44 aerobic cellular respiration diagram
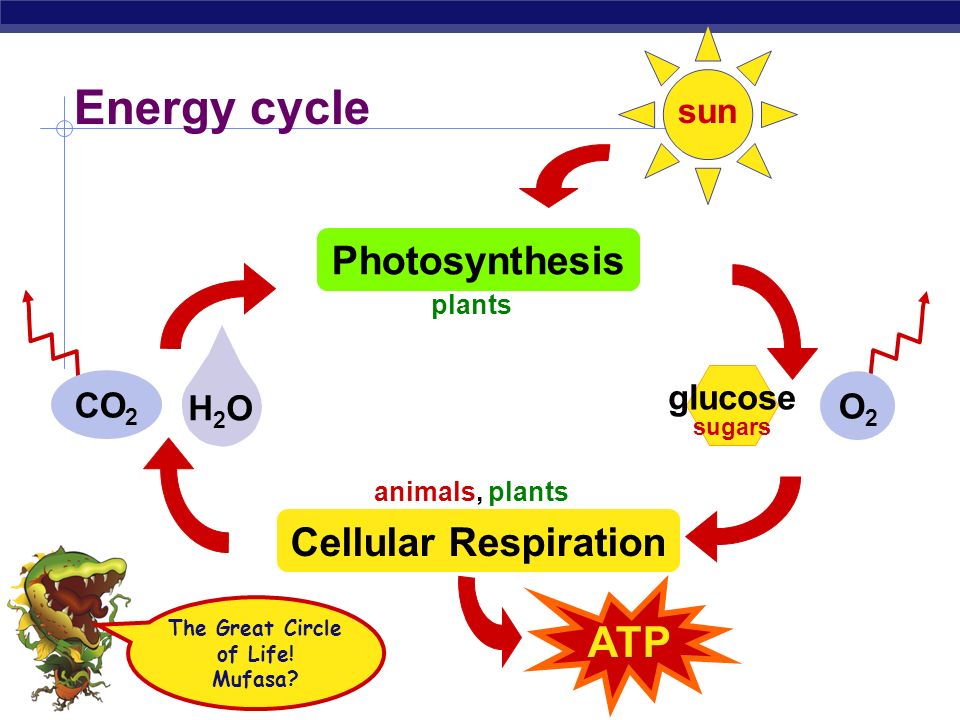
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration venn diagram usa test prep You need to know how photosynthesis and cellular breathing are connected (which one's products are the reagents of the other). You must know the reagents, products and basic functions of photosynthesis, aerobic and anaerobic breathing. Start studying AEROBIC CELLULAR RESPIRATION (DIAGRAM). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
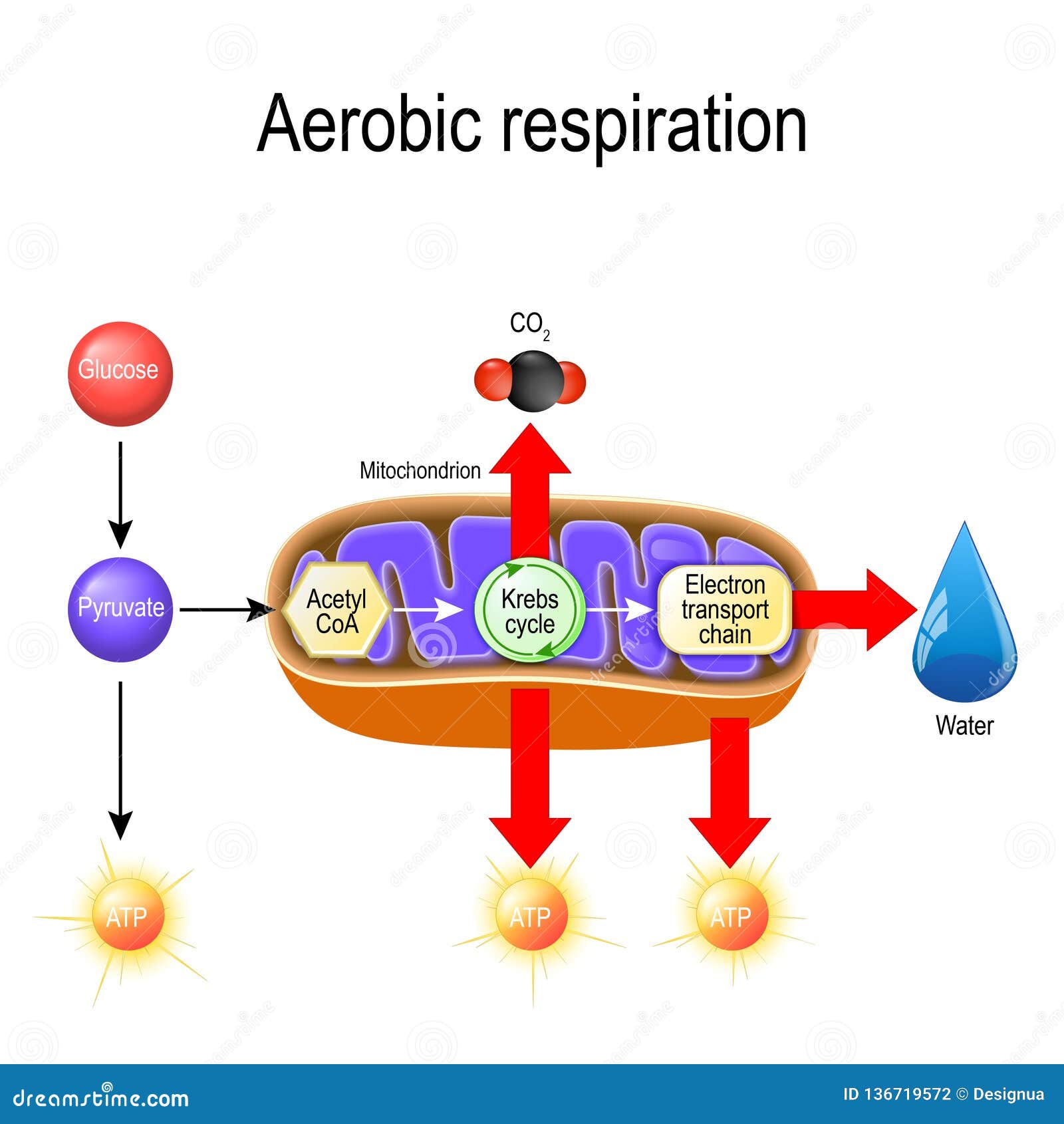
Aerobic respiration is a biological process that takes energy from glucose and other organic compounds to create a molecule called Adenosine TriPhosphate (ATP). ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system.

Aerobic cellular respiration diagram
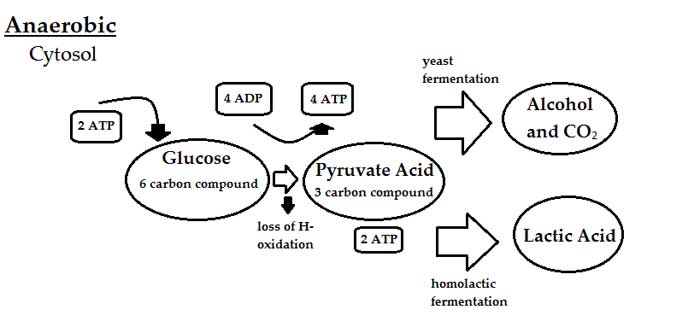
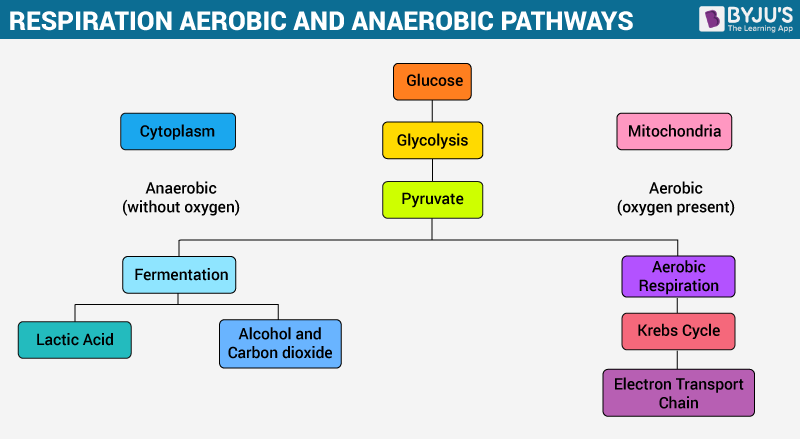
Aerobic implies that the process requires oxygen. In contrast, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. The Venn diagram compares aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. mcjpg Which statement could b Get the answers you need. The by-product of this process produces carbon dioxide along with ATP - the energy currency of the cells. Aerobic Respiration: The Krebs Cycle ª Review: During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is split to form two pyruvate molecules, with a net profit of two ATP. The two pyruvate molecules then enter the mitochondria, where they are converted to acetyl CoA. Cellular Respiration: (2 kinds—Aerobic and Anaerobic) •Cellular respiration is the process by which the energy of glucoseis released in the cell to be used for life processes (movement, breathing, blood circulation, etc…)
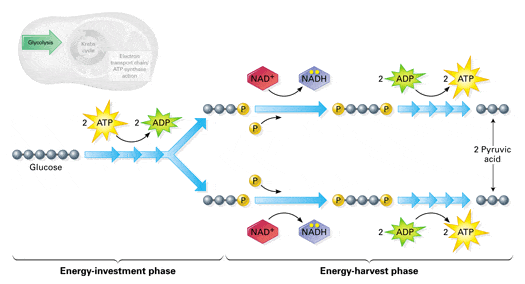
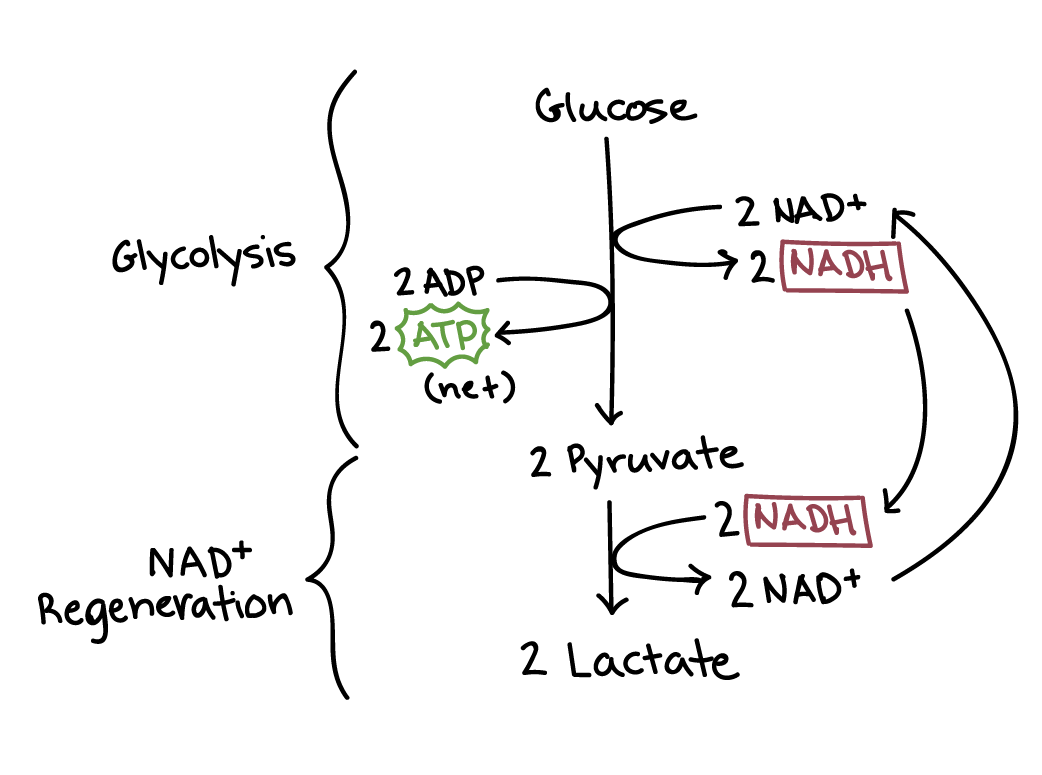
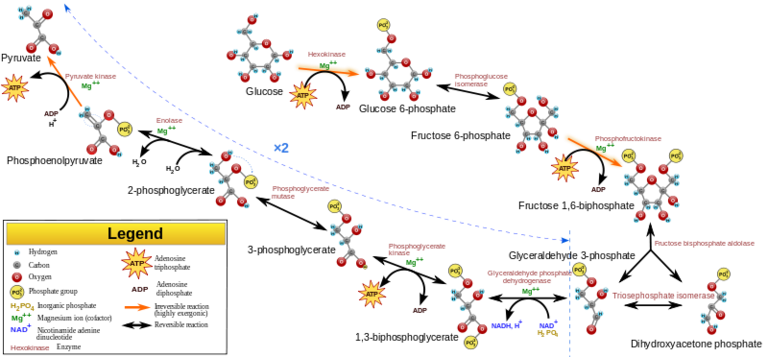
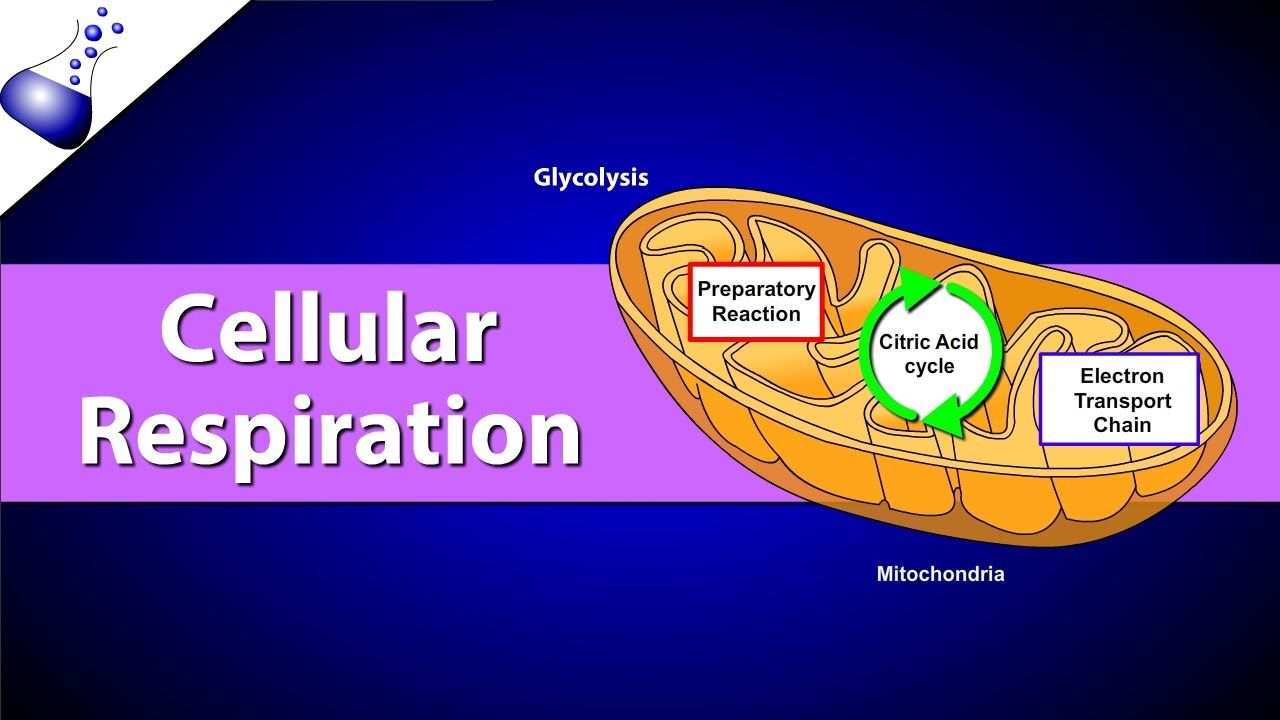
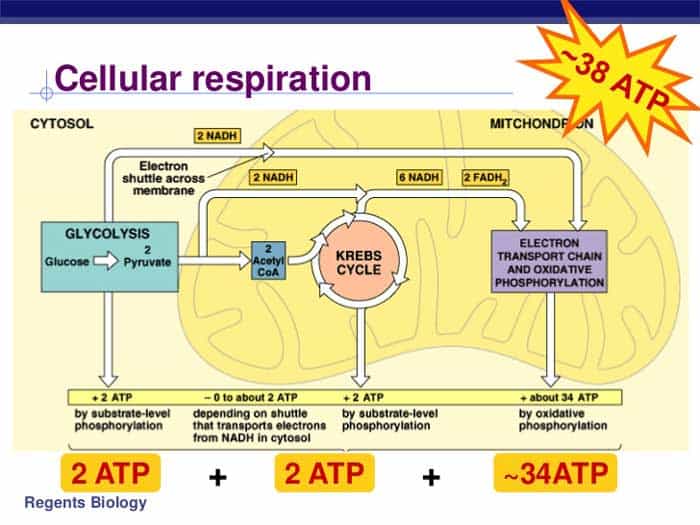
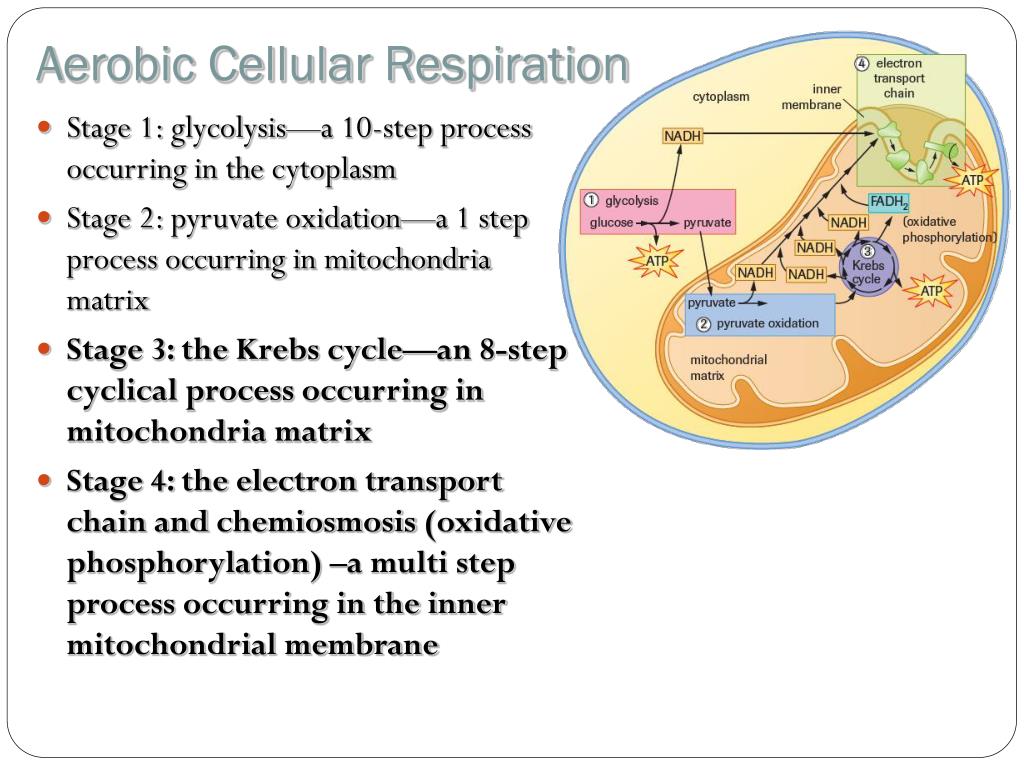
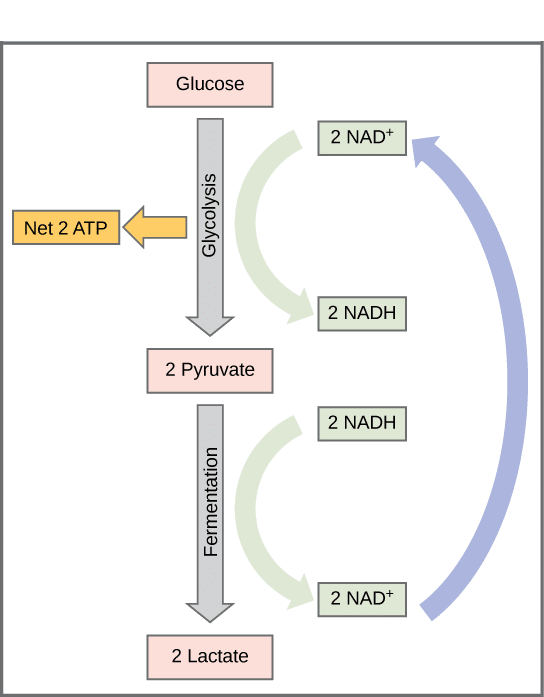
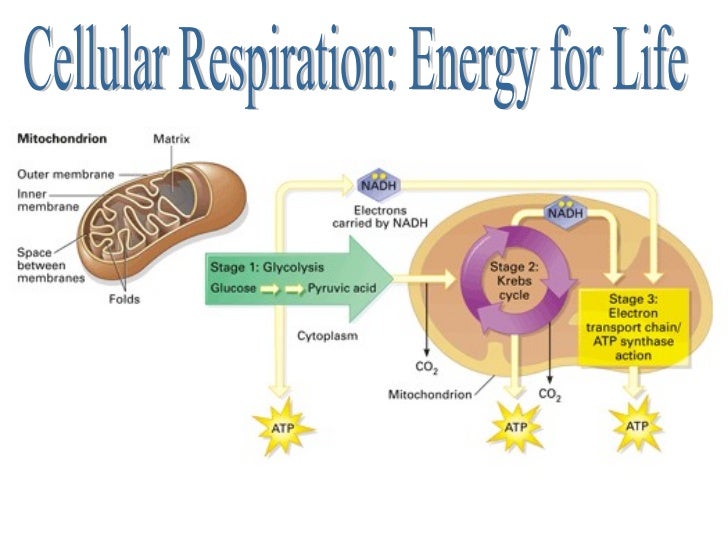
Aerobic cellular respiration diagram. Jun 12, 2021 — Aerobic Respiration; Photosynthesis Equation; Cellular Respiration ... As shown in the above diagram, glycolysis takes place in the cytosol. For the cellular respiration diagram, see the next section below. ... Below are examples of aerobic respiration and anaerobic cellular respiration: lactic ... Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ... What is Cellular Respiration? Cellular or Aerobic (in air) Respiration is a series of chemical reactions in the mitochondrion where molecules of glucose are broken down to make CO 2, water, and ATP. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water 38 ATP
Aerobic cellular respiration refers to the process by which living organisms convert nutrients into energy for the body to use via the oxidization of nutrients. During aerobic respiration, catabolic reactions convert larger complex organic molecules into ATP, the chemical that drives most physiological processes in the body.In other words, respiration is the key way that a cell gets chemical ... Start studying Respiration Diagram, Cellular Respiration. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Feb 29, 2012 — Identify advantages of aerobic and anaerobic respiration. ... This is clear from the diagram in Figure below. The products of photosynthesis ... Organelle found in all organisms that is the site of aerobic cellular respiration. ... Krebs Cycle. Step in aerobic respiration that takes pyruvate from glycolysis to produce carbon dioxide and high energy electrons. Takes place in mitochondria. Net gain of 2 ATP. ... Diagrams. Flashcards. Mobile. Help. Sign up. Help Center. Honor Code ...
Organelle found in eukaryotic organisms that is the site of aerobic cellular respiration. Krebs Cycle Step in aerobic respiration that takes pyruvate from glycolysis to produce carbon dioxide and high energy electrons. Analysis of diagrams of the pathways of aerobic respiration to deduce where decarboxylation and oxidation reactions occur. Aerobic Respiration and Fermentation (With Diagram) The reactions of glycolysis have no specific requirement for oxygen. Oxidation reactions do occur, such as the removal of two hydrogen's from glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate, and NAD + is reduced to NADH, but oxygen per se is not consumed. Aerobic cellular respiration is a part of cellular respiration, and it plays an important role in producing the energy that is required for various functions of a cell. All organisms are made up of tiny cells which carry out various functions. Energy is required for processing these functions. This energy is provided by the cells, and is ...
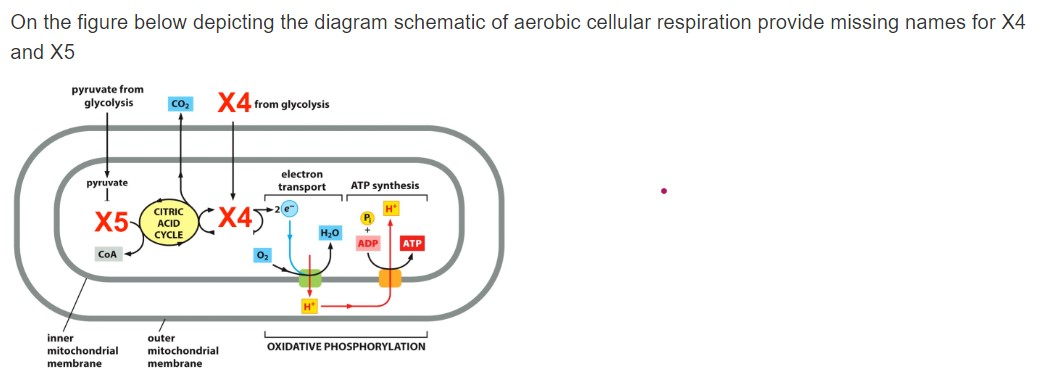
In which step of aerobic cellular respiration is ADP phosphorylated to produce ATP using energy released by oxidation? Electron transport chain Electrons are passed from carrier to carrier, using the energy to pump H+ ions from the matrix to the intermembrane space in this first part of oxidative phosphorylation.
Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration - an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O 2 = 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy 2) Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration:
Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products. This process occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell. Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water +ATP C 6H 12O

Cellular Aerobic Energy Production Also Known As Cellular Respiration Aerobic Oxidation And Oxidative Phosphorylation Personal Trainer Certification Nutrition Courses Fitness Education
Aerobic Cellular Respiration Flow Chart Beautiful Aerobic. Flowcharts are used in designing and documenting easy processes or programs. bearing in mind extra types of diagrams, they back visualize what is going on and thereby encourage comprehend a process, and perhaps next find less-obvious features within the process, considering flaws and ...
Aerobic Respiration Cellular Respiration Stock Vector Illustration Of Oxidation Educational 136719572
Aerobic implies that the process requires oxygen. If there is no oxygen present after glycolysis, a process called fermentation may occur. We will discuss this in the next lesson. Take a close look at the diagram below. Identify the areas where each step of aerobic cellular respiration occurs:
Aerobic respiration — Aerobic metabolism is up to 15 times more efficient than anaerobic metabolism (which yields 2 molecules ATP per 1 molecule glucose) ...
Sep 13, 2020 — The aerobic respiration diagram given below represents the entire process of aerobic respiration. The different cycles involved in aerobic ...Heart Diagram: Forest ConservationGerm Theory of Disease: What Is an AlleleSexual Reproduction in Fungi: Introns and Exo...What Is Endangered Species: What Is PollutionWhat do you understand by aerobic respiration?What are the different stages of aerobic respiration?
Cellular Respiration: (2 kinds—Aerobic and Anaerobic) •Cellular respiration is the process by which the energy of glucoseis released in the cell to be used for life processes (movement, breathing, blood circulation, etc…)
Aerobic Respiration: The Krebs Cycle ª Review: During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is split to form two pyruvate molecules, with a net profit of two ATP. The two pyruvate molecules then enter the mitochondria, where they are converted to acetyl CoA.
Aerobic implies that the process requires oxygen. In contrast, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. The Venn diagram compares aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. mcjpg Which statement could b Get the answers you need. The by-product of this process produces carbon dioxide along with ATP - the energy currency of the cells.
3 Simple Stages In Cellular Respiration And How They Work By Ernest Wolfe Countdown Education Medium

There Are Two Important Ways A Cell Can Harvest Energy From Food Fermentation And Cel Cell Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Chemical Energy
Solved I Need A Venn Diagram Comparing And Contrasting Photosynthesis And Aerobic Cellular Respiration Course Hero



















0 Response to "44 aerobic cellular respiration diagram"
Post a Comment