41 passive continental margin diagram
Feb 12, 2015 — Thus, passive margins consist of a seawards tapering wedge of continental crust that is dissected by faults, overlain by sedimentary basins ... Passive continental margin. What happens to the abundance of the parent isotope over time? ... Which diagram is the best representation of the relationship between topography and water table? ... Which margin is an active continental margin? Margin B. The …
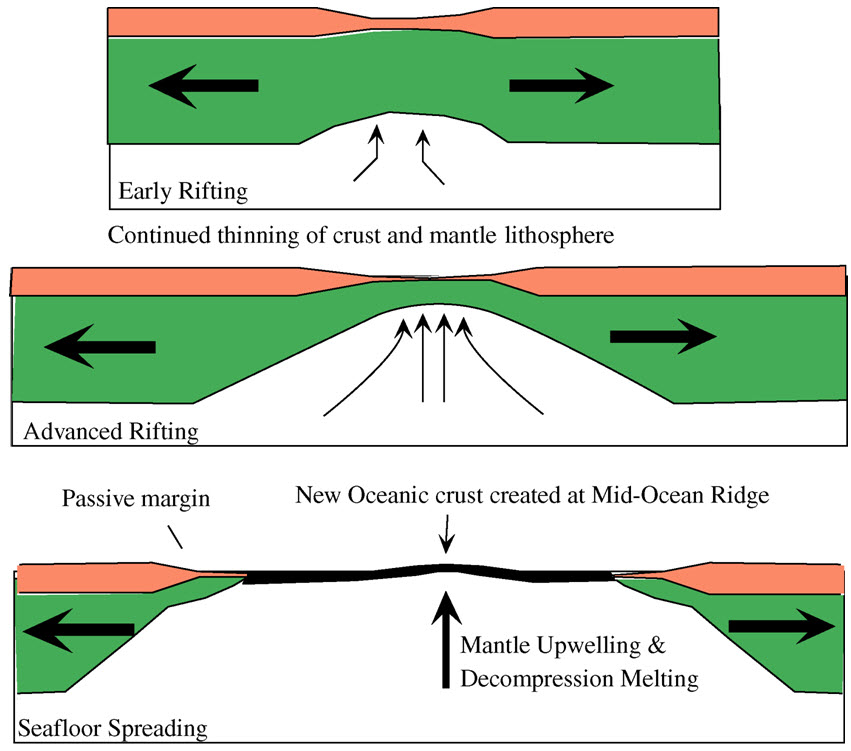
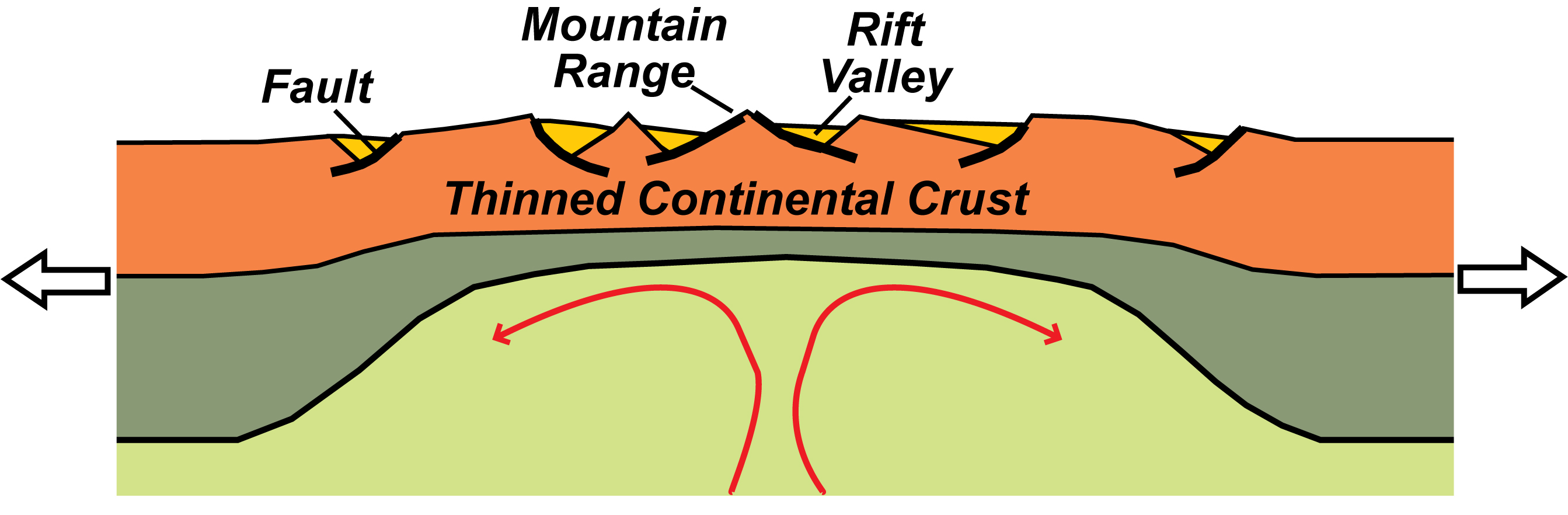
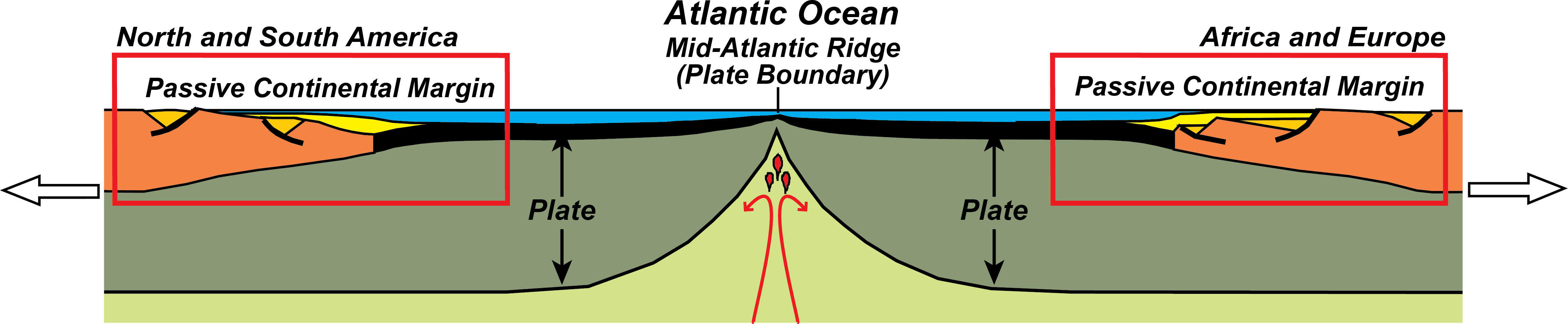
A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin.A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere.Continental rifting creates new ocean basins. Eventually the continental rift forms a mid-ocean ridge and the locus of extension moves away from the continent-ocean boundary.

Passive continental margin diagram
The real situation at passive continental margins is shown in Fig. 6 (below). This is typical of a number of crustal cross-sections across the continental shelf of the eastern Atlantic seaboard of North America, projected down to 30 km -- based largely on gravity and magnetic evidence, plus some seismic profiles -- and some extrapolation from ... Eastern side: Passive margin, Lack of tectonic activity, Wide continental shelf. ... Using the diagram with the figures labeled A, B, and C from left to right, match the name of the plate boundary with its figure letter. boundaries. Intense geologic activity is concentrated at plate _____. Label the different features of the passive continental margin on the diagram below. level: 1 answer: See Figure 13.9 in Earth Science, 11e. 63. What type of continental margin is illustrated in the diagram below? level: 1 answer: active continental margin . 64. Examine Figure 13.C below. Briefly explain the main points of Charles Darwin's ...
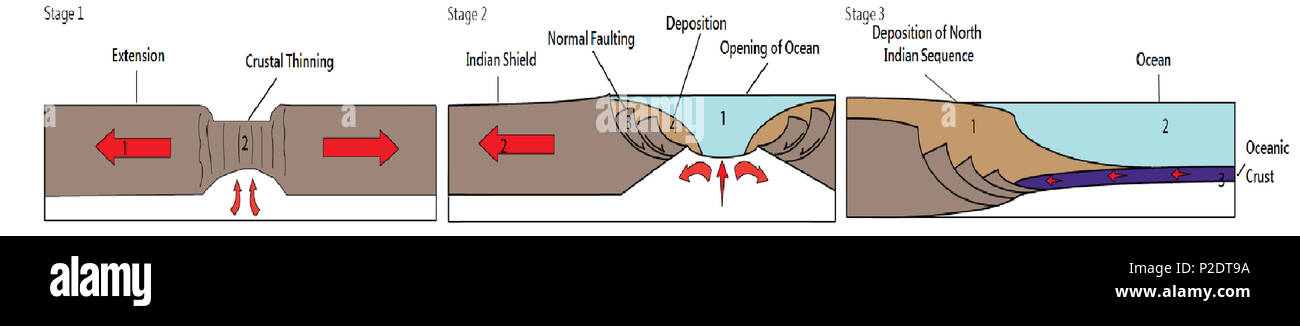
Passive continental margin diagram. A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges.The continental shelf is the relatively shallow water area found in proximity to continents. The continental margin consists of three different features: the continental rise ... Download scientific diagram | 3 Oblique view of the eastern Australian passive continental margin showing the characteristics of the slope and the location of several features discussed in the ... The geodynamic events of continental breakup and origin of northwest Indian Ocean led to the development of passive continental margin, off western India. However, causal mechanisms and relative chronology of these geodynamic events are not clearly known because of complex regional-scale ridges-basin physiography, multi-stage rifting in a short ... Figure 1 is a chronostratigraphic diagram of Cordilleran rock assemblages showing their relationships to major phases of Cordilleran evolution. The Cor-dilleran edge of the Precambrian basement, which forms the Laurentian craton, was first delineated by rifting to form a passive continental margin, along which a
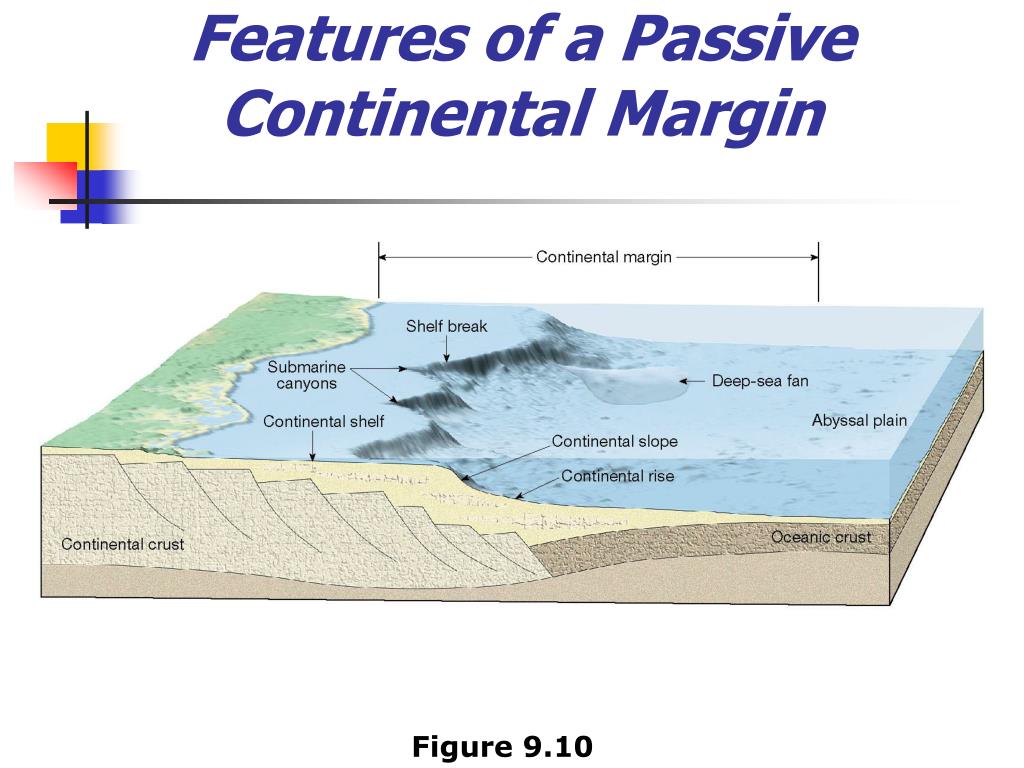
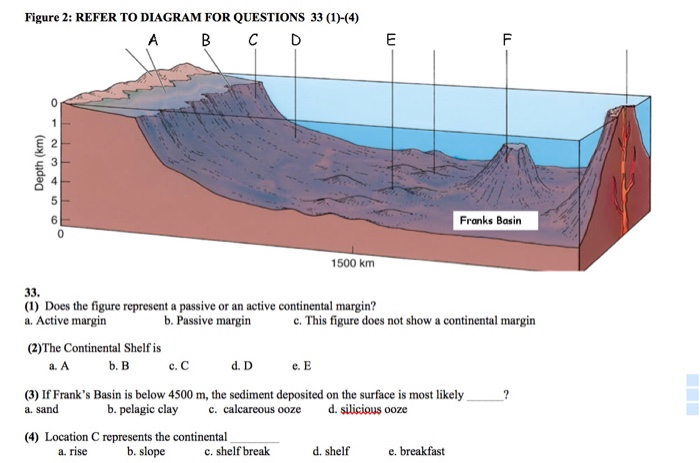
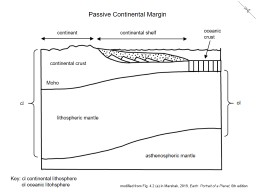
If we then use a conservative convergence rate 17 of 2 cm/yr (20 km/Ma) between the arc/forearc sequence and the passive margin over which it was emplaced, we obtain a minimum length of subducted ... Active and Passive Continental Margins. The continental margins are one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margins are the shallow water areas found in proximity to continents. The continental margins are the zone of the ocean floor that separate the thin oceanic crust from thick continental crust. A passive continental margin has a landward, shallow continental shelf, a deeper continental slope, a continental rise, and a flat abyssal plain (Figure 2).. Figure 2. A Passive Continental Margin. Continental shelves. A continental shelf is a shallow, almost flat platform that extends seaward from the edge of the continent. The nearshore sediment is mostly sand that grades outward toward ... On this perspective view of a passive continental margin, match the following letters with the correct features. D: continental slope G: shelf break A: continental shelf C: continental crust B: Abyssal plain F: continental rise E: oceanic crust. On the diagram of a passive continental margin shown below, match the letters with the correct ...
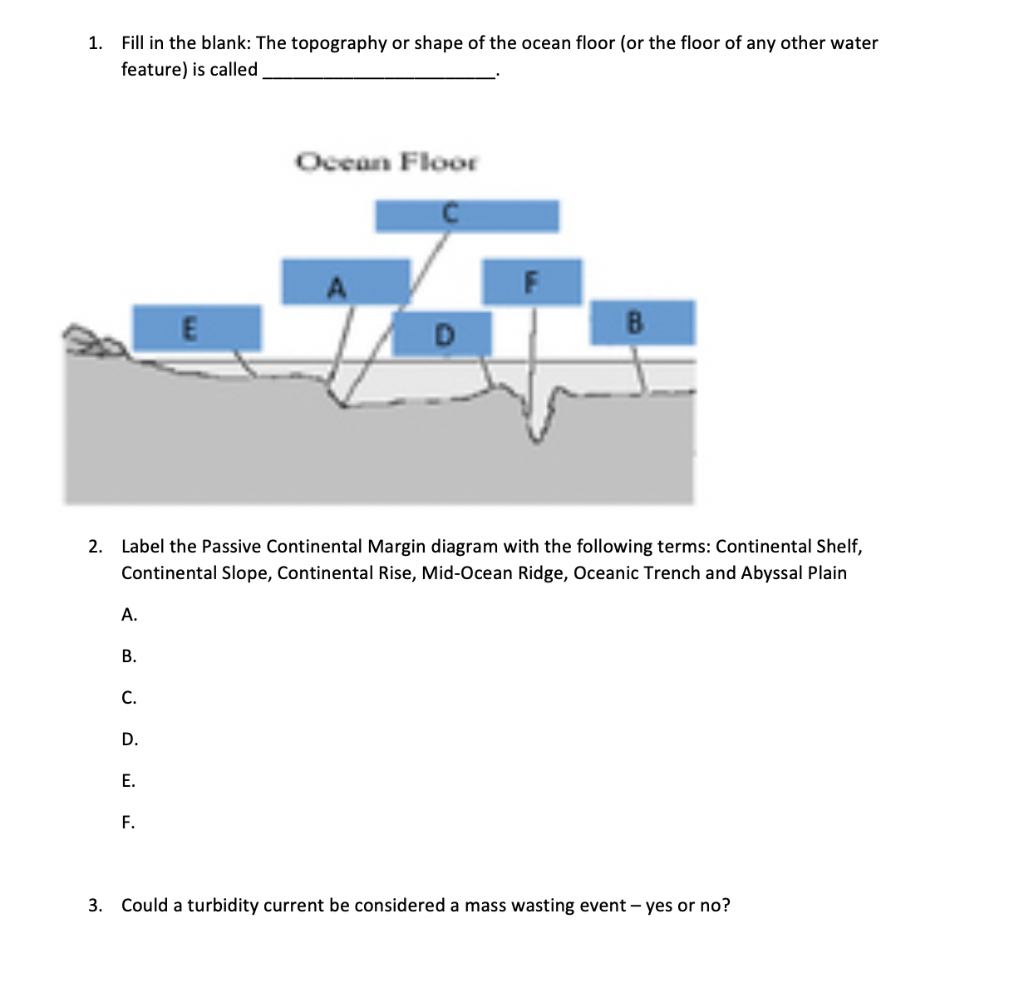
Continental Shelf. Continental Rise. Continental Slope Those portions of the outer edges of the continents that lie under water are referred to as the continental margins. These margins are of two types, depending on the tectonic condition that they represent. Margins located at the edges of diverging plates are called . passive margins Subduction initiation (SI) at passive continental margin plays a key role in the Wilson cycle of plate tectonics; however, the long-lived, stable Atlantic-type margin challenges this hypothesis. The spontaneous SI at passive margin is difficult, which could be instead induced by far-field tectonic forces. Passive continental margins are found along the remaining coastlines. Because there is no collision or subduction taking place, tectonic activity is minimal and the earth's weathering and erosional processes are winning. This leads to lots of low-relief (flat) land extending both directions from the beach, long river systems, and the ... Continental margin Sea lavel Shell Continental 1 km 1km 12 m 70 m 2 Depth (km) Continental 3 4 1 km 9 m Continental 5 Ocean Noor 0 300 500 700 800 100 200 400 500 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 Distance from shore (km) Label the major parts of this diagram of a continental margin. This diagram illustrates a passive continental margin.
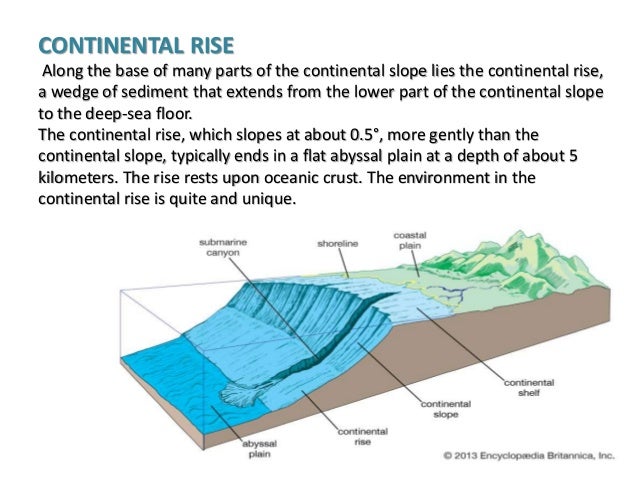
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF A PASSIVE MARGIN • A broad shelf leading to a slope characterize passive continental margins •The continental rise is typified by the overlapping deposits of submarine fans composed of turbidity current‐transported sediments.
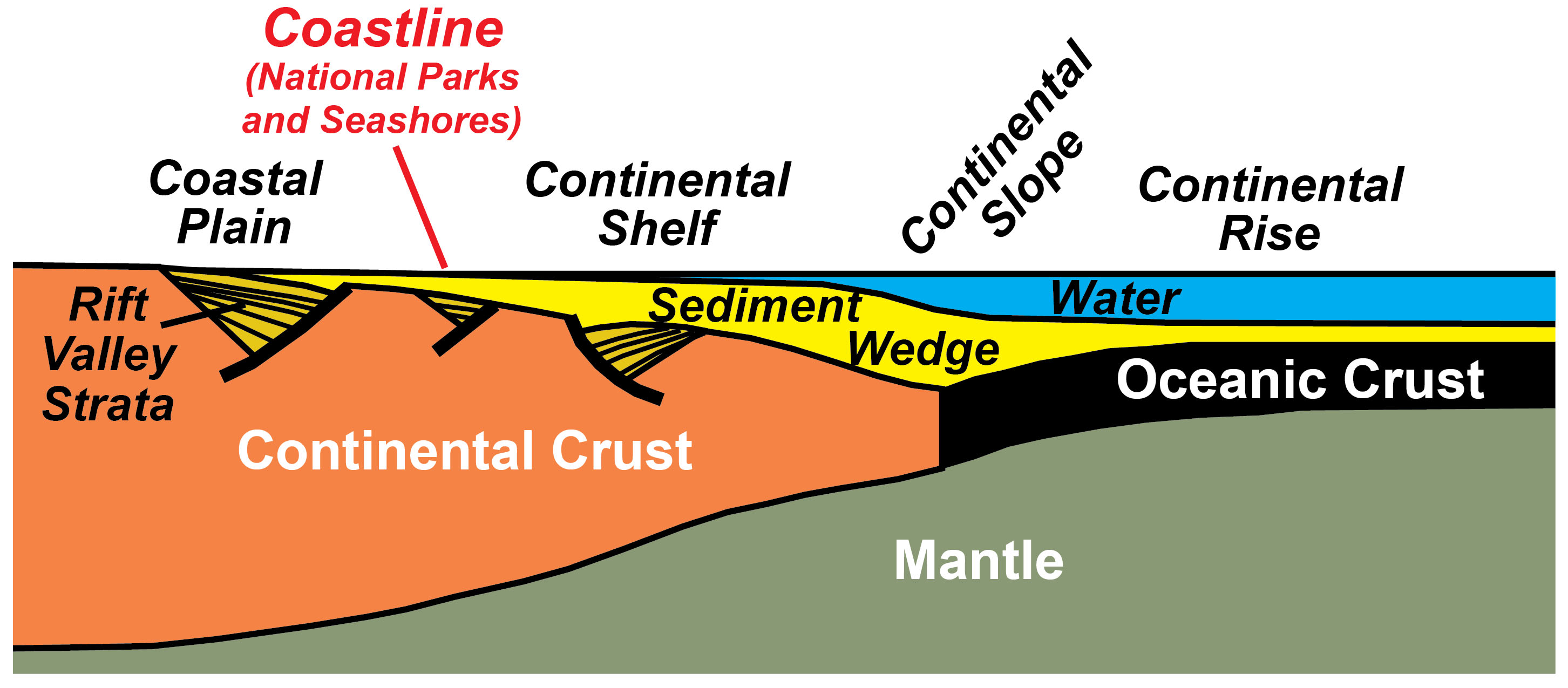
by W Frisch · 2011 — 4.2 Diagram of a passive continental margin. Above the thinned continental crust and the bordering oceanic crust a thick wedge of sediment is.
An accretionary wedge or accretionary prism forms from sediments accreted onto the non-subducting tectonic plate at a convergent plate boundary.Most of the material in the accretionary wedge consists of marine sediments scraped off from the downgoing slab of oceanic crust, but in some cases the wedge includes the erosional products of volcanic island arcs formed on the overriding plate.
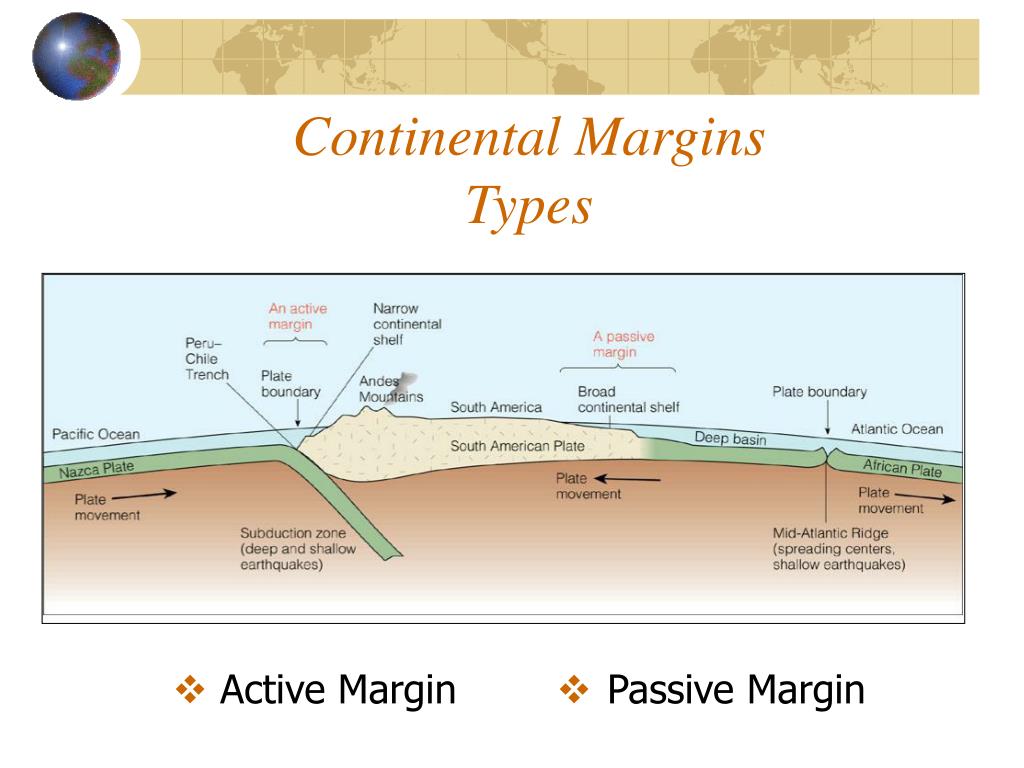
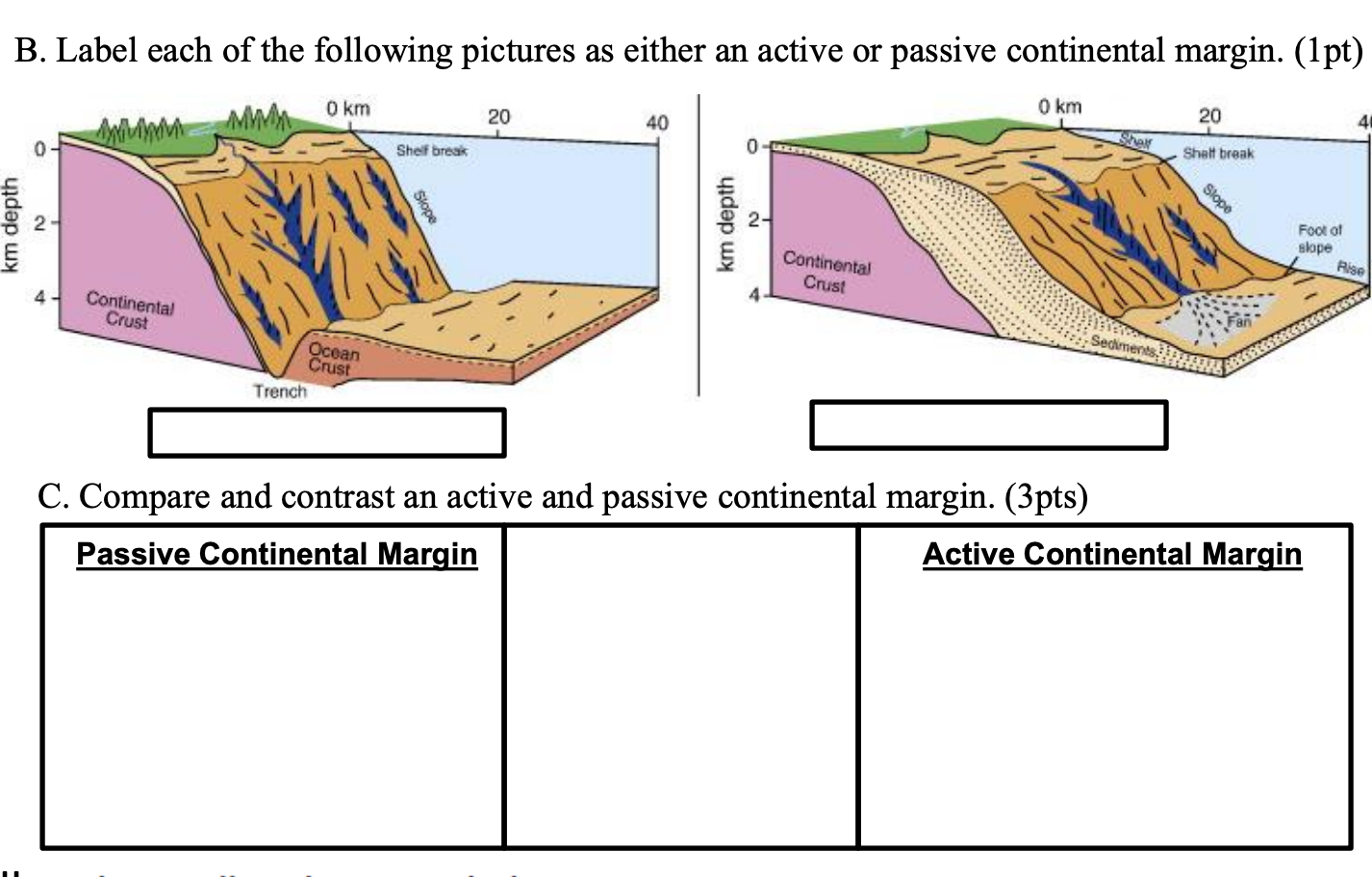
What's the difference between an active and passive continental margin? This is an easy one. The earth's crust is broken into sections, called plates.There are two (2) basic types: oceanic plates which are composed of basalt, and continental plates, which are mostly granite.The continental plates are in motion, and literally bounce around on the surface like giant air hockey pucks.
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. Two types of technology share the name "sonar": passive sonar is essentially listening for the sound made by vessels; active sonar is ...

A Tectono Stratigraphic Review Of Continental Breakup On Intraplate Continental Margins And Its Impact On Resultant Hydrocarbon Systems Sciencedirect
The passive continental margins of eastern North America, eastern South America, western Africa, and western Europe began to form about 200 million years ago when Pangaea began to break up. The rift or crack that caused them to split, known as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, now lies on Two types of continental margins exist: active margins and passive ...

The Transition From A Passive To An Active Continental Margin In The Jiamusi Block Constraints From Late Paleozoic Sedimentary Rocks Sciencedirect
Feb 14, 2021 — Continental margins typically fall into two classes: "active" and "passive." An active continental margin is a coastal region that is ...
Start studying Active vs Passive Continental Margins. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The Atlantic Continental Margin is an example of a "passive" margin, with a well developed, wide, gently-sloping shelf. The deepest part of the ocean depicted above is the abyssal plain. This is a flat, almost featureless, part of the sea floor that has become mantled with a sediment cover so that the bottom irregularities have been almost ...
General diagram showing the series of fusion steps that occur in the sun. ... At passive margins, continental crust grades into oceanic crust at passive margins, ... out and moved eastward beneath the continental plate affecting the overlying continent hundreds of miles east of the continental margin and building high mountains.
Download scientific diagram | Passive continental margin. from publication: Coastal Landforms and Processes at the Cape Cod National Seashore, ...
Passive continental margin basins are generally located along the coasts of the Indian Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. The continental borders of these three regions account for approximately 60 percent of the global total (Feng 2003).According to a considerable body of research, passive continental margin basins are often rich in oil and gas reserves and represent the most important ...
The North American plate also serves to illustrate this difference between the topographic landforms of active and passive continental margins. The west coast is the active margin, and is the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains. The Eastern Seaboard is a passive margin, as is the Gulf Coast.

Passive Margin A Passive Margin Is The Transition Between Oceanic And Continental Crust Which Is Not An Active Plate Margin It Is Constructed By Sedimentation Above An Ancient Rift Now Marked By Transitional Crust Continental Rifting Creates New Ocean
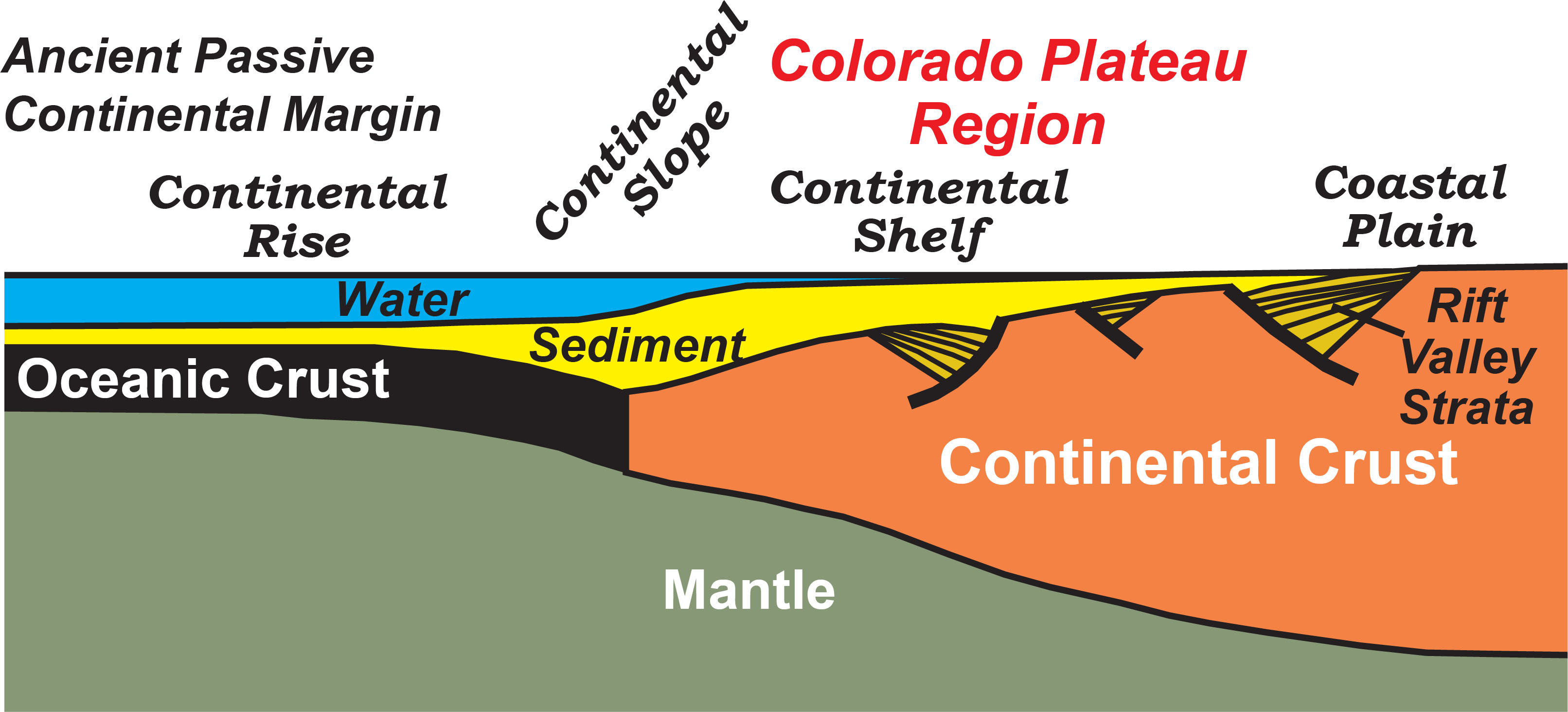
A passive continental margin occurs where the transition from land to sea is not associated with a plate boundary. The east coast of the United States is a good example; the plate boundary is located along the mid Atlantic ridge, far from the coast. Passive margins are less geologically active. Figure 1.2.1 shows an idealized passive margin.
Modern Passive Continental Margin. The overall form of a passive continental margin results from the crust thinning from the continent to the ocean. Where crust is thick, its buoyancy makes it stick up far above the denser mantle; conversely, thin oceanic crust sits down much lower.

Structure And Evolution Of The Atlantic Passive Margins A Review Of Existing Rifting Models From Wide Angle Seismic Data And Kinematic Reconstruction Sciencedirect
Along its two coasts, 25 passive continental margin basins (Figure 1) have been explored, 80% basins are in deepwater setting; currently, a total of 111 giant oil and gas fields with recoverable ...
In terms of end members, the type of subducted continental crust is either (1) normal thick continental crust or (2) the crust of a rift zone later transformed to a passive margin, which is influenced by strong extension, high-temperature metamorphism due to thinning of even the subcontinental mantle lithosphere and intense bimodal magmatism.
The passive margin generally consists of two parts, a continental lithosphere and an oceanic lithosphere. For the continental lithosphere, there are generally three layers, the upper continental crust of granite, the lower continental crust of intermediate and basic rocks, as well as the depleted continental lithospheric mantle (Wedepohl, 1995; Hofmann, 1988; Carlson et al., 2005; Niu et al ...
continental margin, the submarine edge of the continental crust ... …shelf areas produced as passive continental margins develop during the early stages of ...

Extra Credit Option Attend The Public Lecture By Prof Antonio Lazcano On Tuesday Tomorrow Evening Feb 11 At 7 30 Pm In Gammage Auditorium Here On Ppt Download
Transcribed image text: GEOL 5026 GLOBAL TECTONICS HOMEWORK #1 - ISOSTATIC EQUILIBRIUM (1) Draw a block diagram of a passive continental margin in Airy isostatic equilibrium assuming the following: • topography at sea level over the continent • ocean water depth of 5.0 km • water density of 1.03 g/cm3 • crustal density of 2.67 g/cm3 for both the oceanic and continental regions ...

Global Distribution Of Large Submarine Canyons Geomorphic Differences Between Active And Passive Continental Margins Sciencedirect
passive or extensional continental margins, ranging in age from mid-Proterozoic to Holocene. These passive (or Atlantic-type) continental margins may extend out from cratons into marginal basins located behind magmatic arcs, or they border major ocean basins (Heezen, 1974).
Label the different features of the passive continental margin on the diagram below. level: 1 answer: See Figure 13.9 in Earth Science, 11e. 63. What type of continental margin is illustrated in the diagram below? level: 1 answer: active continental margin . 64. Examine Figure 13.C below. Briefly explain the main points of Charles Darwin's ...
Eastern side: Passive margin, Lack of tectonic activity, Wide continental shelf. ... Using the diagram with the figures labeled A, B, and C from left to right, match the name of the plate boundary with its figure letter. boundaries. Intense geologic activity is concentrated at plate _____.
The real situation at passive continental margins is shown in Fig. 6 (below). This is typical of a number of crustal cross-sections across the continental shelf of the eastern Atlantic seaboard of North America, projected down to 30 km -- based largely on gravity and magnetic evidence, plus some seismic profiles -- and some extrapolation from ...
Https Sites Google Com Site Mrtrenge Final Exam Review Questions Click On The All Files By Unit Tab To The Left Then Scroll Down And Select The 2017 Final Exam Review Review For Oceanography Portion Of The Final Exam Zones Based On Depth















0 Response to "41 passive continental margin diagram"
Post a Comment