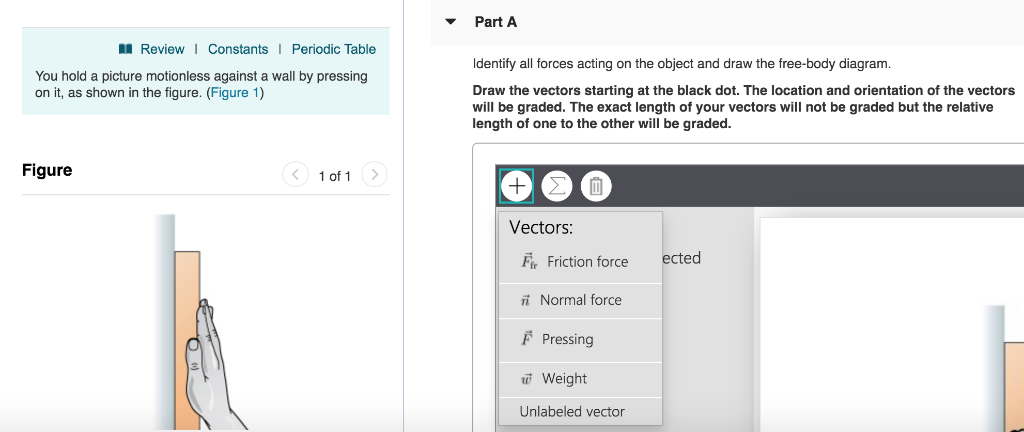
44 identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram.
A free-body diagram is a visual representation of an object and all of the external forces acting on it, so to draw one you'll have to have this information calculated. They are very important for working in engineering or physics problem solving since drawing them helps you to understand what is going on in a problem. Draw a free body diagram of the system skydiver parachute.. Part a identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free body diagram. It is a drawing of a system and the loads acting on it. Black dot is mid screen. He free body diagramis the most im portant tool in this book.
A free body diagram is defined as an illustration that depicts all the forces acting on a body, along with vectors that are applied by it on the immediate environs. Apart from the acting forces and subsequent work done, the moment magnitudes are also considered to be a part of such diagrammatic representations.
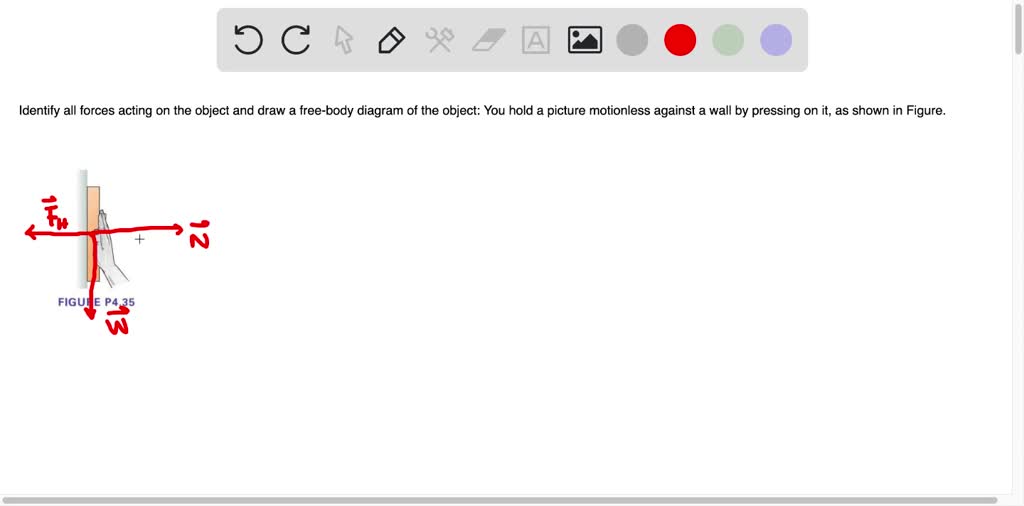
Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram.
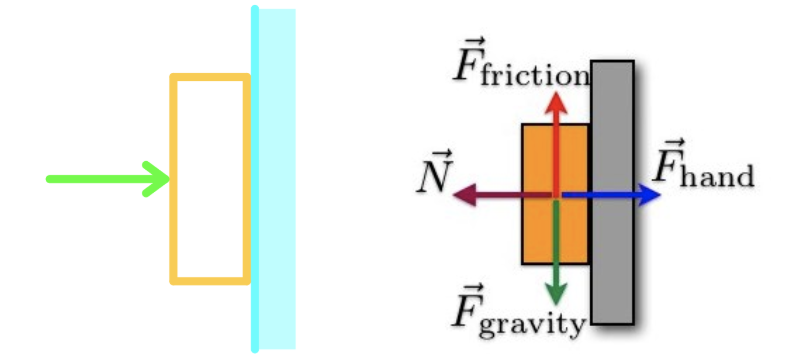
A free body diagram models the forces acting on an object. The object or 'body' is usually shown as a box or a dot. The forces are shown as thin arrows pointing away from the centre of the box or ... Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. Draw a free-body diagram of a bag of sugar being lifted by your hand at a constant speed. Specifically identify the system. Label all forces with their agents and make the arrows the correct lengths.
Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram.. Only forces acting on the object should be shown, since you are trying to understand what causes the motion of the object. The free body diagram maps directly into the left side of ∑F=ma. Acceleration is the result not the cause—if you wish to sketch the acceleration, make sure that you do so off to the side and not on the sketch of forces. 1 identify all forces acting on the object. Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free body diagram. 3 represent the object as a dot at the origin of the coordinate axes. Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free body diagram. Free body diagrams closed your car is accelerating to the right from a stop. Draw a careful sketch of the situation. Determine the system of interest. Draw a free-body diagram. That is, draw and label all external forces acting on the system of interest. Identify the pivot point. If the object is in equilibrium, it must be in equilibrium for all possible pivot points––chose the one that simplifies your work the most. We must draw a separate free-body diagram for each object in the problem. A free-body diagram is a useful means of describing and analyzing all the forces that act on a body to determine equilibrium according to Newton's first law or acceleration according to Newton's second law.
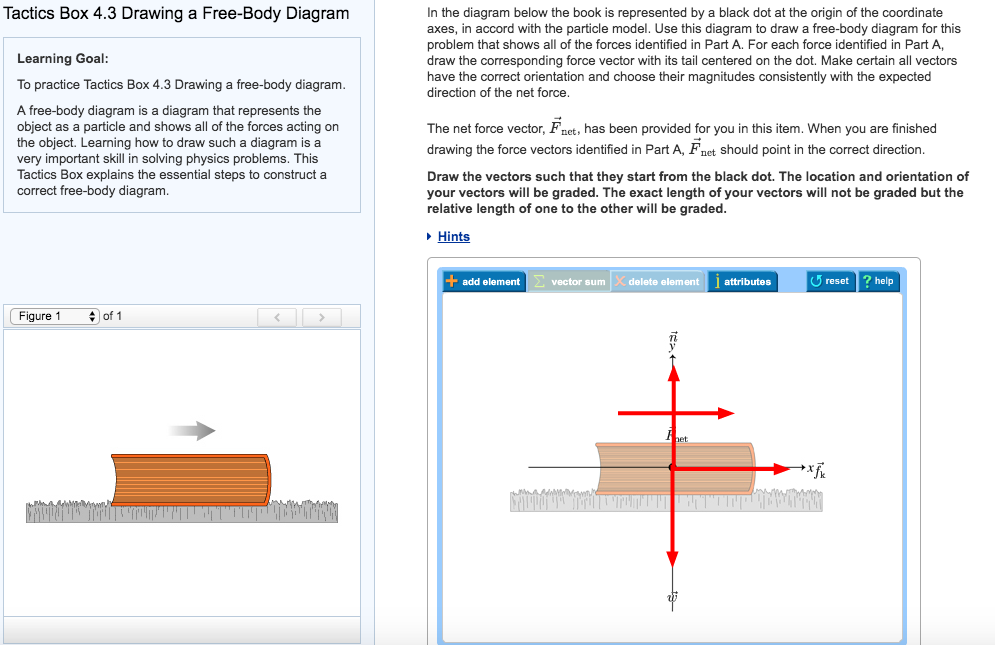
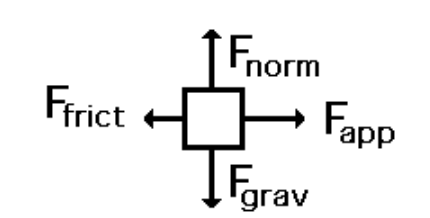
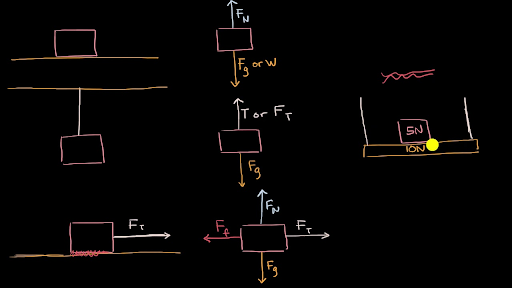
Free Body Diagrams (FBD) are useful aids for representing the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. The first step in analyzing and describing most physical phenomena involves the careful drawing of a free-body diagram. Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... To draw a free-body diagram use the following steps: Isolate the object of interest. It is customary to represent the object of interest as a point in your diagram. Identify all the forces acting on the object and their directions. Do not include forces acting on other objects in the problem. Also, do not include quantities, such as velocities ... Transcribed image text: Drawing a free-body diagram Identify all forces acting on the object. This step was described in Tactics Box 5.2. Draw a coordinate system. Use the axes defined in your pictorial representation. If those axes are tilted, for motion along an incline, then the axes of the free-body diagram should be similarly tilted.
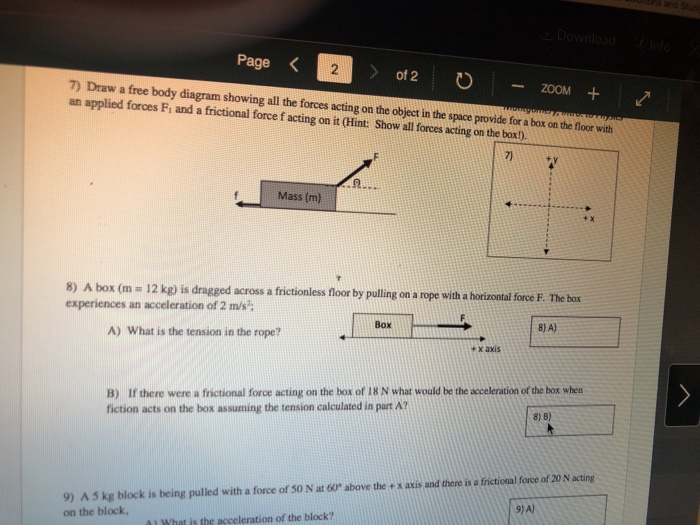
combination of all the forces acting on an object 5N 5N 5N 5N 5N 10 N Net Force = 10N East ... Draw a free-body diagram. (Neglect air friction) The force of gravity is the only force described. (no air resistance). Problem 8 A car runs out of gas and is coasting down a hill. Find step-by-step Physics solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: For the problem, identify all the forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram of the object. An ascending elevator, hanging from a cable, is coming to a stop.. And to be clear, this five newtons, this is equal to the weight, the magnitude of the weight of the object. So that was pretty straightforward, the free body diagram for just the block. And it's really important to see that, because notice, in the free body diagram, all you see is the block. But now let's draw the free body diagram for the shelf. How to draw free body diagram. Step 1: Draw the object with no extra features. Step 2: Identify the forces acting on the box. The box has mass, so it should also have weight, and a force acting downward. Because the stationary box is on a surface, there is a normal force that acts perpendicular to the surface.
A force diagram is simply a diagram showing all the forces acting on an object the forces direction and its magnitude. We must draw a separate free body diagram for each object in the problem. The length of the vectors will not be graded.
Unit 3, introduction to forces worksheet 5, forces in equilibrium answers. Unit 3, introduction to forces worksheet 5, forces in equilibrium answers.
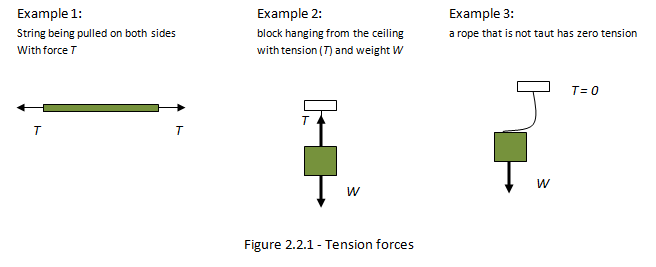
A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
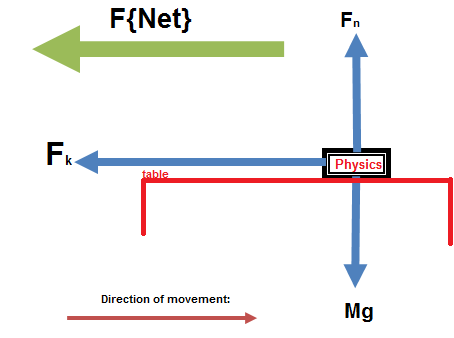
Identify all Forces. Vita August 12, 2012 General Physics 0 Comments 3139 views. Your physics textbook is sliding to the right across the table. Identify all forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram. Your physics textbook is sliding to the right across the table.
A free body diagram is used to calculate static and dynamic forces acting on an object. In other words, a free body diagram is the starting point to develop a mathematical model to find and calculate various forces acting on a body. The purpose of the free body diagram is to simplify the situation for easy analysis. Figure :1.
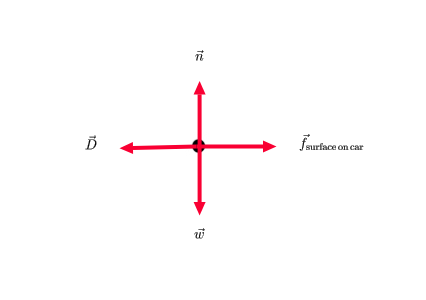
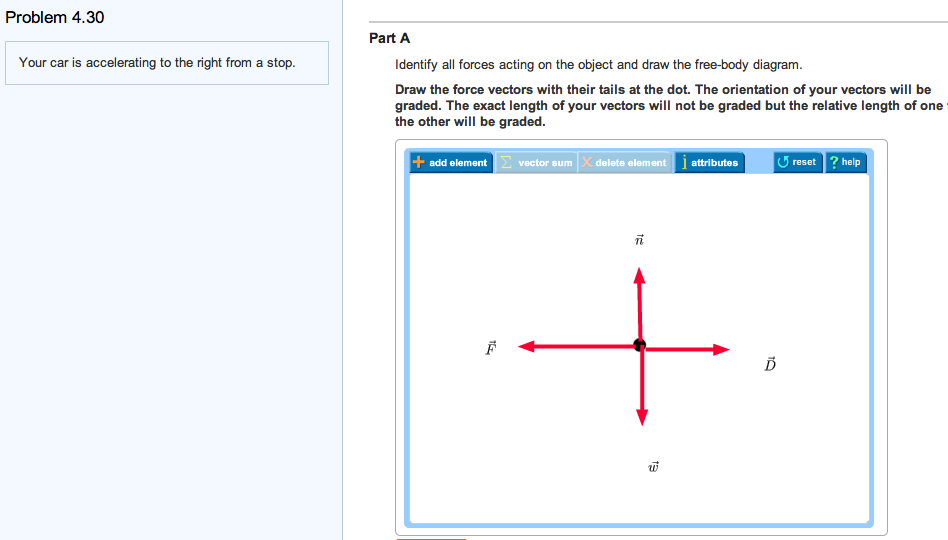
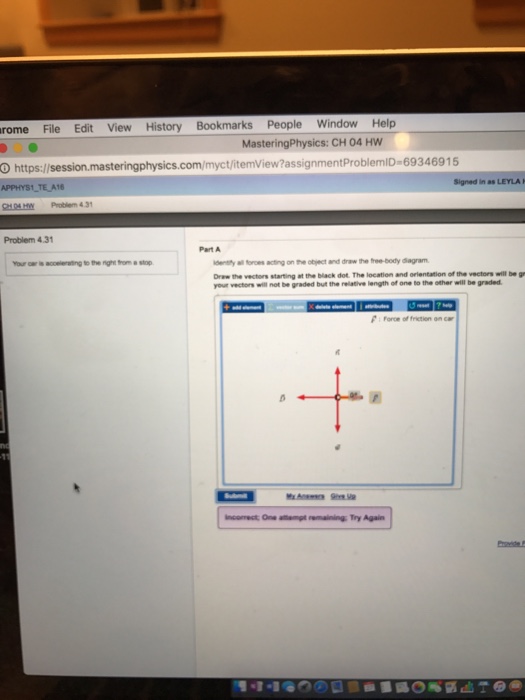
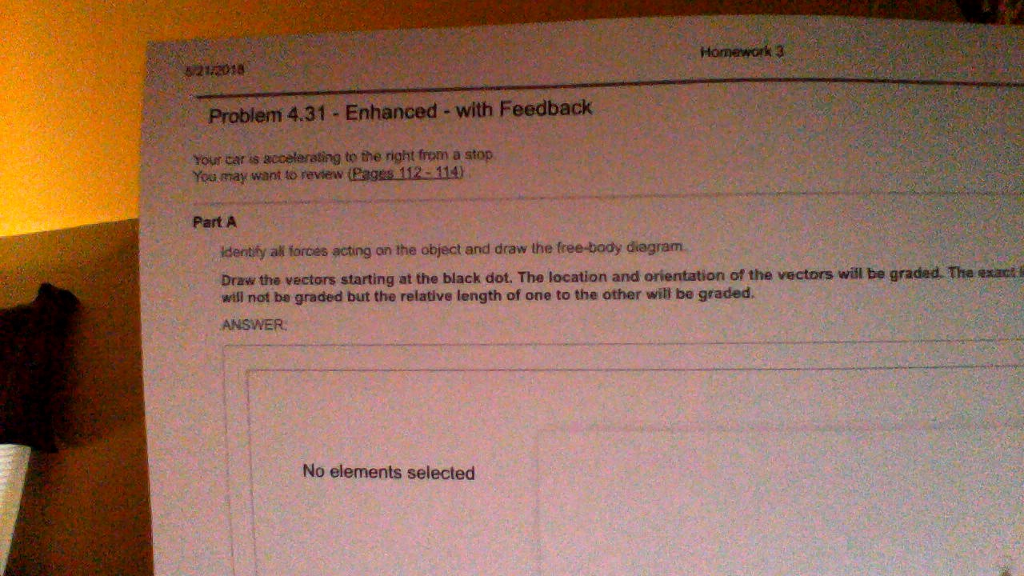
FREE Expert Solution. The weight acts downward. The normal force acts upward. 90% (64 ratings) Problem Details. Your car is accelerating to the right from a stop. Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram. Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot. Frequently Asked Questions.
Identify all the forces acting on the system skydiver parachute. Draw a free body diagram use the fact that upthrust weight of water displaced. There is an arrow up for air resistance and an arrow down for gravity. An example of a free body diagram is shown at the right. Part a identify all forces acting on the object and draw the freebody diagram.
Draw a free body diagram ... Identify all the forces and show a free-body diagram. Thrust, F⃗ thrust Kinetic friction force, f⃗ k ... At this moment, what can we say about the frictional force acting on the box of cereal? There is a static frictional force pointing in the box's direction of motion, parallel to the conveyer belt. ...
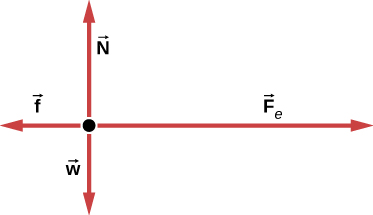
It helps to look at a new free-body diagram showing all horizontal and vertical components of each force acting on the system (). Figure 5.27 When the vectors are projected onto vertical and horizontal axes, their components along these axes must add to zero, since the tightrope walker is stationary.
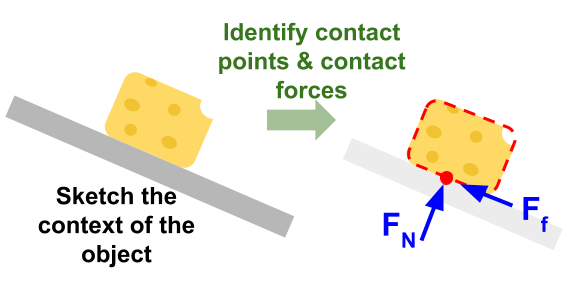
The strategy for identifying all the interactions and then identifying all the forces (and the direction of those forces) is to construct a "free body" diagram. A free body diagram considers the body to be free of the rest of the environment, with all interactions on the body replaced by each of the forces acting on it. There are often numerous ...
The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn.
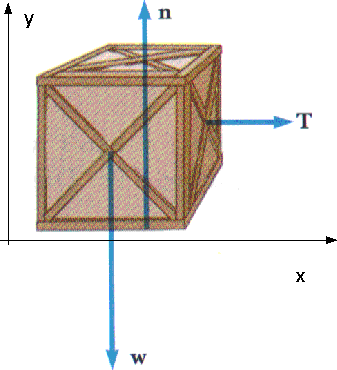
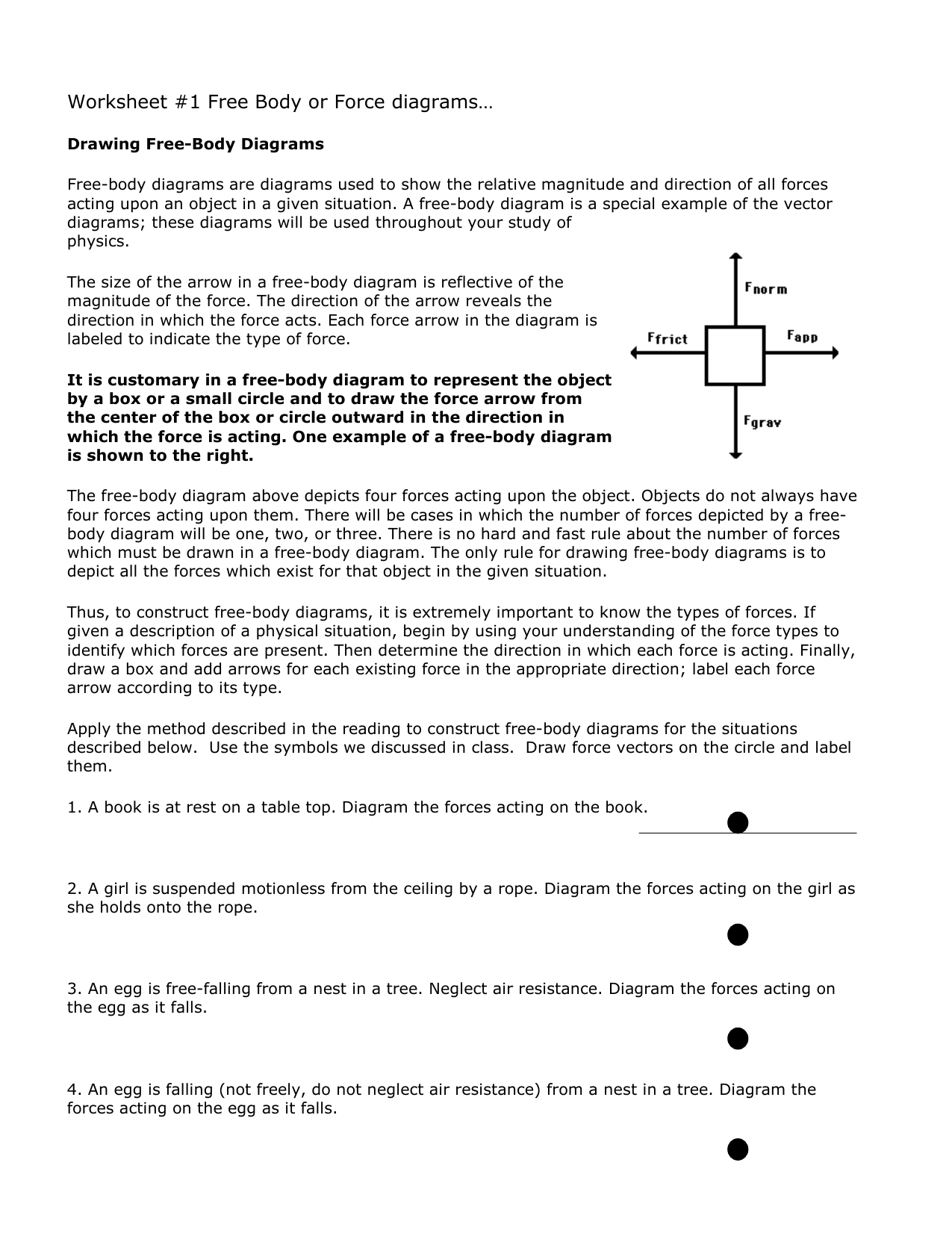
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
14.06.2021 · Calculate the net force acting on your object. A net force is an unbalanced force. If you have two forces opposing each other and one is larger than the other, you will have a net force in the direction of the larger force. Acceleration happens when an unbalanced force acts on an object, causing it to change speeds towards the direction the force is pushing or pulling it.
Your car is accelerating to the right from a stop. Identify all forces (normal, weight, friction, drag) acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram.
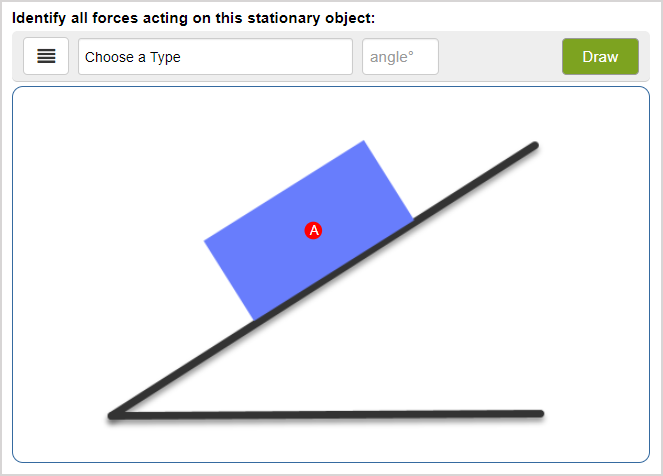
Draw the free-body diagram, showing all the forces acting on the box. View Answer A crate sits on a frictionless ramp that makes an angle of 30 degrees to the horizontal.
Identify; Draw a Picture; Select the Relation; Solve; Understand; In this problem, you are asked to relate motion (of the cartons) to force (the friction between them). Force and motion of a single object are always related through Newton’s Second Law, so this is a force or 2nd Law problem. In addition, note that you must treat the two cartons as separate systems. You don’t know if they ...
Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams Drawing Free-Body Diagrams Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation, A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams; these diagrams will be used throughout your study of physics.
object by using your hand to give either object an acceleration; that is, try to change the objects velocity. 11. Free-Body Diagram Draw a free-body dia-gram of a bag of sugar being lifted by your hand at a constant speed. Specifically identify the system. Label all forces with their agents and make the arrows the correct lengths. 12.
Draw a free-body diagram of a bag of sugar being lifted by your hand at a constant speed. Specifically identify the system. Label all forces with their agents and make the arrows the correct lengths.
Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded.
A free body diagram models the forces acting on an object. The object or 'body' is usually shown as a box or a dot. The forces are shown as thin arrows pointing away from the centre of the box or ...

Draw A Free Body Diagram Fbd To Show Various Forces Acting On A Body Which Is Sliding On An Brainly In
Solved Te To Keep Up To Date With Security Updates Fixes And Improverents Choose Check For Updates And The Vertical Is 1587 Note Refer To The Sketch To The Right The Sketch Shows One Rider
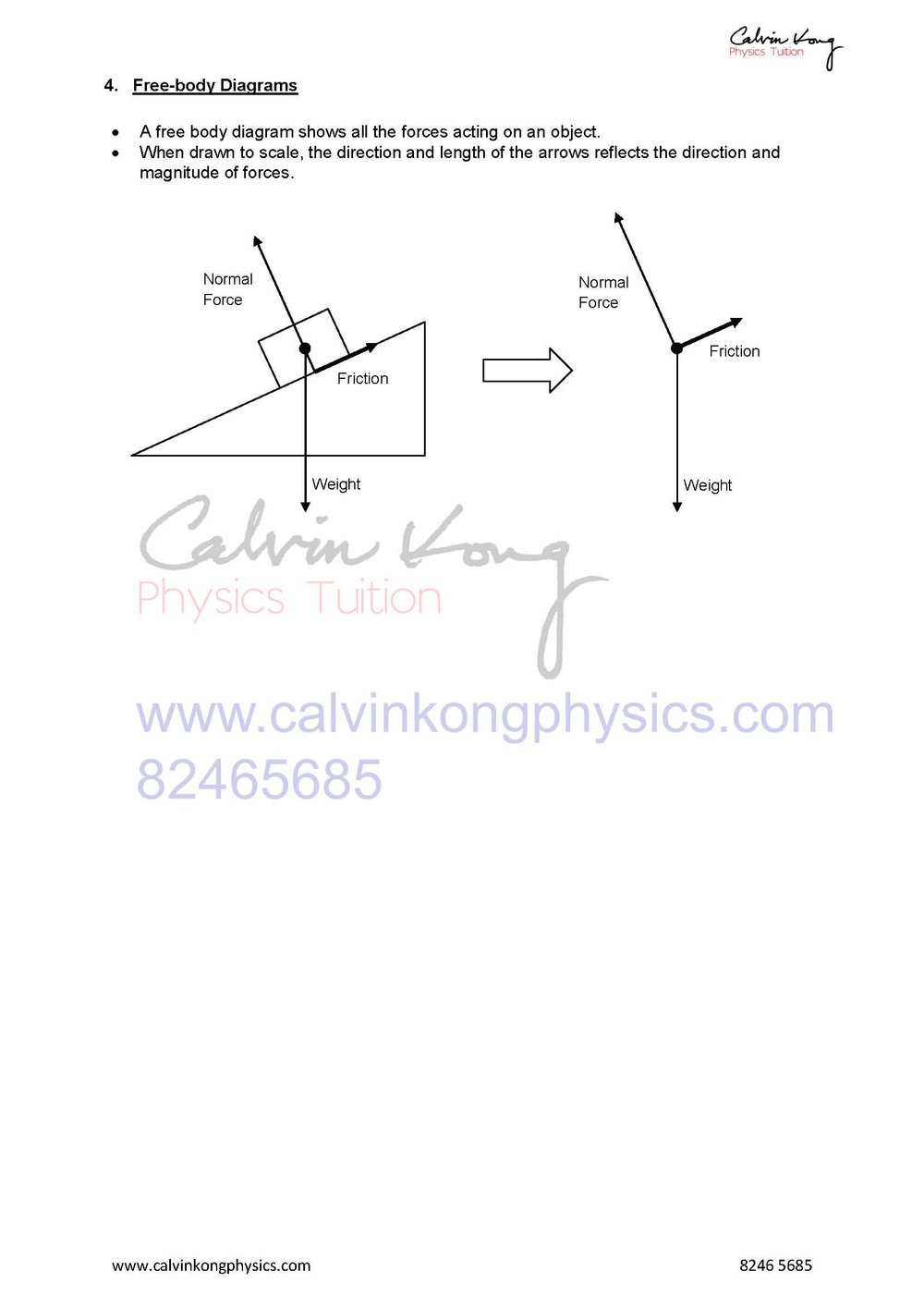
3 4 Types Of Forces And Free Body Diagrams Physics Tuition Centre O Level A Level And Integrated Programme Ip















0 Response to "44 identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram."
Post a Comment