41 co molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. in this video i have discussed about the molecular orbital diagram of co which is the most important ligand in organometalics and coordination chemistry.con...
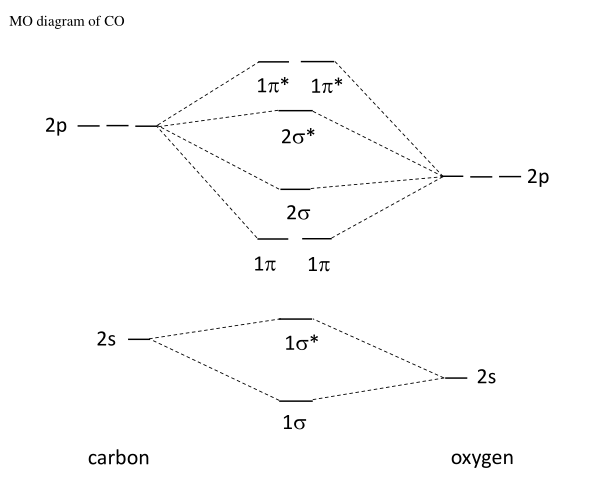
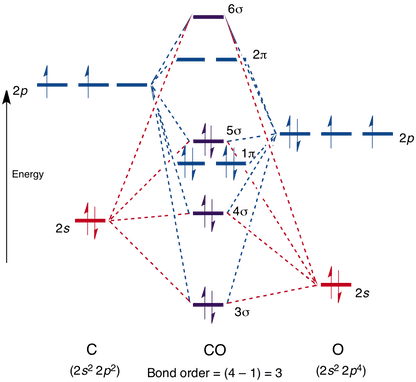
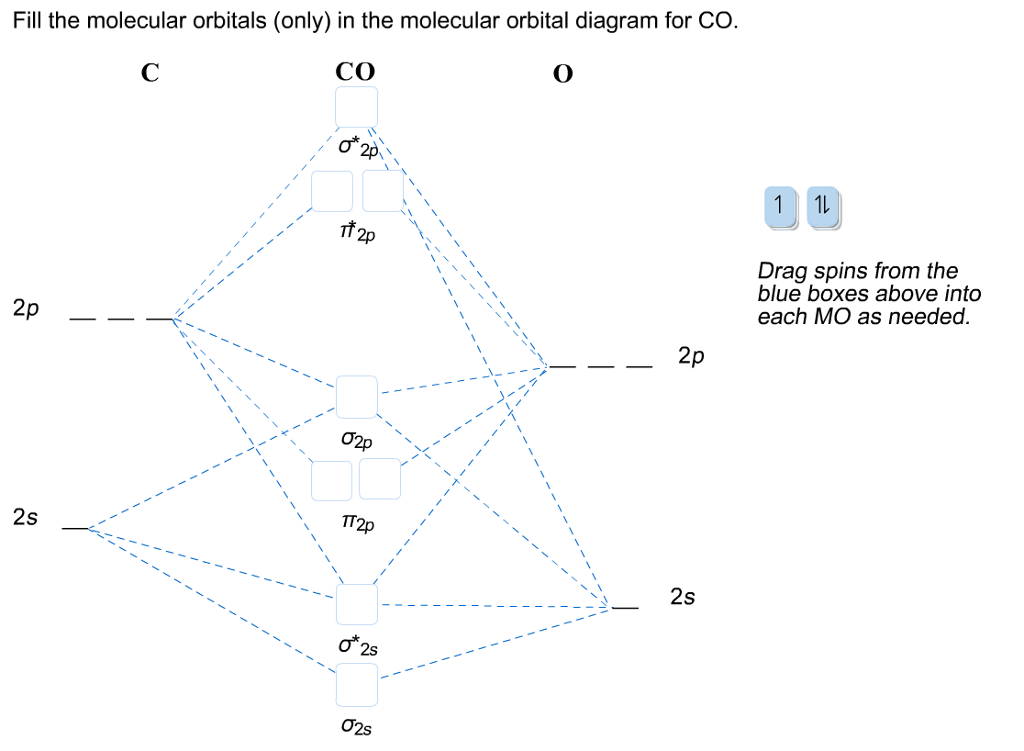
Molecular Orbital diagram of Hetero nuclear diatomic molecule : Molecular Orbital diagram of Carbon monoxide molecule (CO): Total electrons:6+8 =14. CO =σ1s 2,σ*1s 2,σ2s 2,σ*2s 2, σ2px 2, π2py 2 = π2pz 2. Nb=10. Na=4. B.O =0.5 (Nb-Na) B.O=0.5(10-4) B.O= 3. Molecular Orbital diagram of NO(nitric oxide)molecule :

Co molecular orbital diagram
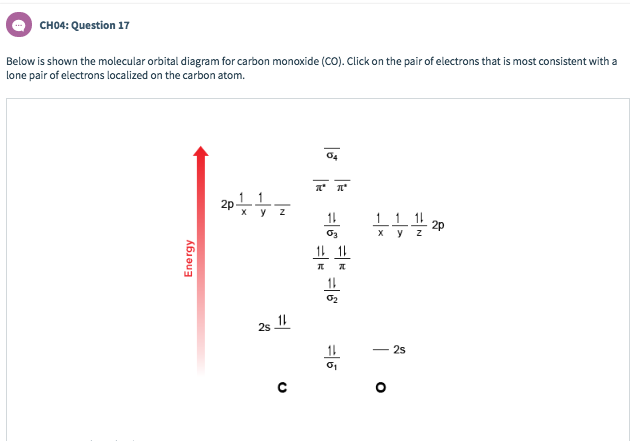
Molecular Orbital diagram for CO 5:09. Taught By. Patrick J O'Malley, D.Sc. Reader. Try the Course for Free. Transcript. Explore our Catalog Join for free and get personalized recommendations, updates and offers. Get Started. Coursera Footer. Start or advance your career. Google Data Analyst ... Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. TAGS; Molecular Orbital Diagram; Previous article Wohl-Ziegler Bromination. Next article Molecular Orbital Diagram of NO. All About Chemistry. https://allaboutchemistry.net. Hello Reader! Thanking for reading this post, If you find it to be informative, pls share it and visit our website. Point out key differences between the diagrams and use the diagram to explain why $\ce{CO}$ acts as a two-electron donor through carbon rather than through oxygen. Understandably, the key difference between these molecules is that $\ce{CO}$ is heteronuclear, and thus will have differences in energy between the molecular orbital and the atoms.
Co molecular orbital diagram. Watch the video solution for the question: Draw the orbital diagram for ion Co 2+.. . can be accommodated in the metal d orbitals. • d0 ions •d7 ions - Fe1+, Ru1+, Co2+, Rh2+, Ni3+, etc. . σ-ML4 Tetrahedral MO Diagram e. Answer to Write orbital diagram for Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. May 05, 2020 · My question concerns the interpretation of the Molecular Orbital of CO. I think I find it clear how you build it but I have some concerns about how you rationalize it. Particularly, from what I read the reason we envision carbon as being partially negatively charged in CO is that the HOMO of the molecule lies closer to the carbon orbitals. Molecular orbital diagram of co. The s orbitals and p z orbitals of both atoms are the correct symmetry to form σ interactions. Molecular electron configuration for o2 σ2σ2σ2π4π2 we can also calculate the oo bond order. You have the here on this side you would have the energy so the energy is going up there. Molecular orbital view of chemisorbed carbon monoxide. Click on the co molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Carbon monoxide lumo lowest unoccupied molecular orbital. In bacteria carbon monoxide is produced via the reduction of carbon dioxide by the enzyme carbon monoxide dehydrogenase an fe ni s ...
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. 12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics Molecular Orbitals for CO. Jmol models of wavefunctions calculated at the RHF/3-21G* level. To view a model, click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown The results displayed may be switched between those from a low level of calculation and those from a high level. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. Which overlap is strongest? During the axial overlap of p-p orbitals, the electron density increases around the axis, so the bond formed is the strongest. Therefore, the strongest bond formed is when p-p orbital overlap occurs. Final answer: The correct answer is Option B- 2p ... Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ... Formation of Molecular Orbitals. An atomic orbital is an electron wave; the waves of the two atomic orbitals may be in phase or out of phase. Suppose Ψ A and Ψ B represent the amplitude of the electron wave of the atomic orbitals of the two atoms A and B. Case 1: When the two waves are in phase so that they add up and amplitude of the wave is ... The molecular orbital diagram for CO molecule is shown in the following figure: (4) CN Molecule The electronic configuration of participating C and N atoms are: The total number of valence electrons is 9 and the electronic configuration of CN molecule can be written as:

Question 13 Molecular Orbitals For Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Using The Above Molecular Orbital Diagram For Co Homeworklib
Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene
Molecular orbital diagram of co. Tricky chemistry basics. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic ...
A Chemistry, Bakura Sammilani Collage (2018) A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation. generic s-p valence MO diagram for carbon monoxide CO chain one can reasonably explain, that the HOMO of carbon monoxide must be of. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not.
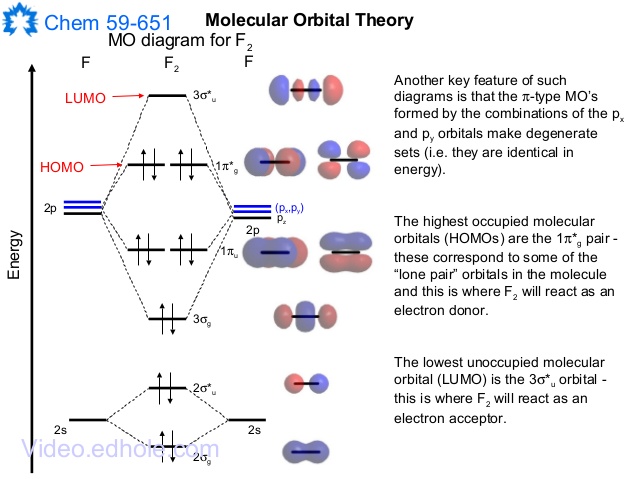
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
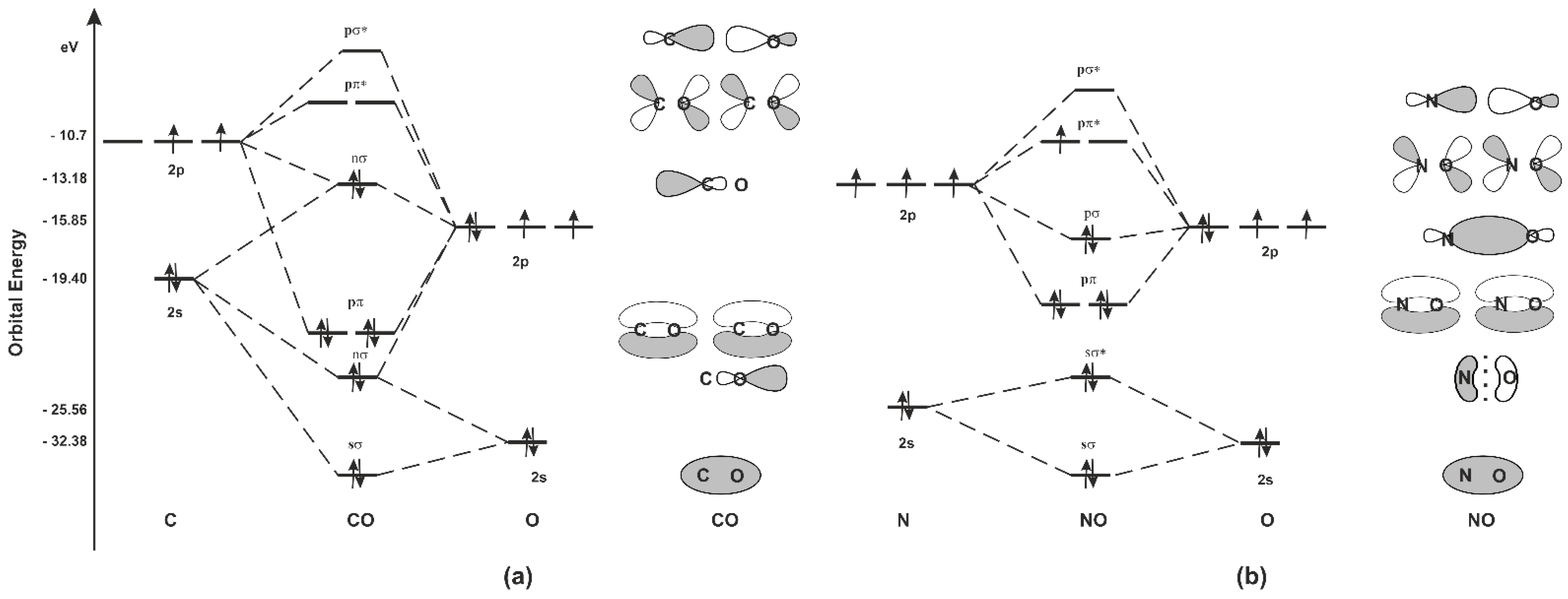
The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide is very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence electrons, together have the same number of electrons as dinitrogen.
May 09, 2018 · There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of carbon and 6.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
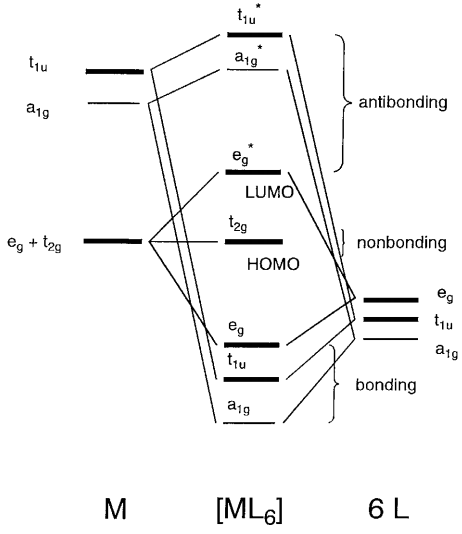
reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection. • The wavefunctions of properly-formed group orbitals can be deduced using the projection operator method. • We showed the following examples: homonuclear diatomics, HF, CO, H3 +, FHF-, CO 2, H2O, BF3, and ...
Also see here... Bond order for "NO"^+ Order by bond length: "NO", "NO"^(+), "NO"^(-) Is "CO" a Lewis acid? "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the ...
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagram of CO. from publication: The Chemistry of Group-VIb Metal Carbonyls | The special interest attached to the chemistry of metal carbonyls ...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Molecular orbital diagram of co. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic methods used by chemists and biochemists to analyse the molecular and electronic structure of atoms and molecules. This results in a larger energy difference between the resulting molecular orbitals ψ 1 and ψ 2 as shown in fig.
Molecular orbitals of carbon monoxide determined by LCAO. Carbon monoxide CO consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. The bond length is 1.128 Å. The molecular orbital Hamiltonian in this case is, rO r → O are the positions of the carbon atom and the oxygen atom and ZC eff = 3.25 Z eff C = 3.25 and ZO eff =4.55 Z eff O = 4.55 are the ...
Point out key differences between the diagrams and use the diagram to explain why $\ce{CO}$ acts as a two-electron donor through carbon rather than through oxygen. Understandably, the key difference between these molecules is that $\ce{CO}$ is heteronuclear, and thus will have differences in energy between the molecular orbital and the atoms.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. TAGS; Molecular Orbital Diagram; Previous article Wohl-Ziegler Bromination. Next article Molecular Orbital Diagram of NO. All About Chemistry. https://allaboutchemistry.net. Hello Reader! Thanking for reading this post, If you find it to be informative, pls share it and visit our website.
Molecular Orbital diagram for CO 5:09. Taught By. Patrick J O'Malley, D.Sc. Reader. Try the Course for Free. Transcript. Explore our Catalog Join for free and get personalized recommendations, updates and offers. Get Started. Coursera Footer. Start or advance your career. Google Data Analyst ...

How To Rationalise With Mo Theory That Co Is A Two Electron Donor Through Carbon Chemistry Stack Exchange
Ijms Free Full Text Carbon Monoxide And Nitric Oxide As Examples Of The Youngest Class Of Transmitters Html

Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Of Metal Ligand Complexes Physical Methods In Chemistry And Nano Science Openstax Cnx





















0 Response to "41 co molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment