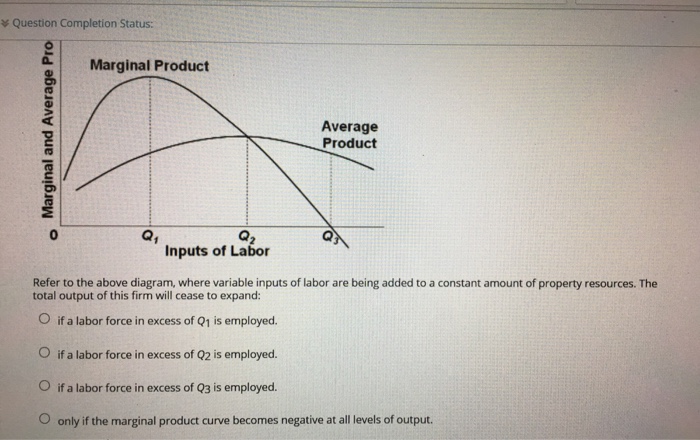
43 refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a
2) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P3, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output F or shut down, as it doesnʹt matter which. C) produce output D. The production of Q1 units of output at an average cost of a is not possible, given present technology and resource prices. Suppose a technological improvement increases the productivity of a firm's capital and, simultaneously, its workers' union negotiates a wage increase.
2) Refer to Figure 13 -17. Suppose the firm is currently producing Q f units. What happens if it increases its output to Q g units? 2) A) Its average cost of production will fall and its profit will rise. B) It will move from a zero profit situation to a loss situation. C) It will move from a zero profit situation to a profit situation.
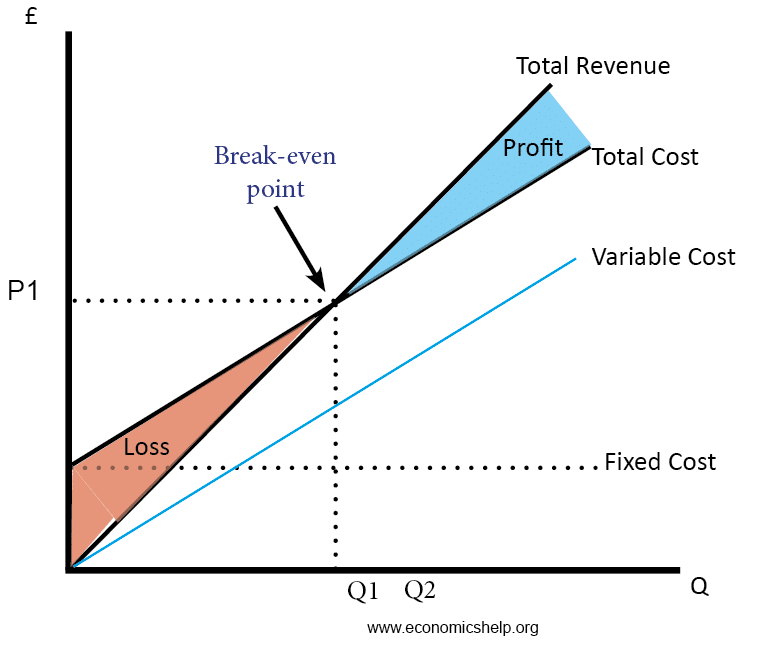
Refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a
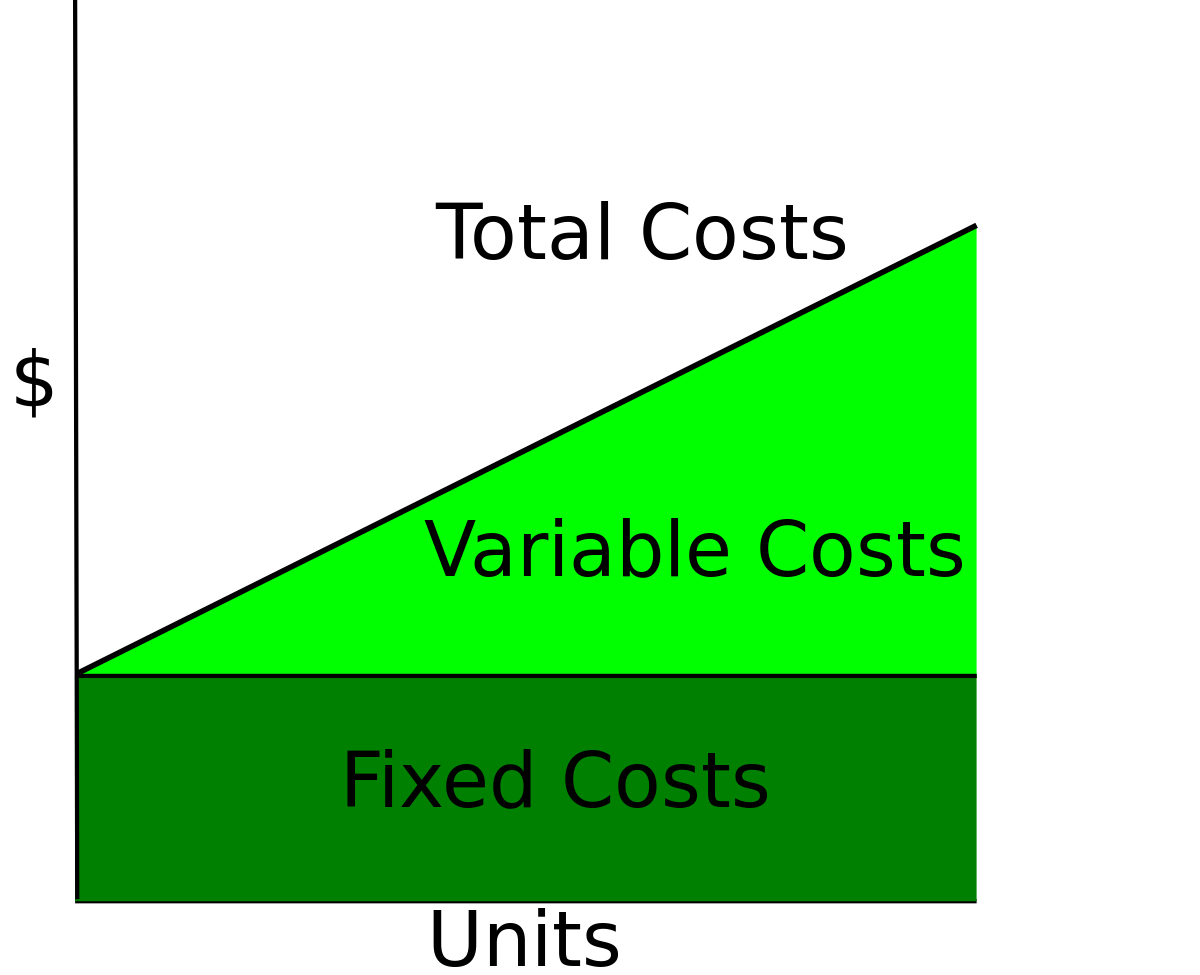
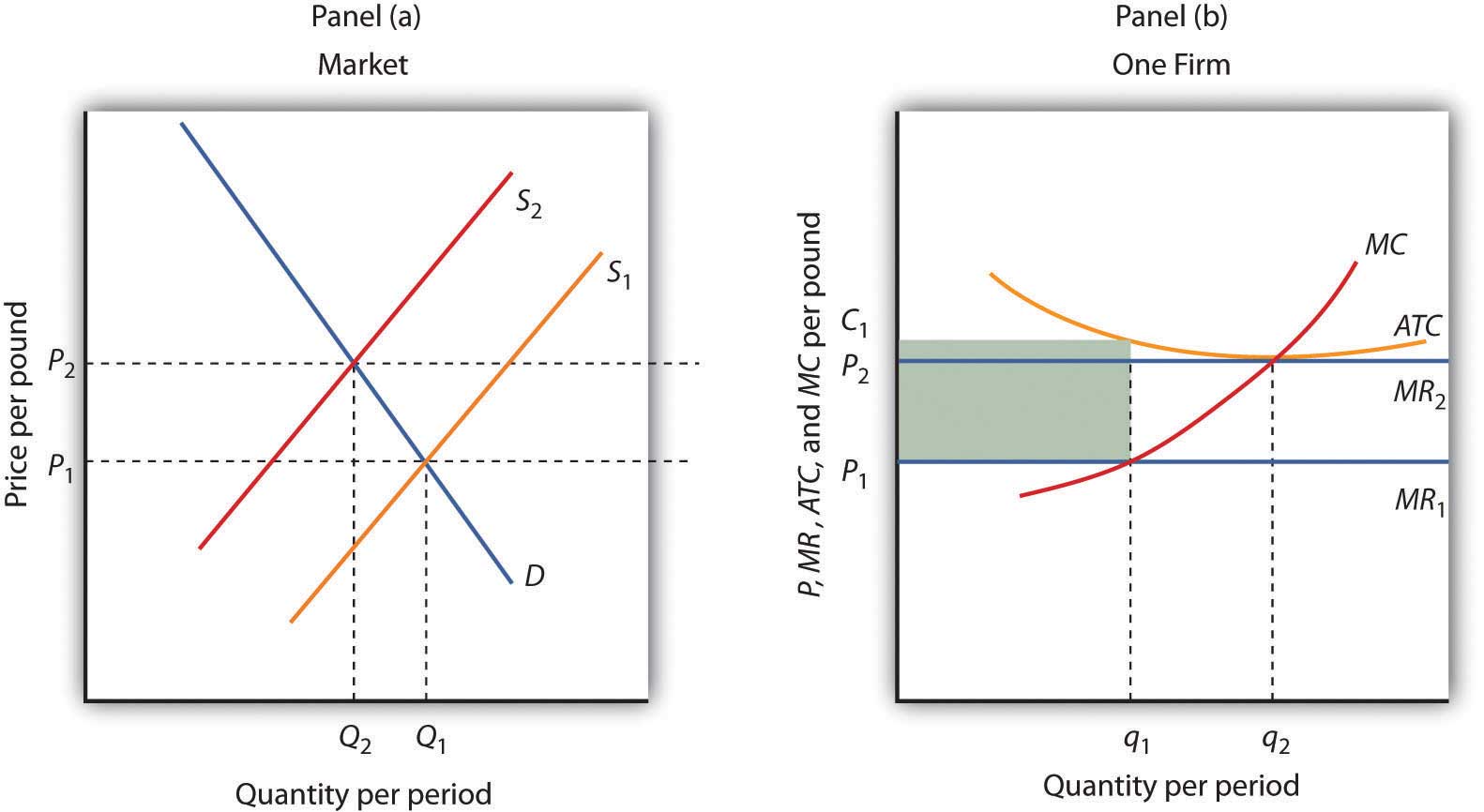
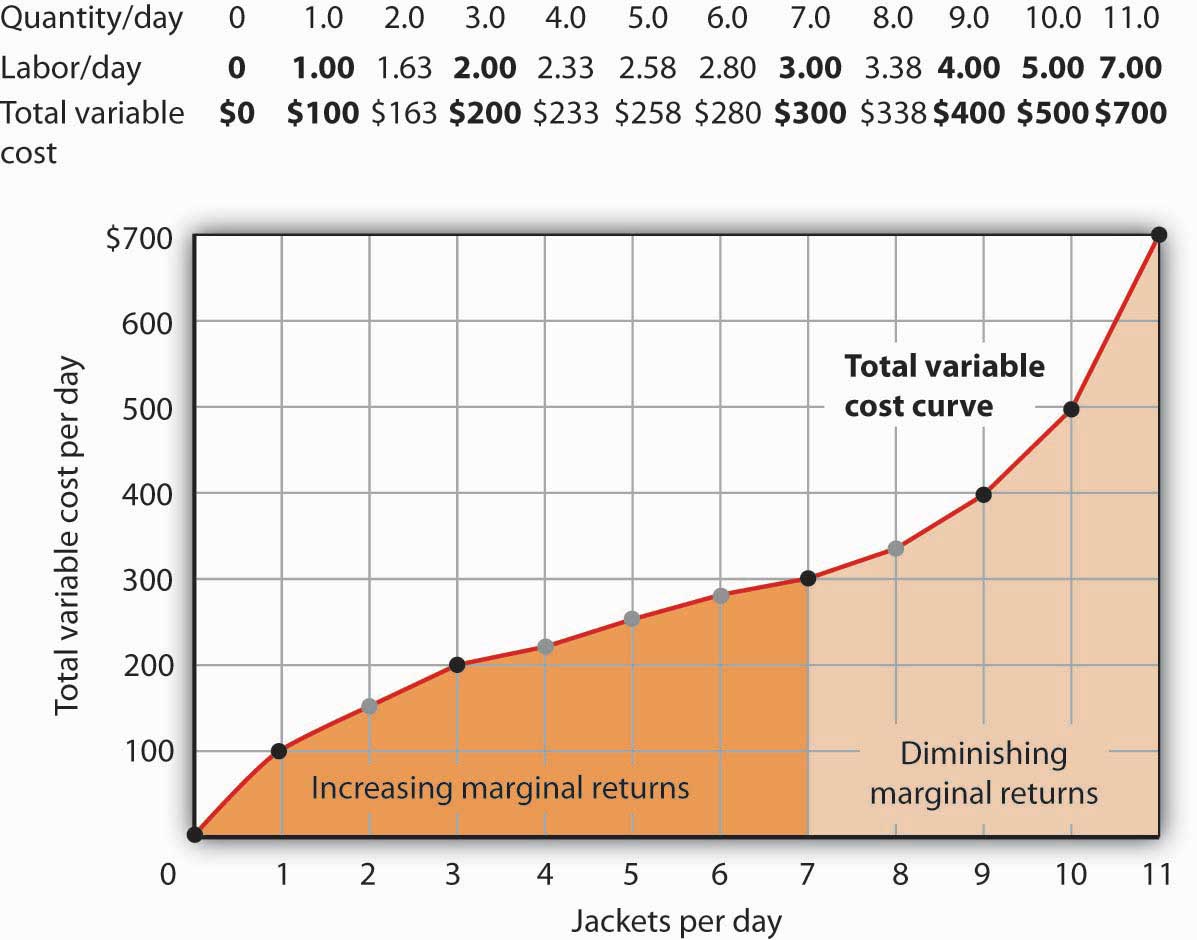
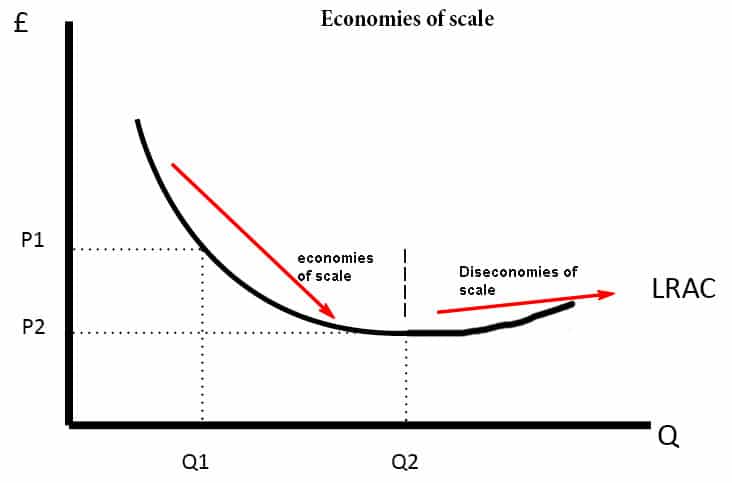
Refer to the figure above. Suppose the firm is currently producing Q2 units. What happens if it expands output to Q3 units? A) Its profit increases by the size of the vertical distance df B) It makes less profit. C) It incurs a loss. D) It will be moving toward its profit maximizing output. Refer to the figure above. If the market price is 530 ... Output (Q) Total Fixed Cost Average Fixed Cost 10 £2000 £1000 20 Fixed costs (FC) are independent of output and must be paid out even if the production stops. Capital-intensive industries with a high ratio of fixed to variable costs offer scope for economies of scale. AFC = Fixed Costs (FC) / Output (Q). Costs Output (Q) Average Fixed Cost If the total variable cost of 9 units of output is $90 and the total variable cost of 10 units of output is $120, then: a) the marginal cost of the tenth unit is $90. b) the average variable cost of 10 units is $10. c) the firm is operating in the range of increasing marginal returns. d) the average variable cost of 9 units is $10.
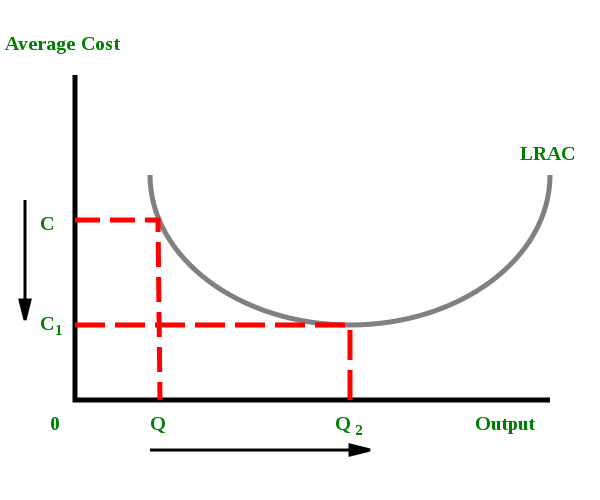
Refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a. Refer to the diagram. This production possibilities curve is constructed so that: the opportunity costs of both bread and tractors increase as more of each is produced. ... The production of Q1 units of output at an average cost of a, which lies below the long-run actual cost curve: 200. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q1: A) resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. B) resources are underallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. C) productive efficiency is achieved, but resources are underallocated to this product. Refer to the long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q2 at an average cost of ATC3, then the firm is. a.incurring X-inefficiency and is failing to realize all existing economies of scale. b.incurring X-inefficiency but is realizing all existing economies of scale. c.producing that output with the most efficient combination ... Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Suppose that total variable cost is $300 at 40 units of output. At that level of output, average fixed cost: A. is $2.50. B. is $4. C. is $100. D. cannot be determined from the information provided.
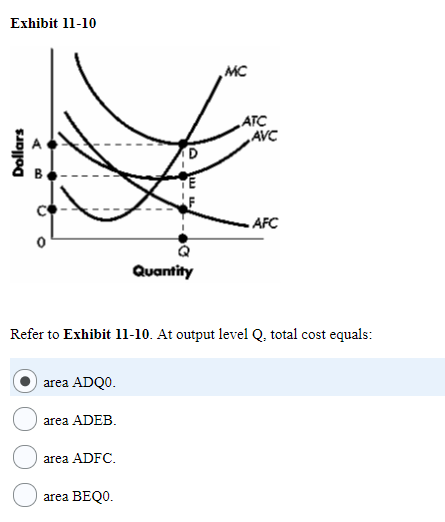
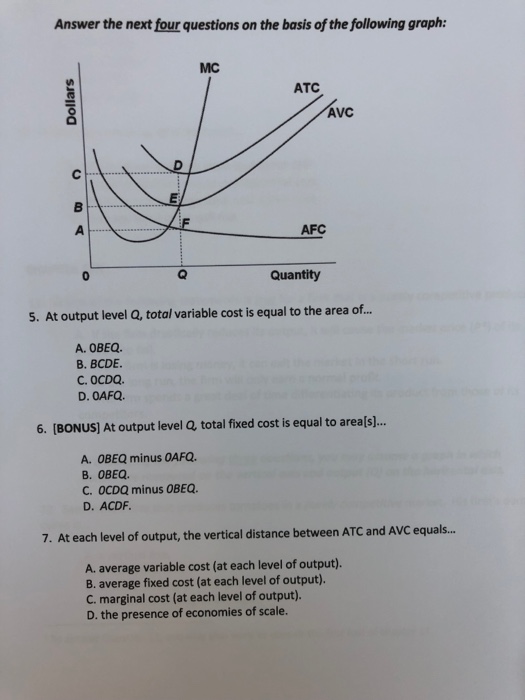
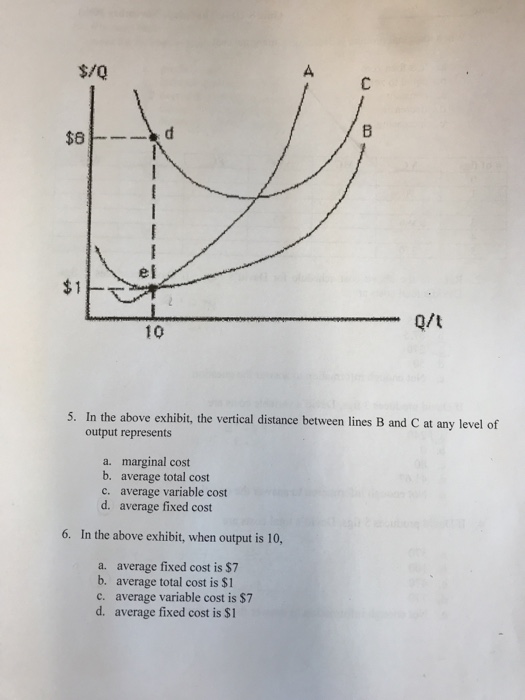
Refer to the diagram. At output level Q: Multiple Choice ... Marginal cost measures the cost per unit of output associated with any level of production. ... divided by its marginal product. D. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and has average variable costs of $150. The firm's ... Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of B are: A) unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B) unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C) obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D) obtainableandimplyleast-costproductionofthisoutput. Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q 1 at an average total cost of ATC 1 , then the firm is: A. a switch in production to a redesigned and retooled facility. The fixed cost of the firm is $500. The firm's total variable cost is indicated in the table. outputTotal Variable Cost1$ 400272031,00041,40052,00063,600. The average total cost of the firm when 3 units of output are being produced is. $500.
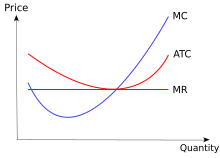
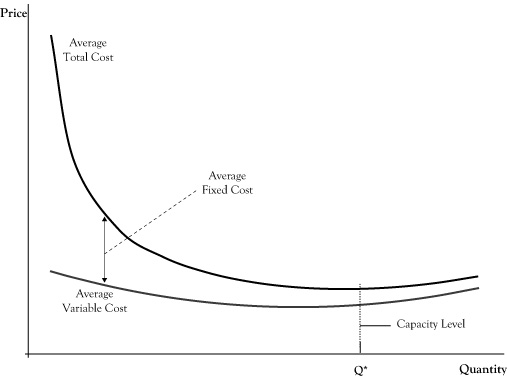
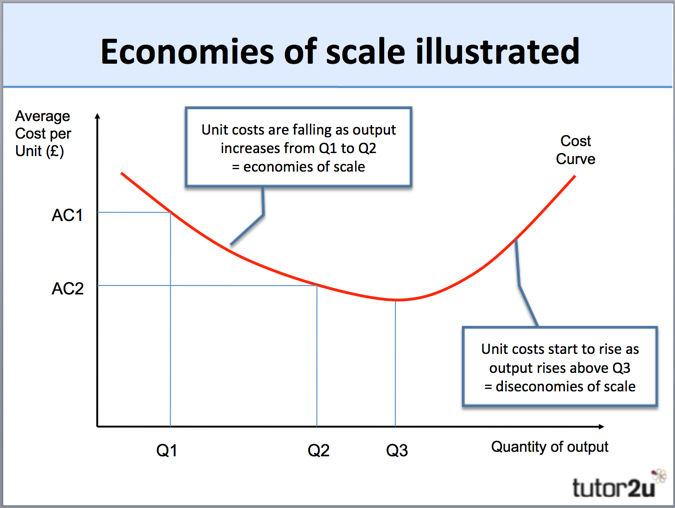
23. Assume fifty years supply commodity Q at location I and fifty at location II. The cost of producing output qi for the ith firm (in either location) is 0.5𝒒𝟐𝒊 . The cost of transporting the commodity to the market from location I is 6 dollars per unit and from location II, 10 dollars per unit. Determine the aggregate supply function. 3. Average Total Cost (ATC) The average total cost is the sum of the average variable cost and the average fixed costs. That is, ATC = AFC + AVC. In other words, it is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. The diagram below shows the AFC, AVC, ATC, and Marginal Costs (MC) curves: It is important to note that the behaviour of ... output can only be increased in batches of 100 units. 7) Refer to Table 12 -1. What is the fixed cost of production? 7) A) $0 B) $500 C) $1,000 D) It cannot be determined. 8) Refer to Table 12 -1. If the market price of each camera case is $8, what is the profit - maximizing quantity? 8) A) 300 units B) 400 units C) 500 units D) 600 units the total cost of producing 200 or 300 units is no greater than the cost of producing 100 units. Tags: Question 14 . ... The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's economic profit ... Refer to the diagram. At output level Q2,
At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by $30; $20.50 Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist.
16) Refer to Table 13 -3. What is its average variable cost of production at its optimal output level? 16) A) $0 (because its optimal output = 0) B) $15 C) $14.75 D) $29 17) Refer to Table 13 -3. What is the best course of action for the firm in the short run? 17) A) It should not cut its price but it should increase its sales by advertising.
Refer to Figure 11-9 above to solve the following problems. asked Jul 8, 2016 in Economics by Trina. a. Calculate the fixed cost of production. b. Calculate the average total cost of production when the firm produces 20 units of output. c. Calculate the average variable cost of production when the firm produces 20 units of output. d. Calculate ...
141. Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q1 at an average total cost of ATC1, then the firm is: A) producing the potentially profit-maximizing output, but is failing to minimize production costs. B) incurring X-inefficiency, but is realizing all existing economies of scale.
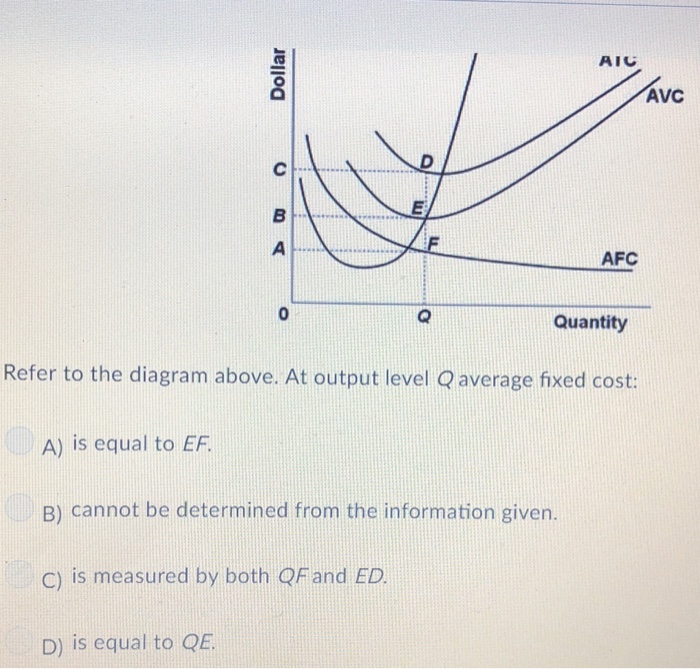
Refer to the above diagram This firms average fixed costs are A not shown B the from ECON 2 at Tarrant County College. Average Cost. The value of average cost is derived by dividing to tal cost with the number of units produced by a firm. The average cost includes average fixed cost as well as an average variable cost. Refer to the diagram of the market for product X. Curve St embodies all ...
Which piece of information would NOT be helpful in calculating the marginal cost of the 75th unit of output? A) The total cost of 75 units. B) The total cost of 74 units ... Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q1 . A) marginal cost is falling. B) average total cost is falling. ... A growing firm's average cost of production will decline over ...
Average variable cost (AVC): is variable cost divided by the quantity of output. AVC Q1 = VC/Q 1 = wL 1 /Q 1 Average total cost (ATC): is total cost divided by the quantity of output. ATC Q1 = AFC Q1 + AVC Q1 Marginal cost (MC): is the change in total cost that results from producing an additional unit of output. MC Q1 = dTC/dQ
178. Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of A are: A) unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B) unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C) obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D) obtainable and imply least-cost production of this output. Answer: B
its output to Q 1 . 14) Refer to Figure 13 -14. It is possible to lower the average cost of production by expanding output ... diagram? 16) A) Q f units B) Q g units C) Q h units D) Q j units 17) Refer to Figure 13 -17. What is the allocatively efficient output for the firm represented in the ... increases its output to Q g units? 19) A) Its ...
Refer to the diagram. If actual production and consumption occur at Q3, A) efficiency is achieved. ... At output level Q1, in this diagram, A) resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. ... If average variable cost is $74 and total fixed cost is $100 at 5 units of output, then average total cost at ...
Long-Run AC 0 Output Refer to the diagram. The production of units of output at an average cost of a Multiple Choice can be achieved if the firm would hire the optimal mix of resources. would entail X-inefficiency is not possible. given present technology and resource prices can be realized if the last dollar spent on each input were equal to ...
If the total variable cost of 9 units of output is $90 and the total variable cost of 10 units of output is $120, then: a) the marginal cost of the tenth unit is $90. b) the average variable cost of 10 units is $10. c) the firm is operating in the range of increasing marginal returns. d) the average variable cost of 9 units is $10.
Output (Q) Total Fixed Cost Average Fixed Cost 10 £2000 £1000 20 Fixed costs (FC) are independent of output and must be paid out even if the production stops. Capital-intensive industries with a high ratio of fixed to variable costs offer scope for economies of scale. AFC = Fixed Costs (FC) / Output (Q). Costs Output (Q) Average Fixed Cost
Refer to the figure above. Suppose the firm is currently producing Q2 units. What happens if it expands output to Q3 units? A) Its profit increases by the size of the vertical distance df B) It makes less profit. C) It incurs a loss. D) It will be moving toward its profit maximizing output. Refer to the figure above. If the market price is 530 ...
















0 Response to "43 refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a"
Post a Comment