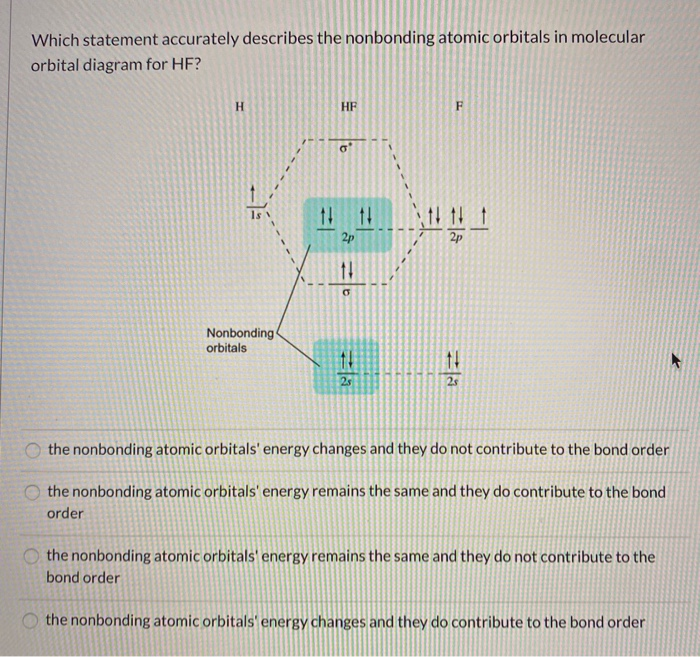
44 hf molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked on the sides by constituent AO energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels ranging from low energy at the bottom to high energy at the top. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Assuming the molecular orbital diagram in Figure 9.16 applies to BrO, write its electron configuration (where Br uses $4 s$ and $4 p$ orbitals). What is the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) for the molecule? Check back soon!

Hf molecular orbital diagram
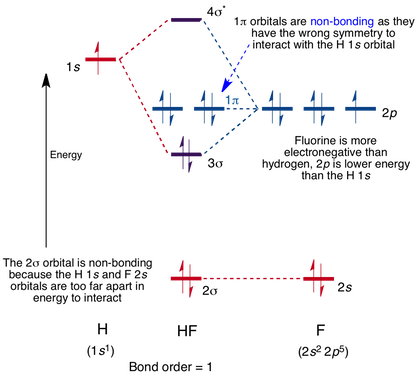
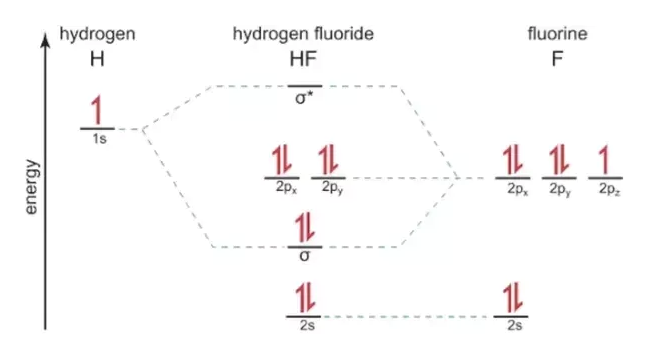
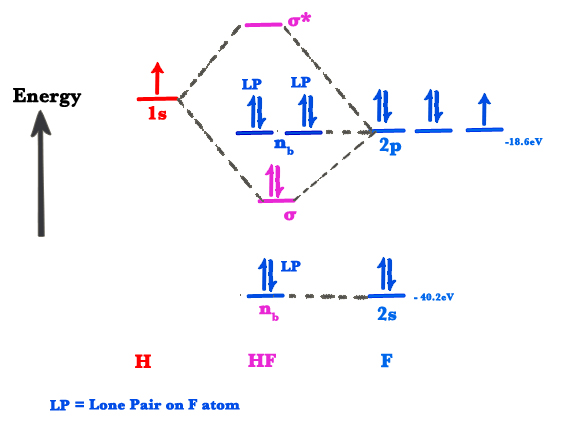
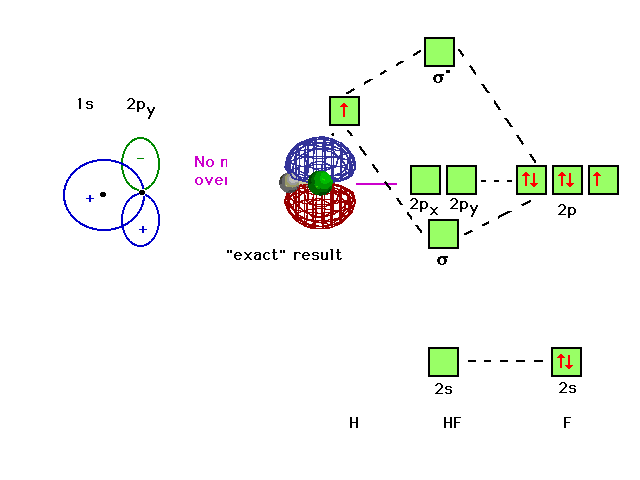
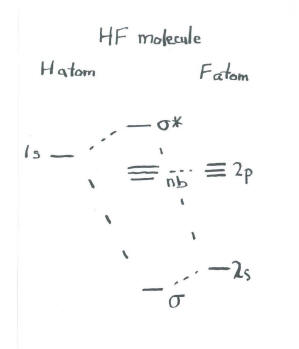
So, in MO diagrams for halogen acids (HF, HCl, etc.), the hydrogen's 1s orbital is shown to interact with a p_z_ orbital to form the molecular orbitals. However, 1s is symmetric to inversion, while p_z_ is anti-symmetric to inversion. From what I know orbitals with different symmetry cannot interact to form MO...I've been googling and combing through textbooks for an hour, what am I missing? edit: clarification, formatting. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Figure 10. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons. Molecular Orbitals for Heterogeneous Diatomic Molecules. Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves). Contributors and Attributions.
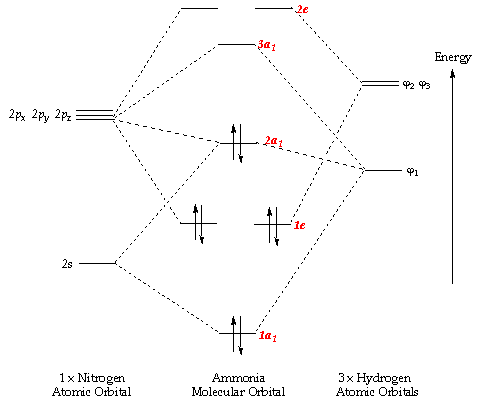
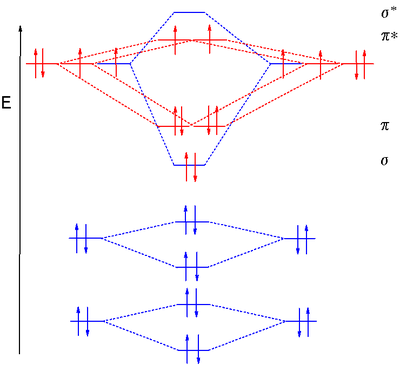
Hf molecular orbital diagram. See also: Molecular orbital theory and Molecular orbital diagram. In hydrogen fluoride HF overlap between the H 1s and F 2s orbitals is allowed by symmetry but the difference in energy between the two atomic orbitals prevents them from interacting to create a molecular orbital. 26 Molecular Orbital Diagram (HF). 27 Energy Levels in HF This diagram shows the allowed energy levels of Valence MOs Energy Levels in HF This 30 Molecular Orbital Diagram (CH4) So far, we have only look at molecules with two atoms. MO diagrams can also be used for larger molecules. A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row Figure 7.14 Molecular orbital energy level diagram for first-row homonuclear diatomic molecules. The 2p, 2py, 2p atomic orbitals are degenerate in an atom and have been separated for Figure 14.1 Schematic molecular-orbital energy level diagram for the molecule O2 in its ground state
H HF F Molecular Orbital Diagram (CH4) So far, we have only look at molecules with two atoms. MO diagrams can also be used for larger molecules. Molecular Orbital Theory MO diagram for F2 You will typically see the F F2 F diagrams drawn in this way. 3σ * The diagram is only showing the u... I know how to draw MO diagrams for certain bonds like NF and CN-, but I don't know how to draw an MO diagram for a bond between a first period element and a second period element. Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive...
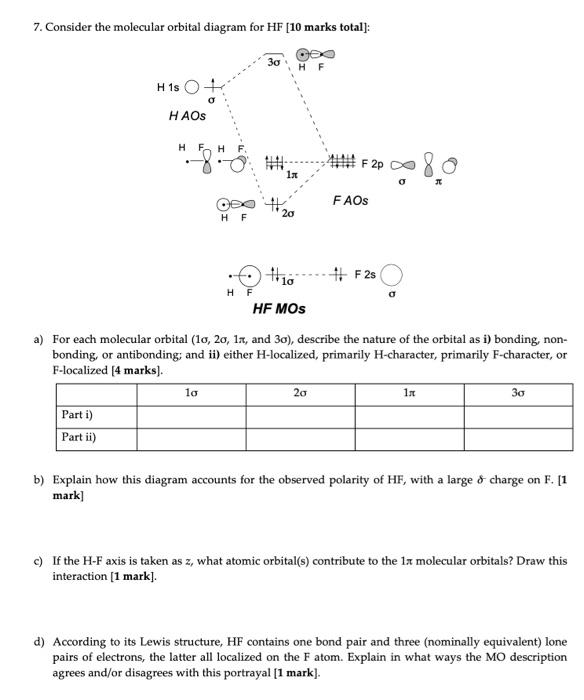
Hydrogen fluoride molecule hf molecule for making any energy level diagram we need to know how many electrons are in a moleculein ca... Hf Molecular Orbital Diagram. Written By JupiterZ Thursday, August 27, 2020 Add Comment Edit. 45 Straightforward How To Draw Bond Order Diagram. Analytic First Derivatives Of Floating Occupation Molecular. Frontiers Molecular Orbital Insights Of Transition Metal. The Crossover. Orbitals. Accordingly, a molecular orbital diagram such as Figure 9-5 is inappropriate for heteronuclear diatomic molecules. If the two elements are Figure 9-8 Formation of sp and s#p molecular orbitals in HF by overlap of the 1s orbital of H with a 2p orbital of F. hydrogen 1s. fluorine 2px. Transcribed image text : The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F This leaves the 2s and two of the 2p orbitals of F as nonbonding orbitals. Complete this molecular-orbital diagram for HF (click on the...
Line Chart. Diagram. Molecular Orbital Diagram of HF.
Download scientific diagram | Qualitative molecular orbital diagram of HF −. The qualitative molecular orbital diagram, as depicted in Fig. 2, also shows the two-center three-electron (2c-3e) σ half-bonding character of HF − (X 2 Σ + ). The 2c-3e hemibonds have in common with electron rich...
As in case of hf hydrogen atoms orbitals combines with that of flourine thus forming molecular orbitals of hf. The molecular orbitals forme...
The bonding molecular orbital is fully filled with two electrons .The rest of the electrons remain in their atomic orbitals. The symmetry occurs because the energies of H(1s) and F(2pz) atomic orbitals are not the same.Molecular orbital diagram for HF molecule is given as.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
Molecular Orbital Theory IV: Period 2 Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules. Molecular Orbital Diagrams Heteronuclear Diatomic HF.
Molecular orbital energy diagram showing the mixing of bonding C-H orbital with anti-bonding C-Cl orbital.png 1,066 × 786; 17 KB. Molecular Orbitals for Water.png 1,249 × 1,620; 137 KB. Molecule HOMO-LUMO diagram.svg 464 × 352; 124 KB.
Molecular electron configuration for o2 σ2σ2σ2π4π2 we can also calculate the oo bond order. Molecular orbitals in hydrogen fluoride hf.
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. We use the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's rule to fill the orbitals in an Aufbau process. The molecular orbital diagram for B₂ then becomes.
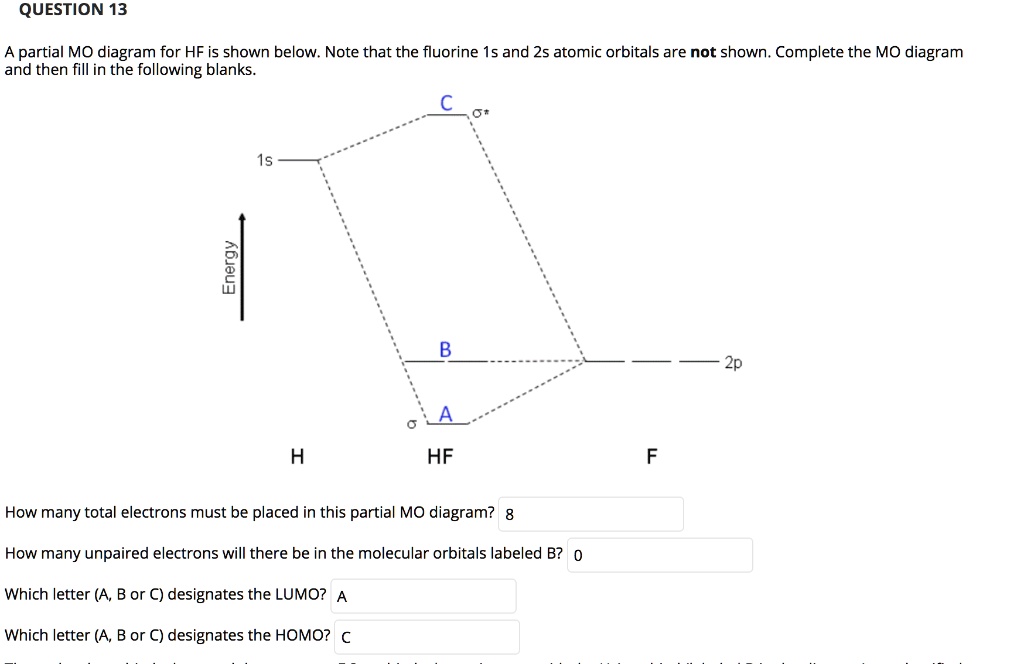
Solved Question 13 A Partial Mo Diagram For Hf Is Shown Below Note That The Fluorine 15s And 2s Atomic Orbitals Are Not Shown Complete The Mo Diagram And Then Fill In The
• Molecule orbital theory (Robert Mullikan). • Electrons are delocalised - Different to Lewis and - Molecular orbital are formed by addition and subtraction of AO's. Æ Linear Combination of Atomic 4. Perform the same analysis for BeH2, HF, BH3, and CH4. 5. Use molecular orbital theory to explan...

Molecular Orbitals Of Heteronuclear Diatomics The Molecular Orbitals Of Heteronuclear Diatomics Hf Co Cn Etc Can Be Predicted Using The Same Principles Ppt Download
8 hours ago Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF.
Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. So when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon.
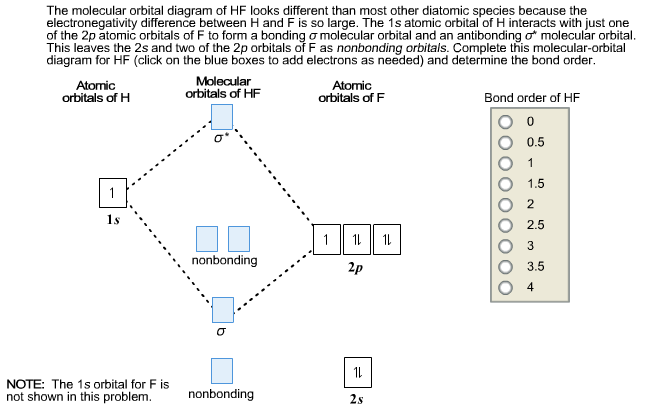
Transcribed Image Text. The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding o molecular orbital and an...
Molecular Orbitals for Heterogeneous Diatomic Molecules. Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves). Contributors and Attributions.
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Figure 10. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons.
So, in MO diagrams for halogen acids (HF, HCl, etc.), the hydrogen's 1s orbital is shown to interact with a p_z_ orbital to form the molecular orbitals. However, 1s is symmetric to inversion, while p_z_ is anti-symmetric to inversion. From what I know orbitals with different symmetry cannot interact to form MO...I've been googling and combing through textbooks for an hour, what am I missing? edit: clarification, formatting.
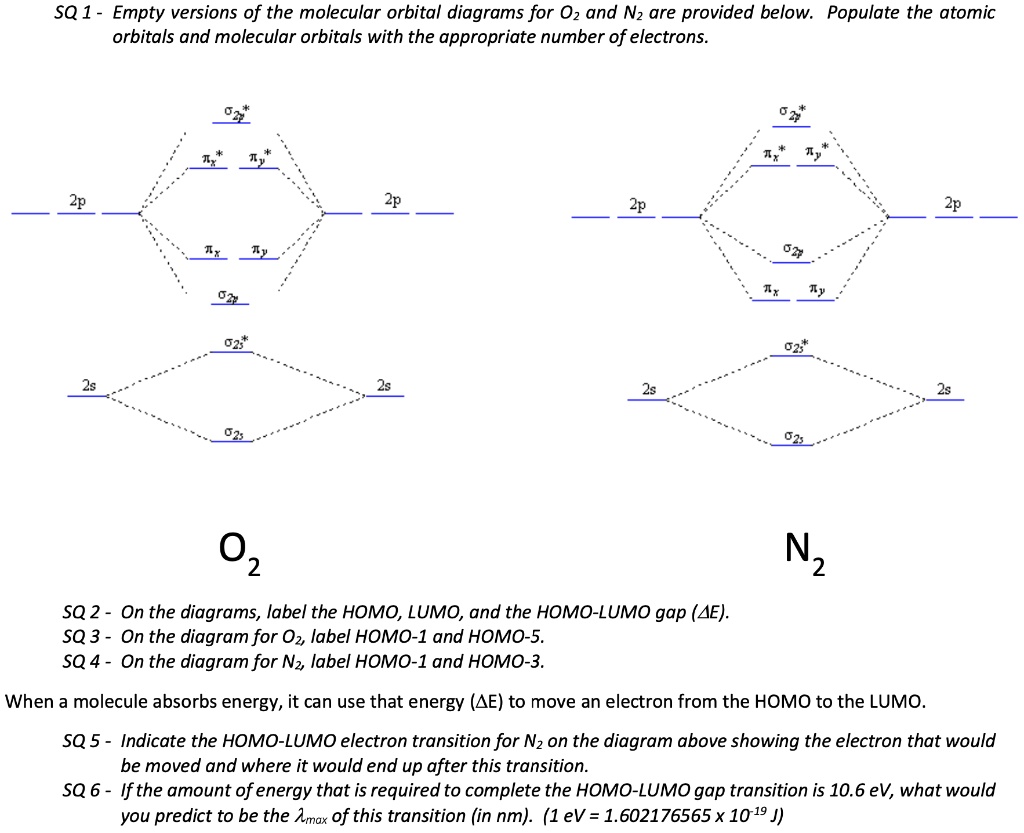
Solved Sq 1 Empty Versions Of The Molecular Orbital Diagrams For 02 And Nz Are Provided Below Populate The Atomic Orbitals And Molecular Orbitals With The Appropriate Number Of Electrons 2p 0z Nz

Oneclass The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Hf Looks Different Than Most Other Diatomic Species Becaus

Chem 102 Workshop 08 Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams Key Fall 2014 General Chemistry 1 Workshop 8 Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams Key Molecular Course Hero


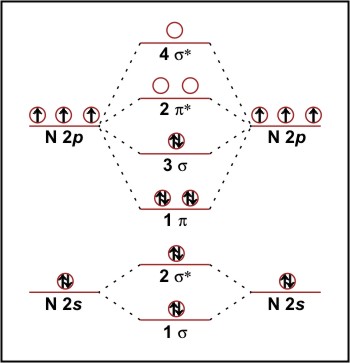














0 Response to "44 hf molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment