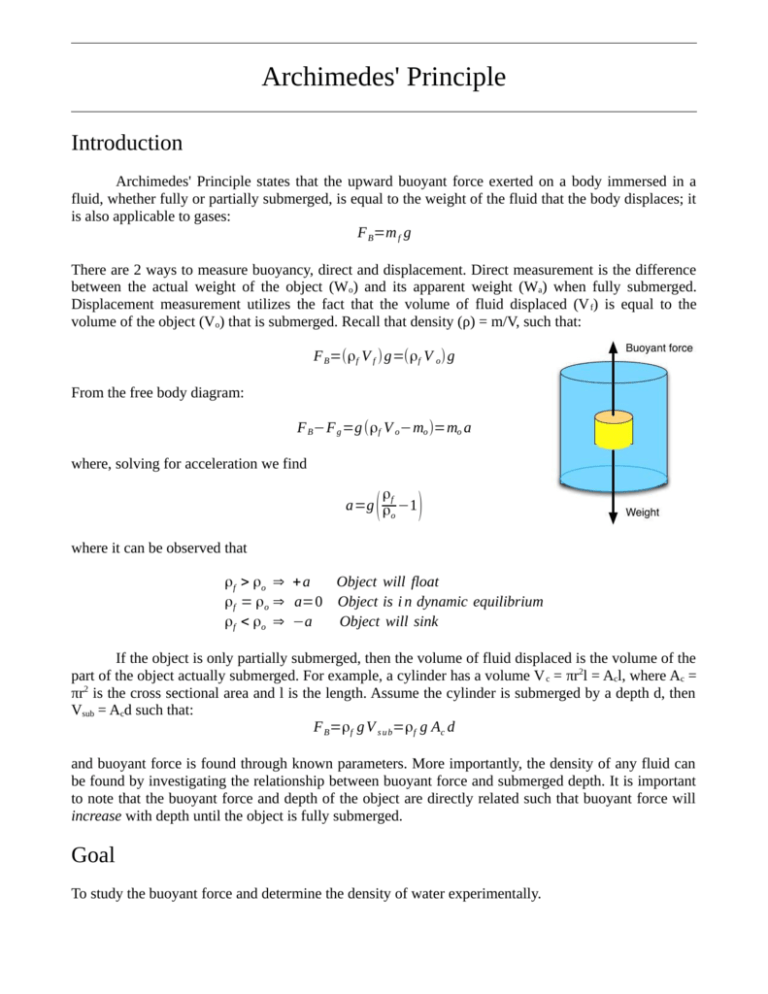
forces free-body-diagram density fluid-statics buoyancy. Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow edited Oct 22 '18 at 20:21. ... Archimedes' principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially submerged, ... second weight, called the "apparent weight" differs from the first due to the buoyant force. Draw the corresponding Free Body Diagram and use it to determine the forces involved, and to solve for the density of the submerged object. Calculate the buoyant force and the density from your measurements. A student's correct free-body diagram for an object floating in water. The students were asked to draw a free-body diagram for this situation as part of the laboratory experiment.
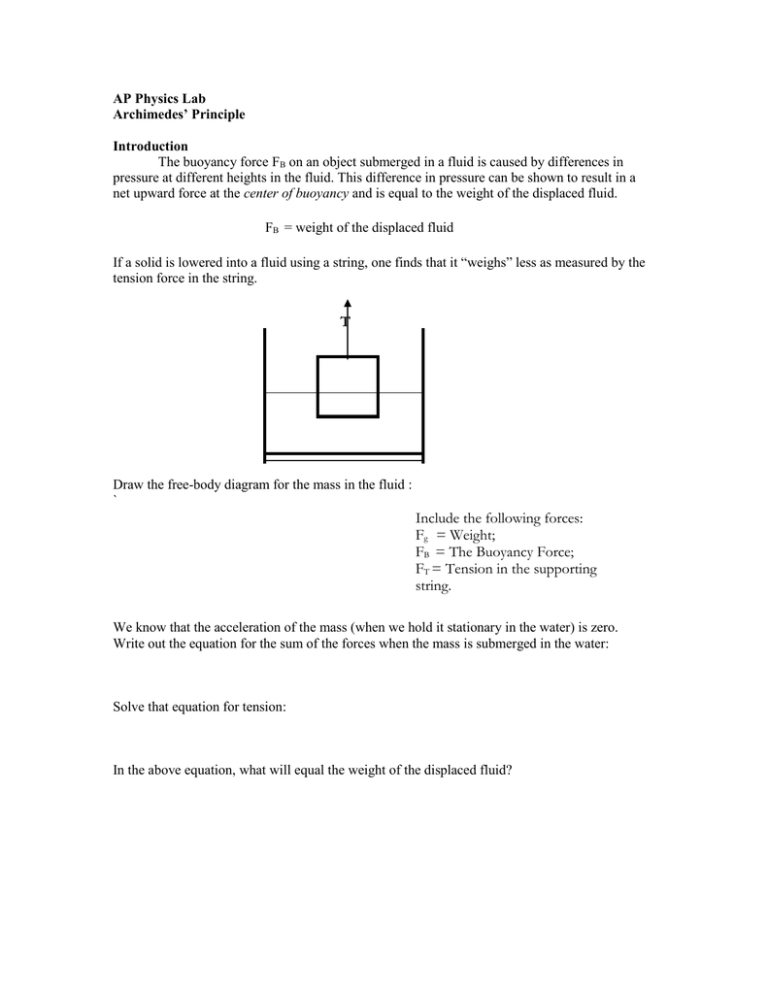
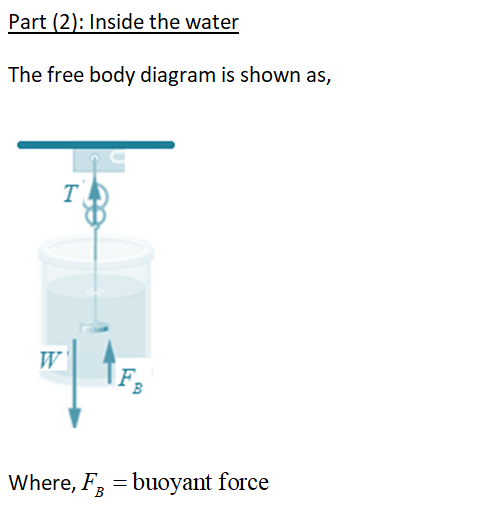
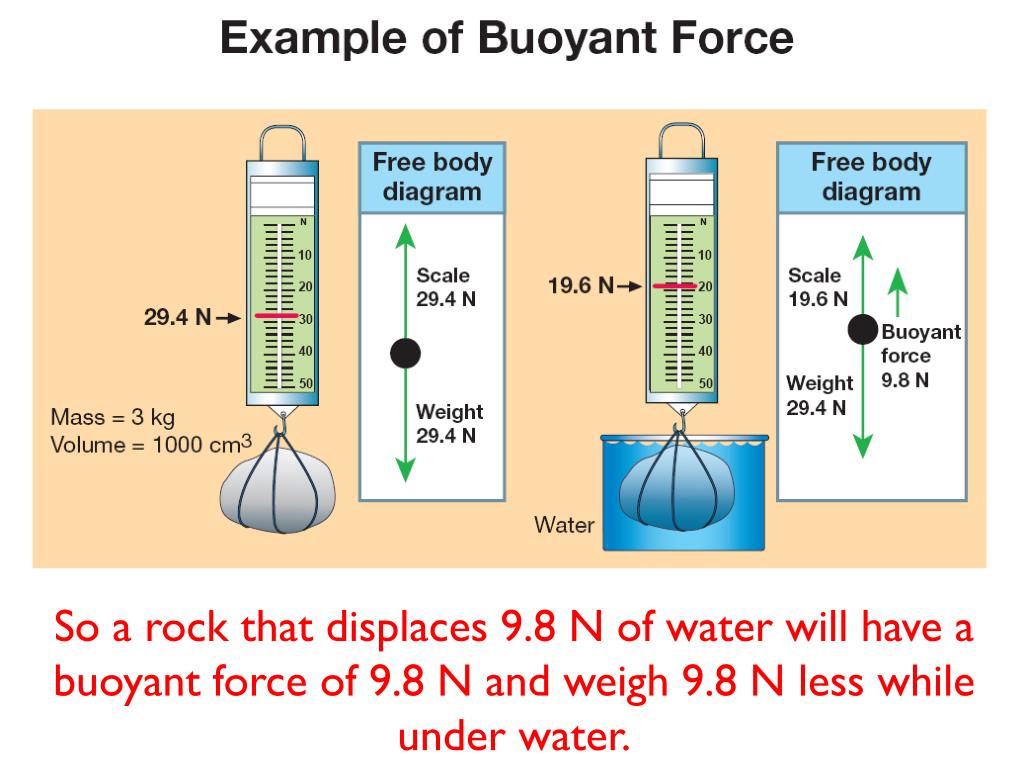
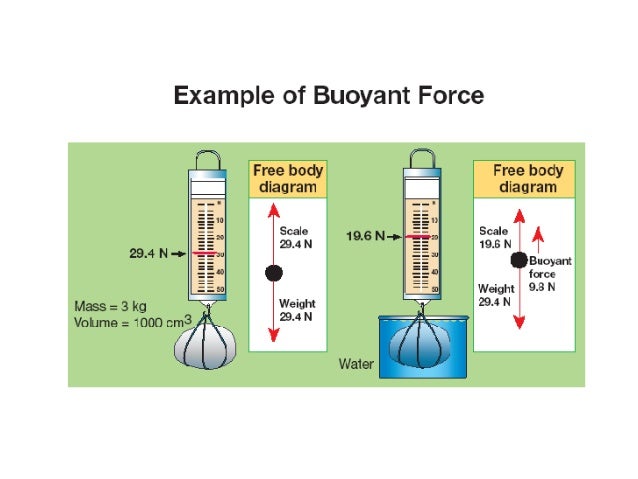
Buoyant force free body diagram. This java applet shows the free-body force diagram for a block sits on an inclined plane. Usage: Click the circle near the right edge and drag the mouse up/down to change the angle of inclination theta 。. 2. Red Arrow represents the gravitational force. ( which has two green force components). Click near the tip of the red arrow and drag the ... Lab 7 Buoyant Force & Archimedes Principle PHY250L " 3. " Apply Newton's second law to your free body diagram in Pre-Lab Question 2 to solve for the magnitude of the buoyant force. " F(buoyant)=mg F(total)=ma Total force is F(buoyant) a= gravity F(buoyant)=mg=w " Experiment 1: Effects of Density " " " Post-Lab Questions " 1. " Sketch and label what the arrangement of ... upward buoyant force to each block. Compare the free-body diagrams in Figure 9.1, when the blocks are in equilibrium on the table, with the free-body diagrams in Figure 9.4, when the blocka Chapter 9 - Fluids Page 9 - 2 Figure 9.1: A diagram of the blocks we will place in a beaker of water, and the free-body diagram Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass before it is submerged in water. Make sure to label your forces. 2. Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass after it is submerged in water. Make sure to label your forces. Which force is measured with the spring scale?
Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass after it is submerged in water. Make sure to label your forces. Which force is measured with the spring scale? Apply Newton's second law to your free body diagram in Pre-Lab Question 2 to derive a general equation for the buoyant force. Show your work. Why isn't buoyant force included on the free body diagram? It is true that air puts a small buoyant force on the child and sled. However, the size of the upward buoyant force compared to the downward force of gravity is very small. (The ratio of the two is given by the ratio of the density of air to the density of the child and sled.) Draw a free-body diagram showing all of the forces on the box. What is the force that is holding the box up, the force that is opposite the weight force? Ch. 5 #10. See chegg for diagram. Answer: Fup = 2fs - w ... The magnitude of buoyant force on an object is always equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. 3. Briefly explain the methods used in Part 1 through Part 3 of this experiment to determine buoyant force. (25 pts) 4. Draw a free-body diagram for an object of mass M, for the following two situations: a. a submerged object suspended by a string; b. a floating object. Draw to scale. (30 pts)
Archimedes' principle states that the magnitude of the buoyant force exerted on an object by a liquid is equal to the weight of the volume of that liquid displaced by the object. Use a free body diagram of a cubical block whose top is submerged a distance d to show that Archimedes' principle applies. the answer is they are simplified diagrams that are used to sh…. the answer is a vector diagram,since each force must have magn…. the answers are gravity,electrical,and magnetic. the answers are normal,buoyant,friction,air resistance tension…. what are free body diagrams. Draw a free body diagram of the aluminum block for when it was submerged in the water, or any of the other fluids because they will be identical, and then write the force summation equation for that free body diagram. Algebraically solve this equation for the buoyant force. (10 points) 11 6. Well, that's correct, but your free body diagram technically has 3 forces acting on the object: its weight down (30N), The buoyant force up (F_b), and tension in the scale's cord acting up (20N). So your FBD equation using Newtyon 1 is from which 20 + F_b -30 = 0, that is, F_b = 10N up, whuch is what you got, but don't take shortcuts.
Buoyant force free body diagram. A basketball floats in a bathtub of water. Ing the buoyant force must be greater than or equal to the weight of the object. In physics and engineering a free body diagram force diagram or fbd is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces movements and resulting reactions on a body in a given ...
Draw a free body diagram for an object of mass M, for the following two situations: a. A submerged object suspended by a string. b. A floating object.
Often a Free Body Diagram is useful or necessary to solve a problem that involves forces. Follow these steps, and you'll solve any problem with little difficulty. 1. Draw one Free Body Diagram for each object (see below for what is a good FBD). 2. Break the forces up into components. 3.
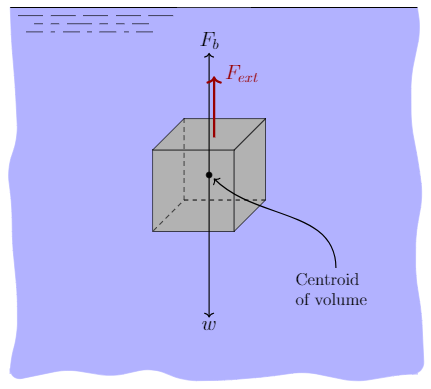
The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. This can be restated in terms of the density of the fluid, ρf, and the volume of the object, V: FB=!fgV (8-3) The free body diagram of an object submerged in a fluid under the influence of gravity is given in Fig. 8-1. Figure 0-1 The free body diagram of an object submerged in a ...
upward buoyant force to each block. Compare the free-body diagrams in Figure 9.1, when the blocks are in equilibrium on the table, with the free-body diagrams in Figure 9.4, when the blocks Chapter 9 - Fluids Page 9 - 2 Figure 9.1: A diagram of the blocks we will place in a beaker of water, and the free-body diagram
This equation, when stated in words, is called Archimedes' principle. Archimedes' principle is the statement that the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. The simplicity and power of this idea is striking. If you want to know the buoyant force on an object, you only need to determine the weight ...
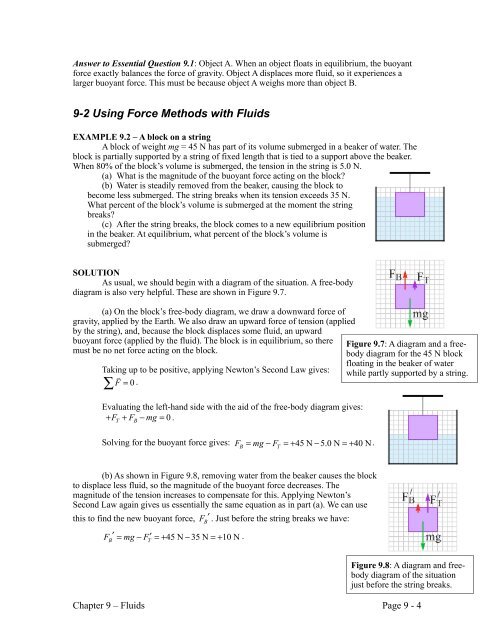
this to find the new buoyant force, . Just before the string breaks we have:. Chapter 9 - Fluids Page 9 - 4 Figure 9.7: A diagram and a free-body diagram for the 45 N block floating in the beaker of water while partly supported by a string. Figure 9.8: A diagram and free-body diagram of the situation just before the string breaks.
the water, and then write the force summation equation for that free body diagram. In the equation, let the tension in the string be the apparent weight. Algebraically solve this equation for the buoyant force. (10 points) 4.
Why isn't normal force included on the free body diagram? Normal force is the contact force between two surfaces. It pushes out from the surfaces and keeps them from falling into each other. In this case, the raft and the chests are in a fluid, and the force due to the pressure of a fluid is called the buoyant force.
Buoyant force free body diagram. This second weight called the apparent weight differs from the first due to the buoyant force. Why isnt normal force included on the free body diagram. It pushes out from the surfaces and keeps them from falling into each other. The upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid whether fully ...
Density, Buoyancy And Free Body Diagrams Updated: 7-Jan-16 Page 4 of 4 11. The red block in the "Same Volume" floats in water. The blue block sinks in water. Using your data from the chart above and your knowledge of buoyant forces and weights, what volume of the blue block would float above the water line if the blue block was placed on
A student's correct free-body diagram for an object floating in water. The students were asked to draw a free-body diagram for this situation as part of the laboratory experiment.
second weight, called the "apparent weight" differs from the first due to the buoyant force. Draw the corresponding Free Body Diagram and use it to determine the forces involved, and to solve for the density of the submerged object. Calculate the buoyant force and the density from your measurements.
forces free-body-diagram density fluid-statics buoyancy. Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow edited Oct 22 '18 at 20:21. ... Archimedes' principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially submerged, ...

Fluids We Now Turn To Exploring Fluids Some Of This Will Be New But Much Of It Will Involve Applications Of Familiar Ideas Like Newton S Second Law Ppt Download
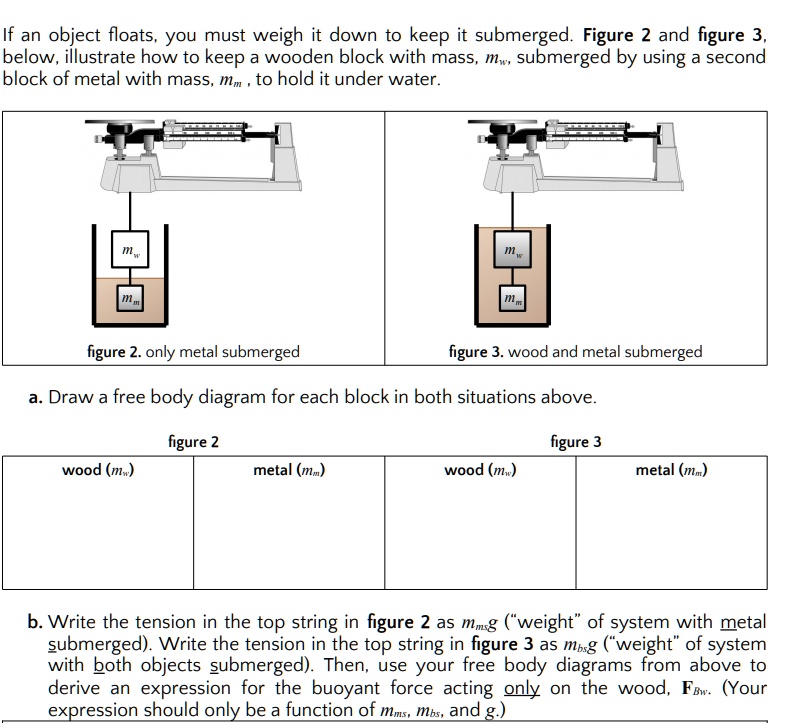
Solved If An Object Floats You Must Weigh It Down To Keep It Submerged Figure 2 And Figure 3 Below Iilustrate How To Keep A Wooden Block With Mass Mws Submerged By Using

Archimedes Principle Vector Illustration Buoyant Force Physics Experiment Explanation Immersed Body In Fluid Is Equal To Displaced Weight Educational Liquid Mechanics Law Visualization Diagram Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration



















0 Response to "45 buoyant force free body diagram"
Post a Comment