40 diagram of eye muscles
These muscles originate in the eye socket (orbit) and work to move the eye up, down, side to side, and rotate the eye. The superior rectus is an extraocular muscle that attaches to the top of the eye. It moves the eye upward. The inferior rectus is an extraocular muscle that attaches to the bottom of the eye. It moves the eye downward. of light entering the eye. Lens: The lens is a clear part of the eye behind the iris that helps to focus light, or an image, on the retina. Macula: The macula is the small, sensitive area of the retina that gives central vision. It is located in the center of the retina. Optic nerve: The optic nerve is the largest sensory nerve of the eye.
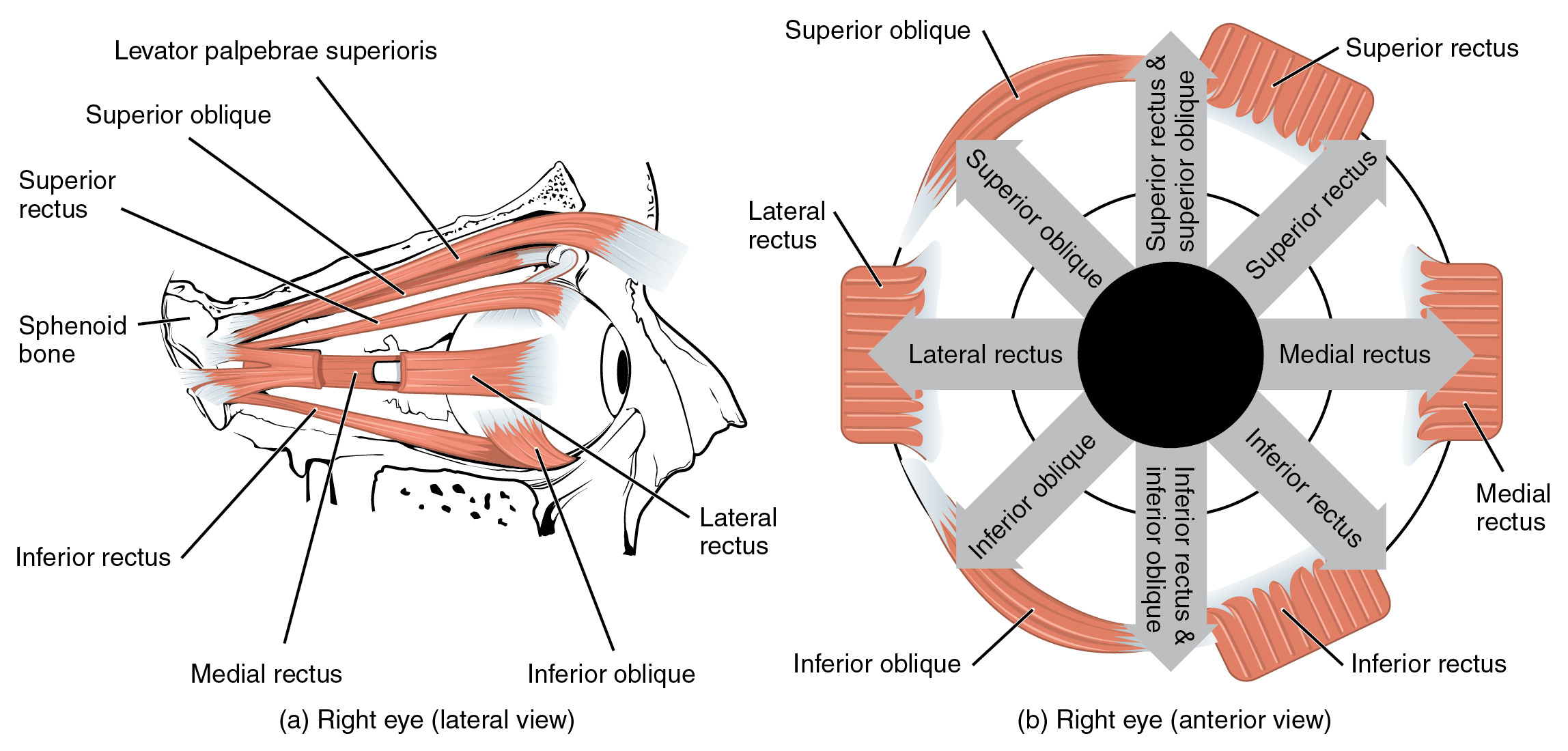
Here is a tour of the eye starting from the outside, going in through the front and working to the back. Eye Anatomy: Parts of the Eye Outside the Eyeball. The eye sits in a protective bony socket called the orbit. Six extraocular muscles in the orbit are attached to the eye. These muscles move the eye up and down, side to side, and rotate the eye.

Diagram of eye muscles
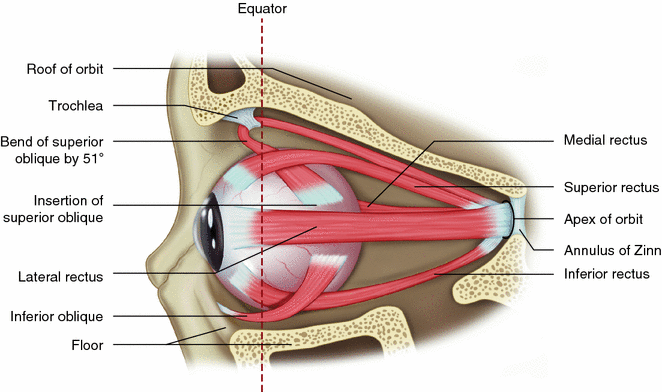
Bony cavity within the skull that houses the eye and its associated structures (muscles of the eye, eyelid, periorbital fat, lacrimal apparatus) Bones of the orbit. Maxilla, zygomatic bone, frontal bone, ethmoid bone, lacrimal bone, sphenoid bone and palatine bone. Structure of the eye. Cornea, anterior chamber, lens, vitreous chamber and ... by PE Ludwig · 2020 · Cited by 3 — The intraocular muscles include the ciliary muscle, the sphincter pupillae, and the dilator pupillae.[1] The ciliary muscle is a smooth muscle ... 21 Nov 2016 — Six special muscles that insert at different sites outside the eyeball work together to control eye movement.
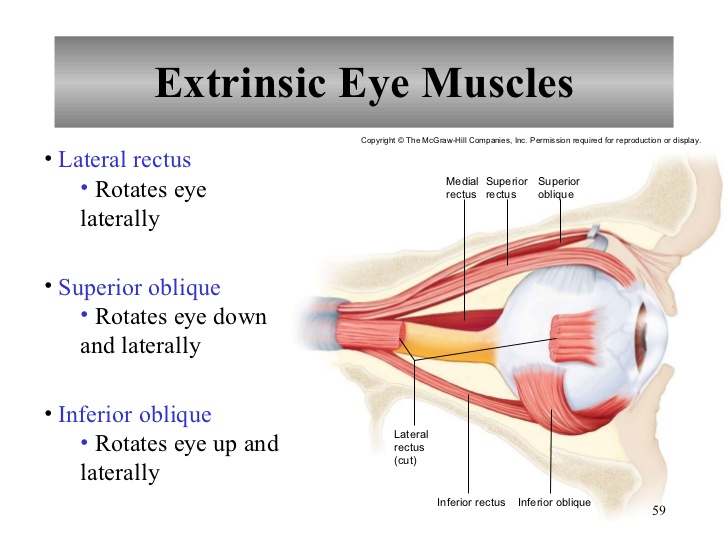
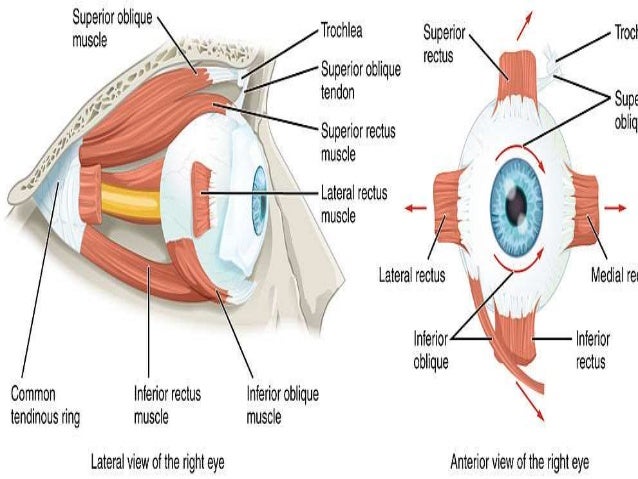
Diagram of eye muscles. Extrinsic eye muscles (also called extraocular muscles) are attached to the outside of the eyeball and enable the eyes to move in all directions of sight. There are six extraocular eye muscles and one muscle that controls movement in the upper eyelid. Though the extraocular muscles are found within the orbit of the eye, they are not located in ... The eye is cushioned within the orbit by pads of fat. In addition to the eyeball itself, the orbit contains the muscles that move the eye, blood vessels, and ... Eye Muscles: There are seven extraocular eye muscles that are present in the eye socket that join the eye to move it. These muscles control to move the eye from side to side, up, down and rotate the eye. Extraocular Muscles. The extraocular muscles are placed in the orbit but are extrinsic and separate from the eyeball itself. The primary job of this muscle is to turn the eye inward. Every eye muscle does multiple jobs, so the superior oblique does contribute to other motions. Inferior Oblique. The inferior oblique has a similar job to the inferior rectus, but it is the muscle that moves the eye upward when the eye is looking in toward the nose, rather than away.
The extraocular muscles are located within the orbit, but are extrinsic and separate from the eyeball itself. They act to control the movements of the eyeball and the superior eyelid.. There are seven extraocular muscles – the levator palpebrae superioris, superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus, inferior oblique and superior oblique. Muscles of the eye study guide by landin_sorenson includes 7 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more. Quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades. A series of muscles helps the eye move. The first set is the superior and inferior rectus muscles, which allow upward and downward motion. The medial and lateral rectus muscles allow the eye to ... The medial rectus, or nose-side, muscles move the eyes inwardly; when working simultaneously, they converge, or cross, the eyes. The lateral rectus, or temple- ...
21 Nov 2016 — Six special muscles that insert at different sites outside the eyeball work together to control eye movement. by PE Ludwig · 2020 · Cited by 3 — The intraocular muscles include the ciliary muscle, the sphincter pupillae, and the dilator pupillae.[1] The ciliary muscle is a smooth muscle ... Bony cavity within the skull that houses the eye and its associated structures (muscles of the eye, eyelid, periorbital fat, lacrimal apparatus) Bones of the orbit. Maxilla, zygomatic bone, frontal bone, ethmoid bone, lacrimal bone, sphenoid bone and palatine bone. Structure of the eye. Cornea, anterior chamber, lens, vitreous chamber and ...

Eye Anatomy 3d Diagram Infographics Layout Showing Human Eyes Muscles In Side View With Labeling Vector Illustration Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image 99563299
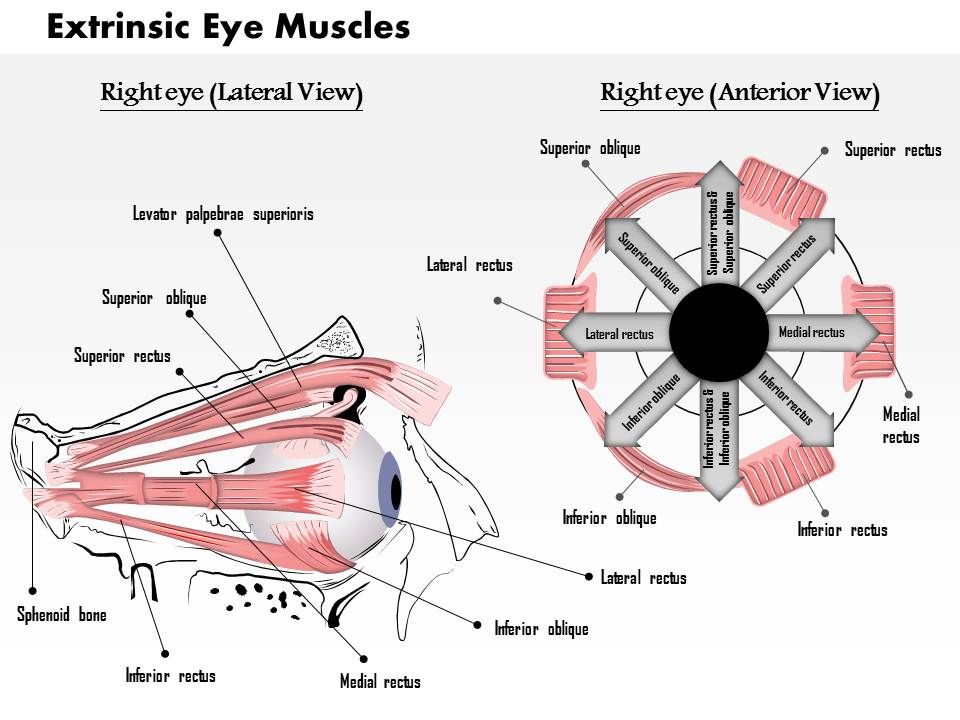
0514 The Extrinsic Eye Muscles Medical Images For Powerpoint Presentation Powerpoint Images Example Of Ppt Presentation Ppt Slide Layouts

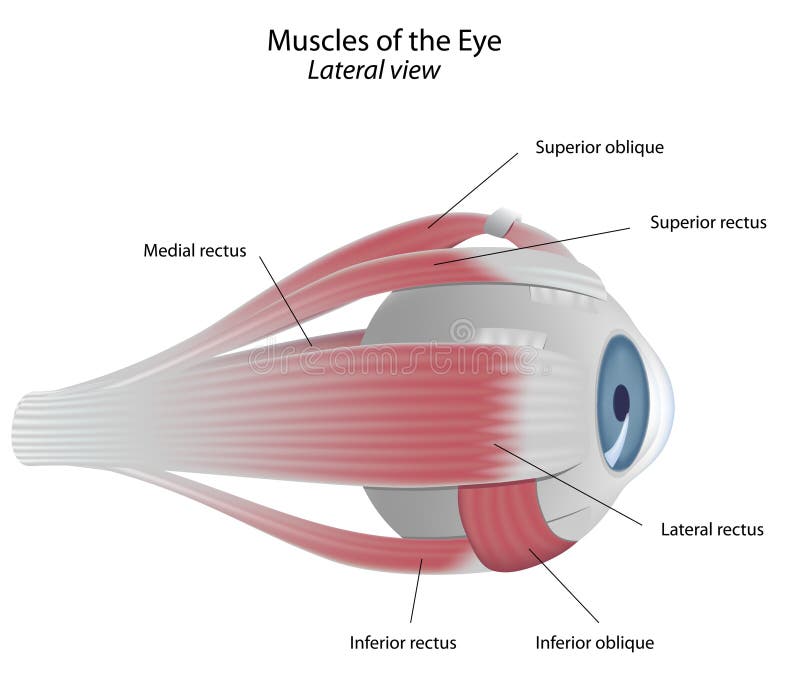


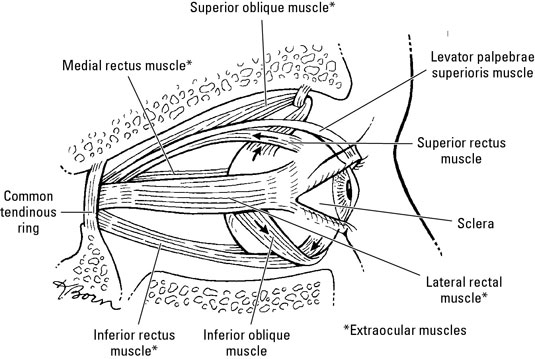






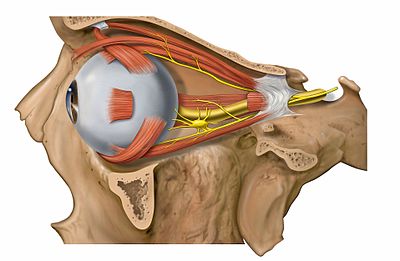







:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10608/Orbit.png)


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/eye-anatomy/BHBDSisq6QoEIDhNqGJQ_fpm3UoJsicanCHWFVT1SyA_Bulbus_oculi_01.png)






0 Response to "40 diagram of eye muscles"
Post a Comment